Structural formula
| Business number | 032C |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H11N |
| Molecular weight | 85.15 |
| label |
hexahydropyridine, piperidine, nitrogen hexane, One nitrogen hexacyclic ring, Type III polypropylene, pepper rings, PPD, 1-Oxa-4-azacyclohexane, Hexahydropyridine, Pentamethyleneamine, Heterocyclic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:110-89-4
MDL number:MFCD00005979
EINECS number:203-813-0
RTECS number:TM3500000
BRN number:102438
PubChem number:24865722
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless clear liquid with an odor similar to ammonia. [12]
2. Melting point (ºC): -9~-7[13]
3. Boiling point ( ºC): 106[14]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.86[15]
5 .Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.0[16]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 3.06 (20ºC)[17]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -3455.2[18]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.65[ 19]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.84[20]
10. Flash point (ºC): 3; 16 (CC) [21]
11. Explosion upper limit (%): 10[22]
12. Explosion Lower limit (%): 1.4[23]
13. Solubility: soluble in water, ethanol, ether, benzene, and chloroform. [24]
14. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 1.486
15. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 1.370
16. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 88.15
17. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, constant volume): 3453
18. Specific heat capacity ( KJ/(kg·K), 25ºC, constant pressure): 2.114
19. Conductivity (S/m, 25ºC): 3.8×10-7
20. Vapor pressure (kPa, 21.13ºC): 3.29
21. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K), room temperature): 0.180
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity:
Oral LD50 in rats: 50mg/kg; Dermal LD50 in rabbits: 320mg/kg; Inhalation LC50 in mice: 6000mg/m3/2H;
2. Moderately toxic, highly irritating to eyes and skin, and a vasopressor. Small doses can stimulate sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia, but large doses can have an inhibitory effect. If taken accidentally, it can cause weakness, nausea, salivation, difficulty breathing, muscle paralysis and suffocation. Poisoned animals show nausea, vomiting, salivation, difficulty breathing, increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, weakness, convulsions and paralysis. Painting the skin of guinea pigs causes severe irritation. Instilled into rabbit eyes, it will cause severe irritation and permanent damage to the cornea.
3. Acute toxicity[25]
LD50: 400mg/kg (rat Oral); 276mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 6000mg/m3�Pyridine and methanol (equal mass ratio) and NHD-99 catalyst (10% of the input amount) are placed in the reaction kettle, sealed, tested for leaks with nitrogen, hydrogen replacement is completed, heated to 170°C, and hydrogen is introduced for reaction . The reaction pressure is 6.5MPa and the time is 6h. After the reaction is completed, it is cooled down and discharged after nitrogen replacement. Filter out the catalyst and bottle it for next experiment. The filtrate is sent for distillation. The solvent and pyridine are recovered under normal pressure, and then the fraction between 102 and 108°C is taken as the product. The yield is above 96%.
Purpose
1. It is one of the common tertiary amine curing agents for epoxy resin. The dosage is 15 parts per 100 parts of resin. The curing condition is 60℃/4h. It is also used as rubber vulcanization accelerator, olefin polymerization catalyst, polyacrylonitrile spinning and solvent for organic synthesis. In medicine, it is used as a raw material for the manufacture of piperidine nitrate, piperidine hydrochloride analgesics, bactericides, wetting agents, and local anesthetics. It can also be used as a stabilizer for diazoamino compounds used in synthetic fiber dyeing and as a preservative for steam equipment.
2. Used as rubber vulcanization accelerator, as well as raw material for analgesics, bactericides, wetting agents and local anesthetics.
3. Used as a solvent for polyacrylonitrile spinning, a solvent for organic synthesis, a catalyst for the reaction between active methylene and aldehydes, a catalyst for olefin polymerization, an epoxy resin curing agent, and a preservative for steam equipment. As well as diazo amino compound stabilizers for synthetic fiber dyeing, rubber vulcanization accelerators, etc. Also used in pharmaceutical industry and organic synthesis.
4. Hexahydropyridine is a secondary amine commonly used in chemical laboratories [1]. It is a typical catalytic reagent used in aldol condensation (Knoevenagel condensation) reaction and Michael addition reaction, a thiophilic reagent used to regulate sulfoxide-sulfinic acid rearrangement, and a reagent for the synthesis of enamines.
