Background and overview[1][2]
Aryl sulfones have special chemical properties and biological activities, and their structures can be found in many drugs. As an important class of organic compounds, their synthesis and applications have been extensively studied. The more commonly used synthesis methods of aryl sulfones include: oxidation of the corresponding aryl sulfide, acid-catalyzed sulfonation of aromatic hydrocarbons, reaction of organolithium, organomagnesium compounds and sulfone esters; and palladium-catalyzed hydrocarbyl sulfinates and aryl sulfones. The coupling reaction of halides, the palladium-catalyzed coupling reaction of arylboronic acid and arylsulfonyl chloride; and the copper-catalyzed Suzuki reaction, Cu(OTf)2·PhH/nitrogen, nitrogen,-di Methylethylenediamine-catalyzed coupling reaction of aryl halides and hydrocarbyl sulfinates.
Traditional methods have many shortcomings. Many functional groups cannot tolerate severe reaction conditions; while palladium catalysts have problems such as being expensive and causing serious environmental pollution. Copper-catalyzed reactions reported in the literature have problems such as the use of stoichiometric catalysts, high temperatures, and limited substrate range. Methyl 4-methanesulfonylbenzoate is an aryl sulfone compound that can be used as a pharmaceutical synthesis intermediate and an organic synthesis intermediate. It is mainly used in laboratory research and development processes and chemical and pharmaceutical synthesis processes.
Preparation[1]
Methyl 4-methanesulfonylbenzoate is prepared as follows:
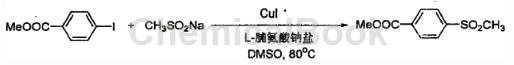
The specific steps are as follows: In a reaction tube, add 262 mg ethyl p-iodobenzoate (MW=262.04, 1.0mmol), and then add 153mg methane sulfonate sodium salt (MW=102.09, 1.2mmol, content 80% ), 28 mg L-proline sodium salt (MW = 137.05, 0.2 mmol), 19 mg CuI (MW = 190.45, 0.1 mmol), 2 ml DMSO as solvent, react in an 80°C oil bath for 36 hours under nitrogen protection, cool and add 4 ml of water, extracted with 10 ml of ethyl acetate each time, repeated three times. The extract was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and the filtrate was distilled under reduced pressure and separated through a silica gel column (eluent petroleum ether: acetic acid Ethyl ester = 3:1), 158 mg of the product 4-methanesulfonylbenzoic acid methyl ester was obtained, with a yield of 77%.
Main reference materials
[1] (CN1651408) Amino acid-promoted CuI-catalyzed coupling reaction of aryl halides and hydrocarbyl sulfinates

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

