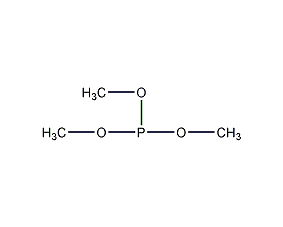
Structural formula
| Business number | 03DL |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H9O3P |
| Molecular weight | 124 |
| label |
Aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:121-45-9
MDL number:MFCD00008350
EINECS number:204-471-5
RTECS number:TH1400000
BRN number:956570
PubChem number:24867000
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid
2. Relative density (25/5℃): 1.0520
3. Refractive index: 1.4095
4 . Flash point (℃): 38 (open cup)
5. Melting point (℃): <-60
6. Boiling point (ºC): 112
7. Solubility: Insoluble in hot water, soluble in ethanol, ether, benzene, acetone, carbon tetroxide and other organic solvents.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity:
Rat oral LD50: 1600mg/kg
Rat inhalation LC50: >10000ppm/4H
Mouse oral Peritoneal cavity LD50: 4180mg/kg
Rabbit skin LD50: 2600mg/kg
2. Other multiple dose toxicity: rat inhalation TCLO: 500ppm/7.5H/8W-I
p>
3. Reproductive toxicity: Rat (female) oral TDLO: 1640mg/kg/6-15D
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
None
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.1
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 27.7
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 31.7
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Colorless and transparent liquid with pungent odor and flammable. Melting point <-60℃, boiling point 112℃, relative density (25/5℃) 1.0520, refractive index 1.4095, viscosity (25℃) 0.58mPa·s, flash point (open cup) 38℃. Insoluble in hot water, soluble in ethanol; ether; benzene; acetone; carbon tetrachloride and other organic solvents.
2. This product is less toxic. The oral LD50 in rats is 2000 mg/kg. Long-term exposure can cause rapid heartbeat, dizziness and other phenomena. The equipment is required to be strictly sealed and well ventilated, and the operators are required to wear protective equipment.
3. Before use, it is generally treated with sodium and then purified by distillation to remove a small amount of water and dialkyl phosphite. Since trimethyl phosphite has an odor, operation should be performed in a fume hood. This reagent should be stored in a dry place with active molecular sieve added.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, dry place filled with argon gas.
2. This product is packed in iron drums or plastic drums. Store in a cool and dry warehouse. It needs to be protected with nitrogen during storage to prevent auto-oxidation to form trimethyl phosphate. by toxic chemicalsProvide for storage and transportation.
Synthesis method
1. Transesterification method: First, phenol reacts with phosphorus trichloride to generate triphenyl phosphite, and then transesterifies with methanol in the presence of sodium methoxide to generate trimethyl phosphite. The crude ester is distilled to remove residual methanol and phenol and becomes the finished product.
Raw material consumption quota: phenol (freezing point ≥40℃) 237kg/t; phosphorus trichloride (96%) 1396kg/t; methanol (98%) 855kg/t; sodium methoxide (27-31 %) 83kg/t.
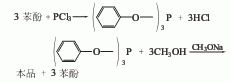
2. Tertiary amine-ammonia The method uses xylene as the solvent, methanol and phosphorus trichloride in the presence of N, N-dimethylaniline to perform an esterification reaction to generate trimethyl phosphite. Then wash with water; dehydrate; distillate to obtain the finished product.
Raw material consumption quota: methanol (95%) 1025kg/t; phosphorus trichloride 1430kg/t; xylene 130kg/t; dimethylaniline 51kg/t
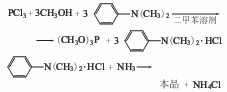
3. In a machine equipped with a reflux condenser, dropping funnel and thermometer In a three-necked flask, put 0.3 mol of methanol, 0.3 mol of amine and 100 ml of diethyl ether. While stirring steadily and maintaining a temperature of 7 to 10, slowly add a solution of 0.1 mol of phosphorus trichloride dissolved in 50 ml of diethyl ether from the dropping funnel. The reaction is completed within 1 to 1.5 hours. The precipitated amine hydrochloride was filtered off. Evaporate the ether from the filtrate, and then distill the residue to obtain trimethyl phosphite.
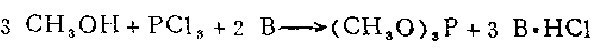
Purpose
1. Organophosphorus pesticide intermediates, used in the production of dichlorvos, phosphoramidite, monocrotophos, pyridoxazole and other insecticides and pesticides, also used as flame retardants for plastics and wood, as well as synthetic polymerization catalysts and Paint additives.
2. Trimethyl phosphite can be used in the synthesis of a variety of phosphonate or phosphate compounds [1~6], and can be used as a reduction agent for a variety of groups Reagent, which takes away oxygen atoms or sulfur atoms[7]. At the same time, trimethyl phosphite can also form a stable complex with copper iodide or methyl copper [8].
Synthesis of phosphonate or phosphate compounds Trimethylphosphite is a very useful phosphorus reagent, which can undergo Arbuzov rearrangement reaction with halogenated hydrocarbons ( Formula 1) [1,2] and Perkow reaction (Formula 2) [3], respectively generate the corresponding Phosphonates and enol phosphates.
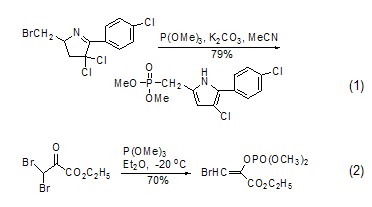
Due to the trimethyl phosphite molecule There is a lone pair of electrons on the phosphorus atom. It attacks the positively charged carbon atom nucleophilically to form a phosphonate compound (formula 3)[4]. It can also attack other positively charged carbon atoms. Sexual heteroatoms, such as attacking azide compounds to obtain phosphoramide[5].
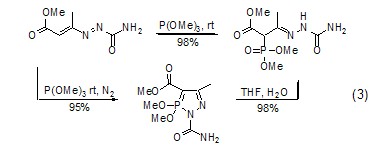
Deoxygenation (sulfur) ReactionThe phosphorus-oxygen bond is relatively stable and its bond energy is relatively large. Therefore, phosphite can be used as a deoxidizer. After deoxidation, a relatively stable trimethylphosphate is generated, which can be used to reduce compounds such as sulfone or sulfoxide ( Formula 4)[6]. Similarly, trimethyl phosphite can also be used as a desulfurizer in certain reactions to generate trimethyl phosphorothioate.
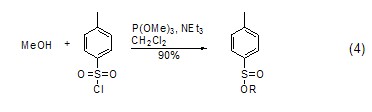
As a metal compound BodyIn the trimethylphosphite molecule, the phosphorus atom has a lone pair of electrons, so it can serve as a metal ligand to catalyze certain reactions (Formula 5). For example, trimethyl phosphite can form a stable complex with copper iodide (CuI), CuI/P(OMe)3, which can react with lithium salt to form copper salt, thereby playing a catalytic role [7]. Trimethyl phosphite, CuI and pyrazine can form a stable complex[8].


 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

