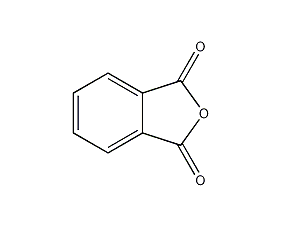
Structural formula
| Business number | 01VT |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H4O3 |
| Molecular weight | 148.12 |
| label |
1,3-isobenzofurandione, Epoxy resin hardener, pesticides, Rubber processing aids, photosensitive materials, acidic solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:85-44-9
MDL number:MFCD00005918
EINECS number:201-607-5
RTECS number:TI3150000
BRN number:118515
PubChem number:24887514
Physical property data
1. Character: white needle-like crystal[1]
2. Melting point (℃): 131.2[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 295[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 1.53[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 5.2[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (96.5℃)[6]
7. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.72[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient : 1.6[8]
9. Flash point (℃): 151 (CC); 165 (OC) [9]
10. Ignition temperature (℃): 569[10]
11. Explosion upper limit (%): 10.4[11]
12. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.7[12]
13. Solubility: insoluble in cold water, slightly soluble in hot water and ether, soluble in Compatible with most organic solvents such as ethanol, pyridine, benzene, and carbon disulfide. [13]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[14]
LD50: 4020mg/kg (rat oral)
2. Irritation[15]
Rabbit transdermal: 500mg (24h) , mild stimulation.
Rabbit eye: 100mg, severe irritation.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity[16] Long-term inhalation of this product by animals may cause damage to the reproductive system . Inhalation of 0.2,1mg/m3 in rats caused sperm survival time to be shortened.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data yet
2. Biodegradability[17]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 24~168
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 96~672
3 .Non-biodegradability[18]
Aqueous phase photolysis half-life (h): 224~274
Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 485~4847
First-level hydrolysis half-life (h): 0.45
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 35.68
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 102.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 283.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 58.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3):14.14
Compute chemical data
1. Hydrophobic parameter calculation�Reference value (XlogP): 1.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Yes Number of rotational chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 43.4
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 187
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Flammable. It easily sublimates below the boiling point and has a slight odor. It is flammable. Steam and air can form an explosive mixture, with an explosion limit of 1.7%-10.4% (volume fraction). Has moderate toxicity.
2. Stability[19] Stable
3. Prohibited use Materials[20] Strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidants, strong reducing agents
4. Conditions to avoid contact[21 ] Humid air
5. Polymerization hazard[22] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[23] Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging must be sealed and protected from moisture. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, acids and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
Currently, there are two raw material routes for phthalic anhydride in industrial production, namely the o-xylene method (ortho-method for short) and the naphthalene method. There are three production processes: fixed bed oxidation method; fluidized bed gas phase oxidation method and liquid phase method. The world’s phthalic anhydride production is dominated by ortho-process fixed bed oxidation technology, accounting for more than 90% of the total phthalic anhydride production capacity.
1. Ortho-xylene oxidation method generally uses vanadium-based catalysts based on vanadium pentoxide for gas-phase oxidation of o-xylene, and most of the reactors are tubular fixed beds. The filtered dust-free gas is compressed and preheated, mixed with the gasified o-xylene vapor and then enters the reactor for oxidation reaction at 400-460°C. The feed space speed is 2000-3000h-1, and the o-xylene in the air Toluene concentration is 40-60g, m2 (standard), and the reaction heat is taken out by the molten salt circulating outside the tube. The reaction product enters the steam generator, and the cooled reaction gas is further cooled to recover crude phthalic anhydride. The tail gas is washed with water to recover maleic anhydride and then vented. The crude phthalic anhydride is crudely distilled under reduced pressure, and low-boiling maleic anhydride, methylmaleic anhydride and benzoic acid are separated from the tower. The bottom material is vacuum distilled to obtain the phthalic anhydride product. Raw material consumption quota: o-xylene (98%) 1138kg/t.
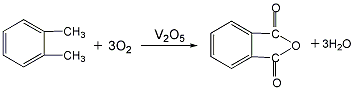
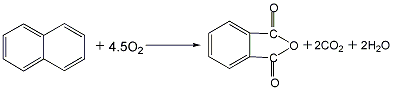
2. Naphthalene catalytic oxidation method: After naphthalene is melted and gasified, it is catalytically oxidized with air in an ebullating bed or fixed bed reactor in the presence of the catalyst vanadium pentoxide to generate phthalic anhydride gas, which is obtained by condensation and hot melting. Crude anhydride is obtained by heat treatment, distillation under reduced pressure, condensation and separation to obtain refined phthalic anhydride. Raw material consumption quota: naphthalene (more than 95%) 11250kg/t.
3.Preparation method:
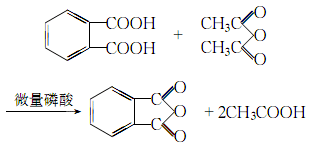
Purpose
1. Phthalic anhydride is one of the most important organic chemical raw materials. Its main derivatives include dibutyl phthalate; dioctyl ester and diisobutyl ester, etc., which are used as plasticizers for PVC; they can also be used It is used in the production of unsaturated polyester resins; alkyd resins; dyes and pigments; a variety of paints; food additives; phenolphthalein, a laxative in medicine; phosmetin in pesticides; bentazone and saccharin sodium, etc.
2. This product is used as epoxy resin curing agent. This product is an important organic chemical raw material, mainly used in the production of phthalate plasticizers, coatings, saccharin, dyes and important intermediates of organic compounds, pesticides, fungicides, rubber processing aids, and photosensitive materials wait.
3. Used as analytical reagent. Organic synthesis intermediates. In the dye industry, it is used to prepare important intermediates such as anthraquinone, 2-chloroanthraquinone, and 1,4-dihydroxyanthraquinone, and dyes such as phthalocyanine blue BS, phthalocyanine blue BX, and phthalocyanine blue B.
4. Used as a curing agent for epoxy resin, the reference dosage is 30 to 50 parts by mass, and the pot life of 100g of resin complex is rt/6h, 120℃/1.5h. Curing conditions: 100/2h+150℃/5h or 100℃/12h, 140℃/8h, 200℃/6h. It generates little heat during curing, and the cured product has good electrical properties and mechanical strength, with a heat distortion temperature of 110 to 152°C.
5. It is an important organic chemical raw material. In the synthetic resin industry, it is used to produce polyester resin, amino resin, unsaturated polyester resin, alkyd resin, etc. In the dye industry, it is used to prepare dye intermediates such as anthraquinone and chloroanthracene dihydroxyanthraquinone and dyes such as phthalocyanine blue BS, phthalocyanine blue BX, and phthalocyanine blue B. It is used in the plastics industry to prepare plasticizers such as dibutyl phthalate, dioctyl phthalate and their mixed esters. It is also an important intermediate in the manufacture of various drugs, paints and organic compounds.
6. Used in the manufacture of plasticizers, dibutyl phthalate, resins and dyes, etc. [24]
Polyester and other plasticizers. It is also an important intermediate in the manufacture of various drugs, paints and organic compounds.
6. Used in the manufacture of plasticizers, dibutyl phthalate, resins and dyes, etc. [24]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

