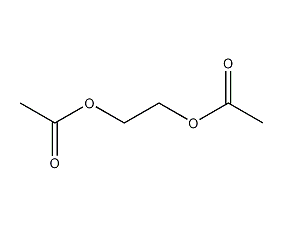
Structural formula
| Business number | 033S |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H10O4 |
| Molecular weight | 146.14 |
| label |
Ethylene glycol diacetate, Ethylene diacetate, 1,2-Ethanediol diacetate, aliphatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:111-55-7
MDL number:MFCD00008718
EINECS number:203-881-1
RTECS number:KW4025000
BRN number:1762308
PubChem number:24874480
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid
2. Density (g/mL, 20/20℃): 1.1043
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air =1): 5.04
4. Melting point (ºC): -31
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 185~190
6. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.1052
7. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.4162
8. Flash point (ºC, opening): 96
9. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 3.13
10. Flash point (ºC): 635
11. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.094930
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 20ºC): 0.033
13. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol): 50.7
14. Normal temperature refractive index (n20): 1.4159
15. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 263.6
16. Body expansion coefficient (K-1): 0.00106
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): 8.4
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): 1.6
19. Solubility: easily soluble in alcohol and ether, difficult to dissolve in petroleum systems Aliphatic hydrocarbons. Oils and fats, except castor oil, are insoluble. It dissolves 21.3% in water at 20℃; water dissolves 21.2% in ethylene glycol diacetate.
20. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 20.532
21. van der Waals area ( cm2·mol-1): 1.134×1010
22. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 78.200
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: guinea pig oral LD50: 4940mg/kg; rat oral LD50: 6850mg/kg; rabbit dermal LD50: 8480mg/kg.
2. It is slightly toxic. The toxicity is similar to that of ethylene glycol. If consumed accidentally, it can cause vomiting, drowsiness, difficulty breathing, convulsions, kidney damage, and further lead to uremia and death. Mild irritation to eyes.
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 33.39
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 134.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 320.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 32.1
5. Polarizability (10 -24cm3): 13.23
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 5
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 52.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 114
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with alkali, acid, oxidizing agent and reducing agent. It is a flammable liquid and non-corrosive to metals. It can be stored in iron, mild steel or aluminum containers, but copper containers are not suitable because the acetic acid produced by decomposition is corrosive to copper.
2. Chemical properties: It has the general chemical properties of ester. It is easily hydrolyzed in the presence of caustic alkali and inorganic acid to produce ethylene glycol and acetic acid. Alcoholysis reactions are also prone to occur.
3. Exist in mainstream smoke.
4. Orally administered LD506.86g/kg to mice
Storage method
Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Protect from direct sunlight. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from alkalis, oxidants, alcohols, etc. and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reaction of 1,2-dibromoethane and potassium acetate.
2. Manufactured by the reaction of ethylene glycol and acetic anhydride. The main impurity is ethylene glycol monoacetate. During refining, it is dried with calcium chloride and anhydrous potassium carbonate, and then distilled under reduced pressure.
3. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer and a reflux condenser, add 30 mL of glacial acetic acid and 93 g of 1,2-dibromoethane (2) (0.5 mol), 98 g of newly calcined potassium acetate (1.0 mol), 1.5 g of pyridine, and heat to reflux for 3 hours while stirring. Change to a distillation device to steam out the volatile part until the distillation is complete. Add 2 mL of glacial acetic acid, 93 g (0.5 mol) of 1,2-dibromoethane (2), 98 g (1.0 mol) of newly calcined potassium acetate, and 1.5 g of pyridine to the distillate, and then heat to reflux for 3 hours while stirring. Change to a distillation device for distillation and collect the following various fractions: ① the fraction before 140°C; ② the fraction between 140 and 170°C (30-39g); ③ the fraction between 170 and 190°C (70-78g). Redistill the 140-170°C fraction and collect the 170-190°C fraction (10-16g). Combine the fractions at 170 to 190°C, perform distillation, and collect the fractions at 180 to 190°C to obtain 80 to 90 g of ethylene glycol diacetate (1), collecting 55% to 61%. [1]
Purpose
Used as a solvent in nitrocellulose spray paint, printing ink, cellulose esters, fluorescent coatings and the manufacture of explosives.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

