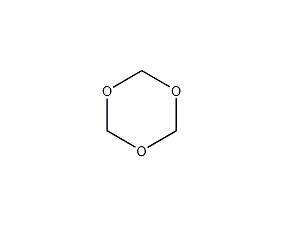
Structural formula
| Business number | 032B |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H6O3 |
| Molecular weight | 90.08 |
| label |
1,3,5-trioxane, 1,3,5-Trioxane, 1,3,5-trioxane, Symmetric trioxane, Triformaldehyde, 1,3,5-Trioxane, trioxane, Trioxymethylene, Meformaldehyde, disinfectant, Colorless and flameless fuel, Heterocyclic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:110-88-3
MDL number:MFCD00006563
EINECS number:203-812-5
RTECS number:YK0350000
BRN number:102769
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: colorless crystals with an odor similar to chloroform.
2. Relative density (g/mL, 65/20℃): 1.17
3. Relative density (g/mL, 65/4℃): 1.1765
4. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 3.1
5. Melting point (ºC): 64
6. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa) :114.5
7. Flash point (ºC): 45
8. Fire point (ºC): 413.9
9. Heat of vaporization (KJ/mol): 41.0
10. Heat of formation (KJ/mol): 181.7
11. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 23ºC): 16568.6±42
12. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): 28.7
13. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): 3.6
14. Solubility: soluble in water, alcohol, ketone , ethers, carbon disulfide, carbon tetrachloride, benzene, aliphatic and aromatic chlorinated hydrocarbons and organic acids. Insoluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons such as pentane and petroleum ether.
15. Refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.1765
16. Standard combustion heat of crystalline phase (enthalpy )(kJ·mol-1): -1515.5
17. Crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -522.5
18. Crystal phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 133.01
19 . Standard free energy of formation in the crystal phase (kJ·mol-1): -348.5
20. Standard heat of combustion (enthalpy) in the gas phase (kJ·mol-1): -1572.1
21. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -465.9
22. Gas phase Standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 288.76
23. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol -1): -338.2
24. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 82.38
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: DNA damage in rat abdominal cavity: 425mg/kg
2. Irritating to eyes, mucous membranes or skin, with risk of burns.
Ecological data
This substance is slightly harmful to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 18.65
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 79.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 193.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 35.2
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 7.39
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 27.7
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 21.5
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with wet moisture. It is forbidden to contact with strong oxidants and acids. It is easy to cause combustion when exposed to open flames, high heat and strong oxidants. It produces toxic and flammable gases when exposed to heat, acid or acid mist. Can form explosive mixtures with air. In the event of a fire, use foam fire extinguishing agents, carbon dioxide, carbon tetrachloride or dry chemical fire extinguishing agents. Formaldehyde can be released by heating or contact with strong acids.
Chemical properties: Trioxane is a cyclic trimer of formaldehyde. Easily sublimates into colorless needle-like or monoclinic crystals. The chemical properties are relatively stable and almost no decomposition occurs when heated at 224°C for 6 hours in a sealed tube. Using potassium sulfate, activated carbon, potassium hydrogen sulfate-silicon carbide and phosphoric acid-silicon carbide as catalysts, when heated to 220~270°C, 89%~90% becomes anhydrous formaldehyde. Stable in neutral or alkaline solutions. It is slowly hydrolyzed and depolymerized in strong acidic aqueous solution. When sulfuric acid is used as a catalyst, the depolymerization speed in acetic acid or other organic solvents is about 1,000 times faster than in water. Trioxane undergoes ring-opening polymerization in gas phase, liquid phase or solution under the action of Friedel-Crafts type cationic catalyst to generate high molecular weight polyoxymethylene. Using perchloric acid and acetylperchloric acid as catalysts, a polymer with a molecular weight of 106 can be obtained. High polymers are also obtained when the solid phase is irradiated with radiation.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire, heat, water and anti-static. The storage temperature should not exceed 30℃. They should be stored separately from oxidants and acidic substances, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
It is produced by continuous distillation of a 60% formaldehyde aqueous solution containing 2%-5% sulfuric acid, and the residual liquid is extracted with benzene and then distilled. Metaformaldehyde can also be generated under certain conditions. The melting point of formaldehyde is 112°C and the boiling point is 175°C. Both parformaldehyde and metaldehyde can be re-decomposed into formaldehyde under the action of acid, and both are special commercial forms of formaldehyde.
Refining method: The main impurity is formaldehyde. Use a water-insoluble solvent such as chloroform to extract the trioxane, and then refine it by distillation under normal pressure.
Purpose
It is used as an intermediate for engineering plastics polyformaldehyde and other chemicals, and as a disinfectant, etc., used in organic synthesis, and used as a disinfectant and colorless and flameless fuel.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

