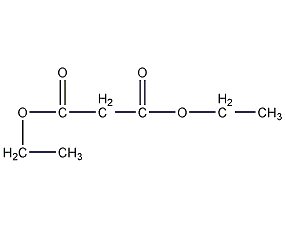
Structural formula
| Business number | 02RU |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H12O4 |
| Molecular weight | 160 |
| label |
Diethylmalonate, Malonic acid diethyl ester, Aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:105-53-3
MDL number:MFCD00009195
EINECS number:203-305-9
RTECS number:OO0700000
BRN number:774687
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with sweet ether smell.
2. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.0490
3. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.0551
4. Melting point (ºC): -50
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 199
6. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 2.15
7. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.4135
8. Flash point (ºC): 100
9. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 290.3
10. Vapor pressure (mmHg, 20ºC): Undetermined
11. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ℃): Undetermined
12. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 54.8
13. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 10.8ºC, constant pressure) : 1.88
14. Conductivity (S/m, 25ºC): 1.2×10-8
15. Solubility (%, 20ºC, water) :2.7
16. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
17. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Solubility: miscible with alcohol and ether, soluble in chloroform, benzene and other organic solvents, slightly soluble in water, solubility in water at 20°C is 2.08g/100mL. It is difficult to dissolve in water and can be mixed with ether and ethanol in any proportion.
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation: Standard Dresser test: rabbit skin contact, 500mg/24HREACTION SEVERITY, slight reaction;
2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 14900μL/kg ; The mouse passing the mouth LD50: 6400mg/kg;
Rabbit skin contact LD50:> 16ml/kg; the guinea pig through the skin LD50:> 10.0ml/kg
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 38.02
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 151.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 360.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 32.3
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7.Polarizability: 15.07
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 6
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 52.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 125
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with oxidants, reducing agents, and alkalis. Chemical properties are more stable than diethyl oxalate. Because it is easily hydrolyzed to produce malonate, which is highly acidic, avoid inhaling the vapor or contacting the skin.
2.This product has low toxicity, the oral LD50 in rats is >1600mg/kg, but it will be hydrolyzed into acid in the body, so contact should be avoided. Wash after contact. Operators should wear rubber gloves.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. They should be stored separately from oxidants, strong bases, and reducing agents, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
2. This product is packed in iron drums or galvanized iron drums, with a specification of 200kg. Store and transport according to regulations on flammable chemicals.
Synthesis method
1. Sodium chloroacetate method: Neutralize chloroacetic acid with sodium carbonate at 30°C to generate sodium chloroacetate, cyanide it with sodium cyanide at 92-95°C, and then hydrolyze it with alkali to generate sodium malonate. After drying, sodium malonate is esterified with ethanol in the presence of sulfuric acid at 70-72°C. The esterification product is washed and distilled to obtain the finished product diethyl malonate. 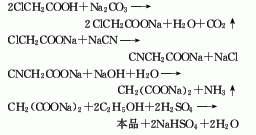
2. Sodium cyanoacetate method is obtained by direct esterification of cyanoacetic acid and ethanol. 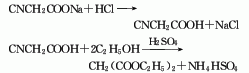
3. Under the catalysis of acid (such as concentrated sulfuric acid), this reagent can be prepared by direct reaction of malonic acid and excess ethanol[1].
4. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, thermometer, and reflux condenser, add 100g (1.06mol) of chloroacetic acid (1) and 250mL of water. Add 90g (1.07mol) of sodium bicarbonate in batches under warm conditions and stir to dissolve at 50-60°C. After the reaction is completed, the pH of the reaction solution is approximately 7. Add 80g (1.23mol) of potassium cyanide in batches, and react at 105 to 110°C for 1 hour after completion. Concentrate under reduced pressure until the internal temperature rises to 130-135°C. Solidifies when cooled. Add 50 mL of absolute ethanol, and then add a mixture of 160 mL of absolute ethanol and 160 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid in about 10 minutes. The reaction is exothermic. The reaction was refluxed for 1 h with stirring. After cooling, add 200 mL of water, filter with suction, wash the insoluble matter with diethyl ether, separate the organic layer, and extract the aqueous layer twice with diethyl ether. Combine the organic layers and wash with sodium carbonate solution until no carbon dioxide gas is generated and the washing liquid becomes alkaline. Dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Evaporate the diethyl ether, then distill under reduced pressure, collect the fraction at 92-94°C/2.13kpa, and obtain 105g of diethyl malonate (1), with a yield of 62%. [2]
Purpose
1. Organic synthesis intermediates. It is widely used in the production of dyes, spices, sulfonylurea herbicides, etc. Mainly used to produce ethoxymethylene, barbituric acid, alkyl diethyl malonate, and then synthesize medicines such as norfloxacin, lomefloxacin, chloroquine, phenylbutazone, etc. and synthetic dyes and pigments such as benzimidazolones Organic pigments. Also used as a plasticizer for nitrocellulose.
