overview[1]
2-cyano-5-fluorobenzoic acid is an organic intermediate that can be prepared from 2-bromo-5-fluorobenzoic acid methyl ester in two steps.
preparation[1]
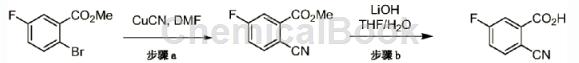
step a: heat a mixture of 2-bromo-5-fluorobenzoic acid methyl ester (5.00g, 21.5mmol) and copper cyanide (2.12g, 23.6mmol) in dmf at 90°c for 1 day. then cool to room temperature, dilute with ethyl acetate (300 ml) and filter. the filtrate was washed with brine (5×50 ml) and then with saturated nahco3 aqueous solution (50 ml). the organic layer was dried over mgso4, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. the product was used in the next step without further purification. ms: the calculated (es) m/z value of c9h6fno2 [m+h]+ is 180.0, and the measured value is 180.0.
step b: add lithium hydroxide monohydrate to a stirred solution of methyl 2-cyano-5-fluorobenzoate (3.85g, 21.5mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (30ml) and water (3ml) at 0°c. (1.11g, 26.5mmol). the reaction was warmed to room temperature and stirred for 1 hour. the solvent was then evaporated and the residue was diluted with water (100 ml) and 2m aqueous hcl (20 ml). the solid was collected by filtration and dried under vacuum to obtain the desired product. ms: the calculated (es) m/z value of c8h4fno2 [m+h]+ is 166.0, and the measured value is 166.0.
apply[1]
cn108697684 reported that 2-cyano-5-fluorobenzoic acid can be used to prepare compound (r)-3-((7-chloro-5-fluoro-1,1-dimethyl-3-oxoisoindole dolin-4-yl)amino)-4-((2,2-dimethyl-1-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)propyl)amino)cyclobut-3-ene-1,2 -diketones. as shown below:
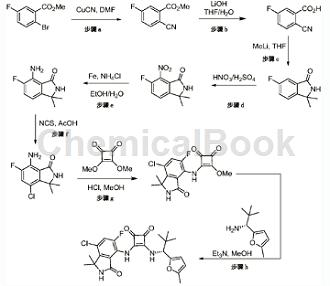
(r)-3-((7-chloro-5-fluoro-1,1-dimethyl-3-oxoisoindolin-4-yl)amino)-4-((2,2 -dimethyl-1-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)propyl)amino)cyclobut-3-ene-1,2-dione is a chemokine modulator. chemokines are chemotactic cytokines that are released by various cells to attract macrophages, lymphocytes, eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils to sites of inflammation (reviewed in schall, cell cytokine, 3:165-183 (1991), schall et al., curr opin. immunol. 6:865-873 (1994) and murphy, rev. immun., 12:593-633 (1994)). in addition to stimulating chemotaxis, chemokines can selectively induce other changes in responding cells, including changes in cell shape, transient increases in intracellular free calcium ions ([ca2+]), granule exocytosis, upregulation of integrins, formation of bioactive lipids (e.g., leukotrienes), and respiratory burst are associated with leukocyte activation. chemokines are therefore early triggers of the inflammatory response, causing release of inflammatory mediators, chemotaxis, and extravasation to sites of infection or inflammation.
main reference materials
[1] (cn108697684) modulator of chemokine receptors

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

