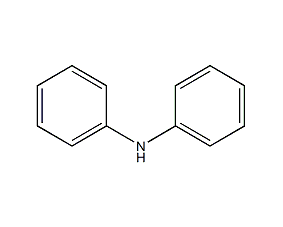
Structural formula
| Business number | 03EY |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C12H11N |
| Molecular weight | 169.22 |
| label |
phenylaniline, aminodiphenyl, N,N-diphenylamine, Anilinobenzene, Difenylamin, N-phenylaniline, Polymerization inhibitor, retarder, rubber accelerator, antioxidant, plastic stabilizer, Fungicide |
Numbering system
CAS number:122-39-4
MDL number:MFCD00003014
EINECS number:204-539-4
RTECS number:JJ7800000
BRN number:508755
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless to light gray crystal. Slightly unique smell.
2. Density (g/mL, 20/20℃): 1.160
3. Flash point (℃): 153
4. Melting point (℃ ): 53~54
5. Boiling point (ºC): 302
6. Autoignition point (ºC): 634
7. Solubility: slightly soluble Soluble in water, ethyl ether, benzene, carbon disulfide and glacial acetic acid.
8. Toxicity: Highly toxic, can irritate the skin and mucous membranes, and cause symptoms such as blood poisoning (production of methemoglobin).
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 2gm/kg
Mouse oral LC50: 1750mg/kg
Guinea pig oral LD50: 300mg/kg
p>
Unknown mammalian oral LD50: 3200mg/kg
2. Other multiple dose toxicity: Rat oral TDLO: 9660mg/kg/92W-C
Large Oral TDLO in rats: 28gm/kg/28D-I
3. Reproductive toxicity: Oral TDLO in rats (female, before fertilization): 7500mg/kg/17-22D
Ecological data
flammable and irritating. Can damage the nervous system, cardiovascular system and blood system. The toxic effects are similar to those of aniline.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 55.62
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 155.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 400.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 44.0
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 22.05
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. RotatableNumber of chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 12
7. Number of heavy atoms :13
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 116
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11 .Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It is weakly alkaline and can form salts with strong acids. It can also precipitate diphenylamine when diluted with water. It turns gray-black when exposed to light. Combustible.
2. Highly toxic, can irritate the skin and mucous membranes, and cause symptoms such as blood poisoning (production of methemoglobin). The pathological phenomena are similar to aniline, but the toxicity is slightly lower than aniline. The maximum allowable concentration in the air is 10 mg/m3. The production site should be well ventilated, the equipment should be sealed, and operators should wear protective equipment to avoid direct human contact with it.
3. Exist in mainstream smoke.
Storage method
1. Packed in gunny bags lined with plastic bags. It should be sealed and stored away from light, and pay attention to fire and heat protection. Storage and transportation according to regulations on flammable, explosive and toxic substances
Synthesis method
1. Aniline hydrochloride method is obtained by the condensation of aniline and aniline hydrochloride.
2. Aluminum trichloride catalytic method Using aniline as raw material, aluminum trichloride as catalyst, and obtained through condensation reaction.
3. Phenol condensation method uses HD92 catalyst and is obtained by condensing phenol and aniline.
4. Aniline uses anhydrous aluminum trichloride as a catalyst to perform a condensation reaction. The reaction product is subjected to hydrochloride precipitation, sodium hydroxide neutralization, boiling and washing, vacuum distillation, crystallization with ethanol, and separation to obtain the finished product.
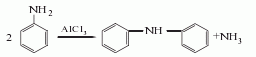 5.Industry 2 Aniline is obtained by refining. 6.Use potassium cyanide to wash industrial diphenylamine with iron and other metals After complexation, it is separated from diphenylamine.
5.Industry 2 Aniline is obtained by refining. 6.Use potassium cyanide to wash industrial diphenylamine with iron and other metals After complexation, it is separated from diphenylamine.
7. Distillate diphenylamine under reduced pressure in nitrogen flow to obtain the finished product.
Purpose
1. Used to prepare azo dyes and other dyes, and also used as a stabilizer for nitrocellulose. 2. Used as free radical polymerization inhibitor and retarder. This product is a mixed component of azo dyes such as acid yellow G, acid orange IV, etc. It is also used in the production of rubber accelerators, antioxidants, plastic stabilizers and veterinary drugs such as sulfurized diphenylamine. 3.For colorimetric determination of nitrate, nitrite, chlorate and magnesium. Used as redox indicator, testing or determination of oxides, organic synthesis and liquid desiccant. 4.Accelerators, antioxidants, plastic stabilizers and veterinary drugs such as sulfurized diphenylamine used in the production of rubber. It can also be used as a safener for nitrocellulose and smokeless explosives. 5.Used as analytical reagents, such as color developers, redox indicators, and liquid desiccants. Also used in organic synthesis.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

