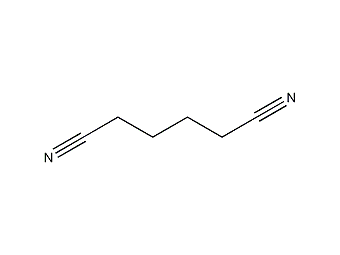
Structural formula
| Business number | 0343 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H8N2 |
| Molecular weight | 108.14 |
| label |
tetramethylene cyanide, tetramethylene dinitrile, 1,4-dicyanobutane, Adipic acid dinitrile, Hexane dinitrile, Tetramethyl cyanide, 1,4-Dicyanobutane, Hexanedinitrile, Tetramethylene dicyanide, Adipic acid dimitrile |
Numbering system
CAS number:111-69-3
MDL number:MFCD00001975
EINECS number:203-896-3
RTECS number:AV2625000
BRN number:1740005
PubChem number:24894156
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless oily liquid with slight odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 1~3[2]
3. Boiling point (℃) : 295[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.96[4]
5. Relative Vapor density (air=1): 3.73[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.267 (100℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -4368.8[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 507[8 ]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 2.80[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: -0.32[10]
11. Flash point (℃): 93 (OC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 550[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 5.0[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.7[14]
15. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol and chloroform, insoluble in ether and carbon disulfide. [15]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 300mg/kg (rat oral)
LC50: 1710mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation No information available
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity[17] Rat inhalation 120~150mg/m3, 4 hours a day for 5 months, proteinuria, increased levels of thiocyanate and urea in the blood, and increased organ weight coefficients and other toxic effects occurred.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[18] TLm: 820mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow, hard water); 1250mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow, soft water); 1250mg/L (24h) (bluegill, soft water)
2. Biodegradability[19] MITI-I test, initial concentration 100ppm, sludge concentration 30ppm, degradation 35%~66% after 28 days.
3. Non-biodegradability[20] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105pieces/cm3, the degradation half-life is 23d (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 39.67
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 114.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 287.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 39.9
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 11.76
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 47.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 113
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. This product is toxic and can cause poisoning through oral inhalation or skin absorption. The LD50 of oral administration to mice was 38.8 mg/kg, and the LD50 of rats was 54.8 mg/kg. Effect on skin: Apply this product to the skin of guinea pigs. After 3, 4 to 16 times of application, some animals died. The maximum allowable concentration in the air is 15~20mg/m3. Chronic poisoning of humans can cause leukopenia and mononucleosis. Inhaling adiponitrile vapor or accidentally swallowing a few milliliters of adiponitrile can cause nausea, vomiting, mucous membrane irritation and dizziness. The victim should be sent to the hospital immediately for treatment and injected with sodium thiosulfate and other drugs to restore the heart and lung organs. Activity is normal. If you have difficulty breathing, rapid pulse, confusion, significant drop in blood pressure, numbness or twitching of limbs and facial tissue, oxygen must be administered. In case of contact with eyes, rinse with plenty of water for 20 minutes before sending to hospital for treatment. In case of skin contact, wash with soap and water. The production workshop should be well ventilated and the equipment should be sealed. Operators should wear protective equipment. For protective measures see Acrylonitrile.
2. Stability[21] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[22] Strong oxidizing agent, strong reducing agent, strong acid, strong alkali
4. Conditions to avoid contact [23] Heat
5. Hazards of aggregation[24] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[25] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, acids, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
At present, the main industrial methods for producing adiponitrile are adipic acid ammoniation method, butadiene method and acrylonitrile dimerization method. Among them, adipic acid ammoniation method is the earliest to be industrialized, has relatively mature technology and has the largest application.
1. Adipic acid amination method: react adipic acid and excess ammonia in the presence of catalyst phosphoric acid or its salts or esters at a temperature of 270-290°C to generate adipic acid. Diammonium acid is then heated and dehydrated to produce crude adiponitrile, which is then distilled to obtain the product. Raw material consumption quota: adipic acid 1606kg/t, liquid ammonia 370kg/t, sodium hydroxide 36kg/t.
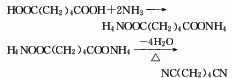
2. Butadiene method: It is further divided into chloride cyanide method and direct hydrocyanation method.
3. Acrylonitrile electrolytic dimerization method: The electrolyte is p-toluene tetraethylamine sulfonate, the temperature is 50-60°C, and the yield of adiponitrile is 92-95%. The acrylonitrile hydrogenation dimerization process can also use the gas phase catalytic hydrogenation method with ruthenium catalyst at 200-300℃, 0.1-0.3MPa. Raw material consumption quota: acrylonitrile 1100kg/t, sulfuric acid 80kg/t.
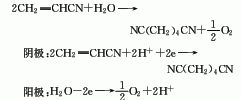
4. Adipamide in amine Under the action of ammonium sulfonate, dehydration can generate adiponitrile:
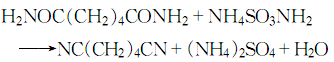
Purpose
1. Used as additives for detergents, spinning solvents for acrylonitrile, methacrylonitrile and methyl methacrylate terpolymers, solvents for wet and dry spinning of polyvinyl chloride fibers, and colorants for polyamides , auxiliaries for fabric bleaching agents, acetate, propionate, butyrate and mixed ester plasticizers; and as extraction agents for aromatic extraction, etc. Gas chromatography stationary solution.
2. Used in organic synthesis as analytical reagents and solvents.
3. Gas chromatography stationary solution. Separate and analyze amine and nitro compounds.
4. Used as an intermediate in the manufacture of nylon and in organic synthesis. [26]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

