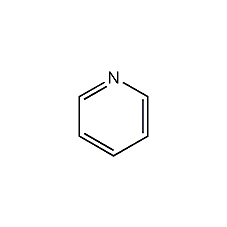
Structural formula
| Business number | 0329 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H5N |
| Molecular weight | 79.10 |
| label |
azabenzene, Azotriene hexacyclic ring, ethylene methanol, Alliol, Azabenzene, Pirydyna, Pyridin(1.Modifikation), Pridinecarboxylicacid,2-(4,5-dihydro-4-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-5-oxo-1h-imidazol-2-yl)-5-methyl, mutagens, catalyst, Solvent for acylation reaction, alkaline solvent, deacidifying agent, silicone rubber stabilizer, Organic corrosion inhibitor materials |
Numbering system
CAS number:110-86-1
MDL number:MFCD00011732
EINECS number:203-809-9
RTECS number:UR8400000
BRN number:103233
PubChem number:24856420
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with special odor.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa): 115.32-115.3
3. Melting point (ºC): -41.6
4. Relative density (g/ mL, 20/4ºC): 0.9831
5. Relative density (g/mL, 25/4ºC): 0.9780
6. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1 ): 2.73
7. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.51016
8. Refractive index (25ºC): 1.5073
9. Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 1.038
10. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 0.952
11. Viscosity (mPa·s, 30ºC): 0.829
12 . Flash point (ºC, closed): 20
13. Fire point (ºC): 482
14. Heat of vaporization (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 40.4277
15. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 7.4133
16. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, liquid): 99.9808
17. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, constant Pressure): 2826.51
18. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, constant volume): 2782.97
19. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 21ºC, constant pressure): 1.64
20. Critical temperature (ºC): 346.85
21. Critical pressure (MPa): 6.18
22. Boiling point rise constant: 2.69
23. Conductivity (S/m, 25ºC): 4.0×10-8
24.&nbs��Refined by the method of mercury forming addition compounds. For example, mix a solution of 424g zinc chloride and 365mL water with 173mL concentrated hydrochloric acid and 345mL 95.6% ethanol, and add 500mL newly distilled pyridine. After a period of time, the product with the composition 2C5H5N·ZnCl2 crystallized out of the solution. After filtration, it was recrystallized twice with absolute ethanol. Decompose the crystals with concentrated sodium hydroxide solution (26.7g of sodium hydroxide per 100g of crystals). Filter, dry the resulting free pyridine with solid potassium hydroxide or barium oxide and then fractionate. To separate pyridine homologues, pyridine can also be added to a solution of oxalic acid in acetone with stirring. Pyridine forms an oxalate precipitate, which is filtered, washed with cold acetone, and alkali is added to regenerate the pyridine. Non-alkaline impurities contained in pyridine can be removed by steam distillation in an acidic solution. In addition, there is also a refining method using oxidant treatment. For example, stir 135mL pyridine, 2.5L water, and 90g potassium permanganate at 100°C for 2 hours, let it sit for 15 hours, then filter, and add about 500g sodium hydroxide to the filtrate to separate the pyridine. The pyridine was decanted, refluxed with calcium oxide for 3 hours and then distilled.
2.Recycle the pyridine base in the coke oven gas generated during the coking process to obtain pyridine. Or pyridine can be obtained from the reaction of acetaldehyde, formaldehyde and ammonia mixture. Pyridine can also be obtained by heating 1,5-pentanediamine hydrochloride for cyclization and dehydrogenation in the presence of a platinum catalyst.
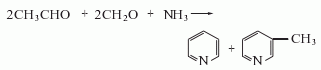
3. Take industrial pyridine as raw material, collect its 114-116°C fraction through atmospheric distillation, and put it into a brown glass bottle to get the finished product. In order to prepare chromatographically pure pyridine, nitrogen can be used as the carrier gas, and industrial pyridine is injected into the preparative gas chromatograph, and its main peak components are collected through separation, and then put into glass ampoules. Just seal it.
4.The synthesis method using aldehydes or ketones and ammonia as raw materials is the most common industrial synthesis method of pyridines. Various cheap and easily available aldehydes or ketones are reacted with ammonia to obtain various pyridines. Reaction of saturated fatty aldehyde and ammonia, 3 mol of saturated fatty aldehyde and 1 mol of ammonia form a pyridine ring. Theoretically, the amount of ammonia used is 1/2 or 1/3 of the aldehyde or ketone, but in order to prevent the yield and catalyst activity from decreasing, the excess is usually 0.9 to 9 times. The reaction conditions are: the air velocity of the mixed gas is 500~1000/h, and the reaction temperature is 400~500℃. Alumina-silica catalysts are usually used, and various metals are added to improve the yield, extend the life of the catalyst and facilitate regeneration. The reaction formula is as follows:
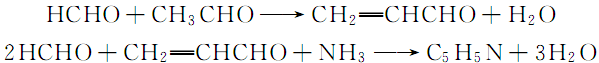
Purpose
1. Used in the manufacture of vitamins, sulfa drugs, pesticides and plastics, etc. In addition to being used as raw materials for medicine and various pyridine compounds, it is also used as an alkaline solvent in the chemical industry and laboratories. It is also an excellent solvent for deacidifying agents and acylation reactions, because pyridine can combine with acylating agents to form N-acylpyridine compounds. Pyridine solutions composed of pyridine and metal salts or organic metal compounds are used as catalysts in polymerization reactions, oxidation reactions, carbonylation reactions of acrylonitrile, etc. in the form of complexes. It can also be used as silicone rubber stabilizer, raw material for anion exchange membrane, etc. 2.Used as a corrosion inhibitor, pyridine has a corrosion inhibition effect on metals. It can be directly added to the pickling solution and utilizes its adsorption effect to achieve corrosion inhibition. 3.It is used as analytical reagent, widely used as solvent and liquid chromatography eluent. Also used in organic synthesis.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

