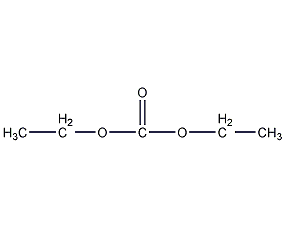
Structural formula
| Business number | 02RZ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H10O3 |
| Molecular weight | 118.13 |
| label |
Ethyl carbonate, Ethyl carbonate, Carbonic acid diethyl ester, aliphatic compounds, Carbonylation reagent |
Numbering system
CAS number:105-58-8
MDL number:MFCD00009107
EINECS number:212-786-4
RTECS number:YE1050000
BRN number:956591
PubChem number:24859278
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with ether smell. [13]
2. Melting point (℃): -43[14]
3. Boiling point (℃): 126~128[15]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.98 (20℃)[16]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 4.07[17]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 1.1 (20℃)[18 ]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2708.2[19]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.39 [20]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.21[21]
10. Flash point (℃ ): 25 (CC) [22]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 445[23]
12. Explosion upper limit (%): 11.0[24]
13. Explosion lower limit (%): 1.4[25]
14. Solubility: Insoluble in water, miscible in most organic solvents such as alcohols, ketones, esters, aromatics, etc. [26]
15. Relative density (g/mL, 15/4ºC): 0.98043
16. Relative density (g/mL, 25/ 4ºC): 0.9693
17. Relative density (g/mL, 30/4ºC): 0.96393
18. Refractive index (15ºC): 1.38654
19 .Refractive index (25ºC): 1.3829
20. Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 0.868
21. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 0.748
22. Flash point (ºC, open): 25
23. Flash point (ºC, closed): 46
24. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 29.53ºC ): 40.2
25. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 36.17
26. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 2700.5
27. Electrical conductivity (S/m, 25ºC): 9.1×10-10
28. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 15~30ºC, constant pressure) : 1.79
29. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1): 0.00119
30. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 22.382
31. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 9.820×109
32. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 67.590 p>
33. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2758.8
34. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ· mol-1): -637.9
35. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2715.2
36. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -681.5
37. Liquid phase standard heat melt (J·mol -1·K-1): 212.1
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[27] LD50: 8500mg/kg (rat subcutaneous)
2. Irritation strong> No data yet
3. Others [28] Hamster abdominal cavity 11.4mg/kg (pregnant rats), has obvious teratogenic effects.
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 28.73
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 120.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 275.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 26.9
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 11.39
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 35.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 62.1
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with oxidants, acids, reducing agents, alkalis, and water. Diethyl carbonate is flammable and should be kept away from fire sources. In case of fire, use foam fire extinguishers, carbon dioxide, carbon tetrachloride or dry chemical fire extinguishing agents. Non-corrosive to metals.
2. Chemical properties: Diethyl carbonate reacts with sodium at room temperature and gradually decomposes into carbon dioxide and sodium ethoxide. If heated to 110°C, the decomposition reaction will be accelerated. Treatment with acetone and decomposition of acetic acid in boiling ether in the presence of sodium powder yields acetoacetate. Treat it with ethyl acetate in boiling benzene in the presence of sodium powder, and decompose it with dilute acetic acid to produce a small amount of diethyl malonate and acetoacetate. Diethyl carbonate can undergo condensation reactions with ketones and organic acid esters in the presence of metal alcoholates. Diethyl carbonate also has general ester properties.
Storage method
Storage Precautions[29] Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37℃. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Absolute ethanol reacts with phosgene to form ethyl chloroformate, which then reacts with ethanol to form diethyl carbonate. Then it is washed and distilled to obtain the finished product. Raw material consumption quota: ethanol 1450kg/t, phosgene 2250kg/t.
Refining method: Diethyl carbonate often contains impurities such as water, acid and monocarbonate. When refining, wash with sodium carbonate or sodium bicarbonate aqueous solution, dry with quicklime or calcium chloride after washing, and distill.
![]()
Purpose
1. Used as a solvent for nitrocellulose, cellulose ether, synthetic resin and natural resin in chemical production. It is used in the pharmaceutical industry to manufacture phenobarbital. Pyrethrum is used in the pesticide industry. Used in the instrumentation industry to manufacture sealing fixatives. Used in analytical chemistry as chemical reagents and lithium-ion battery electrolyte components. Also used in the preparation of special paints for vacuum tubes. In addition, diethyl carbonate is also an important reagent and reaction carrier in organic synthesis.
2. Diethyl carbonate is a commonly used carbonylation reagent and can be used to synthesize ketones, tertiary alcohols and heterocyclic compounds. In addition, diethyl carbonate can also be used as an alkylating reagent for silicon carbonate and nucleophilic substrates.
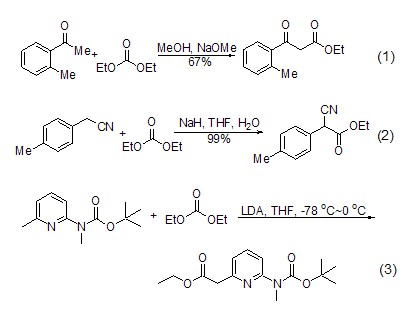
Carbonylation of carbanions Diethyl carbonate is often used for the carbonylation of enol anions. The reaction conditions of this reaction are relatively mild and the yield is high. During the reaction, sodium hydride, potassium hydride, LDA (or a mixture thereof), etc. can be used as a base. At the same time, the selection of reaction substrates is relatively wide, and most of them have molecules with electron-withdrawing groups [such as carbonyl (formula 1) [1], cyano (formula 2) [2] sup>, ester group [3] and enamine [4,5] (formula 3), etc.] can occur at the α-position Carbonylation.
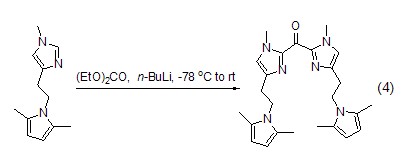
Ketones, tertiary alcohols Synthesis By directly reacting metal organic matter with diethyl carbonate, ketones [6,7] or tertiary alcohols [8,9] can be obtained, as shown by The reaction of imidazole to synthesize the corresponding ketone (Formula 4).
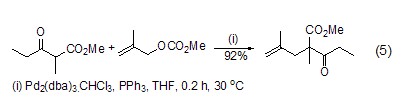
Alkylation or allylation Under appropriate conditions, using palladium-triphenylphosphine as a catalyst can achieve β-carbonyl ester, β-diketone, malonate, cyanide and nitro compound (Formula 5)[10].
Synthesis of heterocyclic compounds Many substrates can react with carbonic acid diester compounds to form heterocyclic compounds, such as 1,2-aminoalcohol and carbonic acid The action of diethyl ester can produce oxazolidinone compounds (formula 6)[11,12].
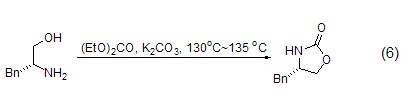
3. Used as solvent and in organic synthesis. [30]
class=”a”>
Synthesis of heterocyclic compounds Many substrates can react with carbonic diester compounds to generate heterocyclic compounds, such as The reaction between 1,2-aminoalcohol and diethyl carbonate can produce oxazolidinone compounds (formula 6)[11,12].
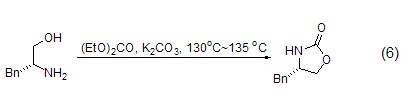
3. Used as solvent and in organic synthesis. [30]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