2. Used as an intermediate for the pharmaceuticals chloroquine, phenylbutazone, sulfonamides and barbiturates.
3. Malonate is a very useful reagent in organic synthesis. It can undergo hydrolysis and decarboxylation reactions. At the same time, methylene is easier to form carbanions and cause acylation, alkylation, and aldol reactions. and Michael’s reaction, etc.
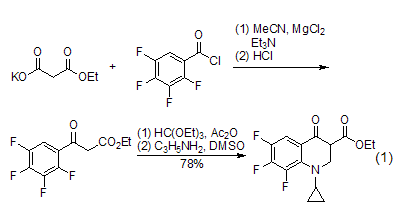
Acylation reaction The acylation reaction of diethyl malonate will be accompanied by partial hydrolysis and decarboxylation reaction. This acylation reaction can be applied to β-Synthesis of ketone esters. Diethyl malonate is hydrolyzed to remove an ester group, and then undergoes an acylation reaction with benzoyl chloride (or similar), and is subsequently converted into a quinolone derivative (formula 1)[2].
Alkylation reaction Under the action of alkali (such as NaH, etc.), the methylene group of diethyl malonate is easier to form carbanions, and then alkylation and other reactions can occur (Formula 2)[3~6 ].
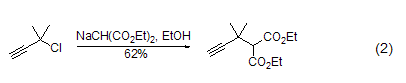
In addition, diethyl malonate The methylene group of the ester can also undergo a chlorination reaction (Formula 3)[7].
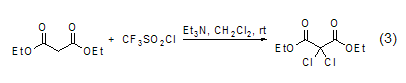
With aldehydes, etc. ReactionsIn reactions with aldehydes or ketones, ring condensation reactions often occur. For example, under the catalysis of copper (II), trimerformaldehyde and diethyl malonate undergo cyclization to form a six-membered ring compound (formula 4)[8].
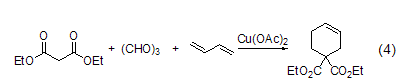
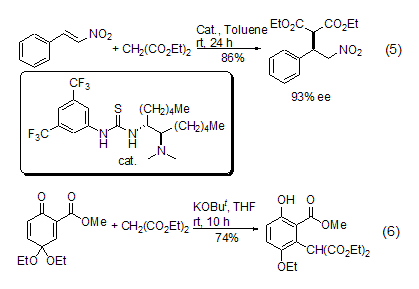
Michael’s reaction
strong> The carbanion formed by diethyl malonate methylene can react with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds (or analogs) to produce 1,4- Conjugate addition reaction (Formula 5, Formula 6)[9~12].
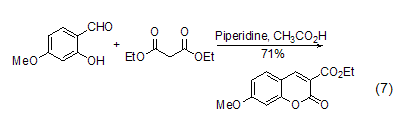
Ring formation reaction In organic synthesis reactions, in addition to the methylene group in diethyl malonate being able to form carbanions and undergo nucleophilic reactions, its ester group part can also undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions, and multiple reaction sites exist. This makes diethyl malonate easily form a ring (formula 7) when reacting with multifunctional compounds [13,14].
Combination reaction. For example, under the catalysis of copper (II), trimerformaldehyde and diethyl malonate undergo cyclization to form a six-membered ring compound (formula 4)[8].
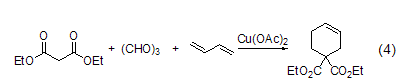
Michael’s reaction
strong> The carbanion formed by diethyl malonate methylene can react with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds (or analogs) to produce 1,4- Conjugate addition reaction (Formula 5, Formula 6)[9~12].

Ring formation reaction In organic synthesis reactions, in addition to the methylene group in diethyl malonate being able to form carbanions and undergo nucleophilic reactions, its ester group part can also undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions, and multiple reaction sites exist. This makes diethyl malonate easily form a ring (formula 7) when reacting with multifunctional compounds [13,14].


 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

