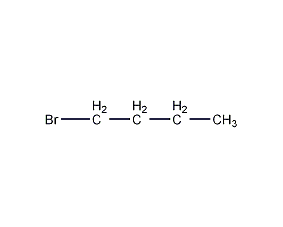
Structural formula
| Business number | 02ZE |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H9Br |
| Molecular weight | 137.02 |
| label |
n-butane bromide, butyl bromide, Bromobutane, n-butane bromide, Bromobutane, Butyl bromide, rare element extraction agent, Alkylating agent, Halogenated hydrocarbon solvents, aliphatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:109-65-9
MDL number:MFCD00000260
EINECS number:203-691-9
RTECS number:EJ6225000
BRN number:1098260
PubChem number:1098260
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless transparent liquid[1]
2. Melting point (℃): -112.4[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 100~104[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 1.276[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 4.72[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 5.58 (25 ℃)[6]
7. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.54[7]
8. Octanol/ Water partition coefficient: 2.75[8]
9. Flash point (℃): 18 (OC)[9]
10. Ignition temperature (℃): 265[10]
11. Explosion upper limit (%): 6.6 (100℃)[11]
12. Lower explosion limit (%): 2.6 (100℃)[12]
13. Solubility: insoluble in water, slightly soluble in Carbon tetrachloride is soluble in chloroform and miscible in ethanol, ether and acetone. [13]
14. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5:18.420
15.van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 8.250×109
16. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 58.760
17. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ· mol-1): -143.76
18. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 152.7
19. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -107.5
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[14]
LD50: 2761mg/kg (rat oral); 4450mg/kg (rat intraperitoneal ); 1424mg/kg (mouse abdominal cavity)
LC50: 47000mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 2h)
2. Stimulation Sex No information yet
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[15] LC50: 36.7mg/L (4d) (fathead minnow)
2. Biodegradability [16] MITI-I test, initial concentration 100ppm, sludge concentration 30ppm, 72% degradation after 28 days.
3. Non-biodegradability[17] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pieces/cm3 hours, the degradation half-life is 6.4d (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 28.31
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 107.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 243.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 26.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 11.22
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 13.1
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[18] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[19] Strong oxidants, strong alkali, potassium, sodium, magnesium
3. Conditions to avoid contact[20] Heat
4. Polymerization hazard[21] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[22] Hydrogen bromide
Storage method
Storage Precautions[23] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. It should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, active metal powders, etc., and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. It is obtained by the reaction of n-butanol and bromine in the presence of red phosphorus; or it is obtained by the reaction of n-butanol and hydrobromic acid in the presence of sulfuric acid. Mix n-butanol and hydrobromic acid, add sulfuric acid dropwise, heat and reflux for 1.5 hours, distill the crude butane bromide, wash with water until the pH is 6-7, and dehydrate with anhydrous calcium chloride.

2. Preparation method:
p>
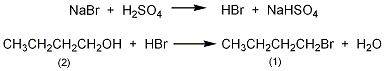
Add 20mL of water into the 250mL reaction bottle, Carefully add 20 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid. Mix well and cool to room temperature. Add 15g (0.2mol) of n-butanol (2) and 25g (0.24mol) of finely ground sodium bromide in sequence. Add 2 grains of zeolite and install a reflux condenser (install an air guide tube on the top to the hydrogen bromide absorption bottle). Heat and reflux for 1.5 hours, shaking the reaction bottle continuously during this period. After cooling, change to a distillation device and heat for distillation until the distillate changes from turbid to clear to obtain crude n-bromobutane. Wash the crude product with water, separate the organic layer, wash with 10 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, then wash with water, saturated sodium bicarbonate, and water in sequence, dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and distill. Collect the fractions at 99 to 103°C to obtain n-bromobutane (1 ) 16~18g, yield 60%~65%. [25]
Purpose
Used as alkylating agent, solvent, rare element extractant and used in organic synthesis. [24]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