Preparation of hexahydropyridine from pyridine In an aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide, pyridine reacts with nickel-aluminum alloy to form hexahydropyridine (formula 1)[1].
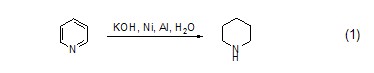
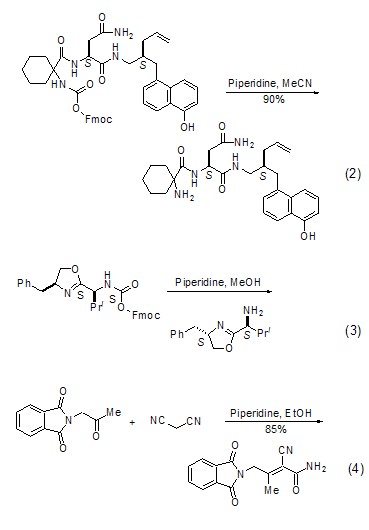
React with amide ester Preparation of aminesHexahydropyridine reacts with amide ester compounds to selectively break the amide bond, thereby obtaining amine compounds (Formula 2, Formula 3)[2,3].
Ketones react with cyano compounds to form unsaturated amides In the presence of hexahydropyridine, ketones react with cyano compounds to form unsaturated amides (Formula 4)[4].
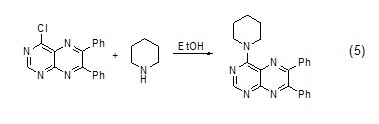
Hexahydropyridine and Coupling reaction of halogenated aromatic compounds In ethanol solution, a carbon-nitrogen bond coupling reaction can occur between hexahydropyridine and halogenated aromatic compounds (Formula 5)[5].
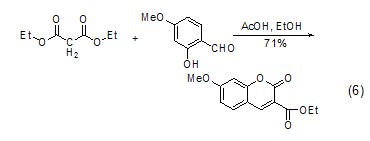
As a condensation reaction CatalystHexahydropyridine is a basic catalyst widely used in aldol condensation, especially for cyclization reactions. It can be used in combination with carboxylic acids in the condensation reaction of aromatic compounds with aliphatic aldehydes, ketones or esters (formula 6)[6].
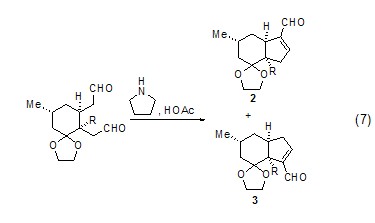
Selection of dialdehyde Sexual cyclization reactionSpecial combinations of secondary amines and acidic catalysts can affect the chemoselectivity and regioselectivity of dialdehyde cyclization, such as compounds 2 and The ratio of >3 is 19:1 (Formula 7)[7].
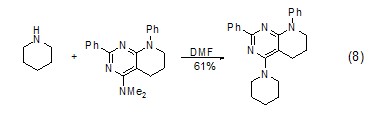
Hexahydropyridine and Reaction of tertiary amines In the presence of DMF as the solvent, hexahydropyridine can react with tertiary amines (Formula 8)[8].
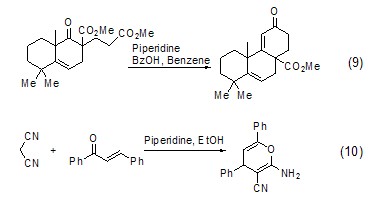
For Robinson ring Condensation reaction and Michael addition reactionHexahydropyridine is also widely used in Robinson ring condensation reaction and Michael addition reaction (Formula 9, Formula 10)[9,10].
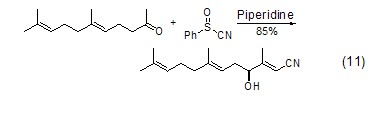
Hexahydropyridine Thiphilic propertiesIn the Knoevenagel sulfoxide-sulfinic acid rearrangement reaction, hexahydropyridine not only acts as a catalyst, but also can cleave the S-O bond (Formula 11)[11].
5. Used as solvent, organic Synthetic intermediates, epoxy resin cross-linking agents, condensation catalysts, etc. [32]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

