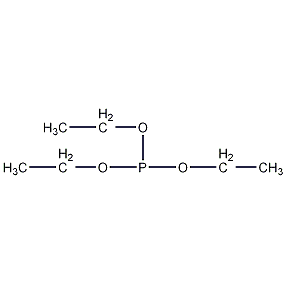
Structural formula
| Business number | 03F4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H15O3P |
| Molecular weight | 166 |
| label |
Aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:122-52-1
MDL number:MFCD00009084
EINECS number:204-552-5
RTECS number:TH1130000
BRN number:956578
PubChem number:24889381
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid
2. Relative density (g/mL, 20/4℃): 0.963
3. Refractive index (nD20): 1.4133
4. Flash point (℃): 54
5. Melting point (℃): -112
6. Boiling point (ºC, room temperature): 157.9
p>
7. Boiling point (ºC, 1.6kpa): 49
8. Solubility: Easily soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and ether, insoluble in water, and easily gradually hydrolyzed into phosphorous acid in water Diethyl ester hydrolyzes faster in acidic media.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity:
Rat oral LD50: 1840mg/kg;
Rat inhalation LC5O: 11063mg/m3/6H ;
Mouse oral LD50: 3720mg/kg;
Mouse inhalation LC5O: 6203mg/m3/6H;
Mouse transperitoneal membrane LD: >500 mg/kg;
Rabbit skin LD50: 2800mg/kg
Ecological data
Slightly harmful to water.
Molecular structure data
None yet
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.2
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 6
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 27.7
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 55.7
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Relatively stable at room temperature and pressure. Since this reagent has a very specific unpleasant odor, it is recommended that the reaction be carried out in a fume hood.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources.
2. This product is packed in iron drums. Store in a cool, dry place and protected with nitrogen. Store and transport according to regulations on toxic chemicals.
Synthesis method
1. Use absolute ethanol, phosphorus trichloride and liquid ammonia as raw materials to perform esterification reaction in xylene solvent to generate triethyl phosphite. The crude ester is washed with water to remove ammonium chloride and diethyl phosphite. , after distillation to remove the solvent, and then rectification to obtain the finished product. Raw material consumption quota: phosphorus trichloride (95%) 950kg/t, absolute ethanol 930kg/t, liquid ammonia 340kg/t.
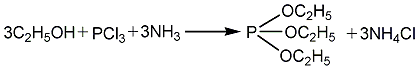
2. Equipped with a closed stirrer and a high-efficiency reflux condenser In a 3-liter three-necked flask with a 500-ml dropping funnel, put 447 grams (477 ml, 3 mol) of absolute ethanol and 1 liter of dry petroleum ether (boiling point 40-60°C) into a 3-liter three-neck flask. ) freshly steamed diethylaniline solution. Put 400 ml of dry petroleum ether and 137.5 g (87.5 ml, 1 mol) of freshly distilled phosphorus trichloride solution into the dropping funnel. The flask was cooled in a cold water bath. Under vigorous stirring, add phosphorus trichloride solution dropwise, and the mixture can be gently refluxed at the dropping speed. It takes about 30 minutes to finish dripping. After the addition is complete, continue heating and stirring to allow gentle reflux for 1 hour. Cool the suspension containing a large amount of diethylaniline hydrochloride precipitate, use a glass core funnel to suction and filter the dry amine salt filter cake on the water pump, and wash with 5 parts of 100 ml dry petroleum ether (boiling point 40-60°C). Combine the filtrate and washing liquid, and use a 75 cm long pine needle-shaped fractionating column on a water bath for distillation and concentration. The residue was transferred to a pear-shaped flask and distilled under reduced pressure with a water pump using a 75 cm long pine needle-shaped fractionating column. After steaming out a small amount of the front fraction, collect the product at 57-58℃/16mm (51-52℃/13mm, 43-44℃/10mm). The yield of the colorless product is 138g (83%)
Wooden method Dimethylaniline can also be used. The hydrochloride produced is easy to filter out and does not absorb moisture.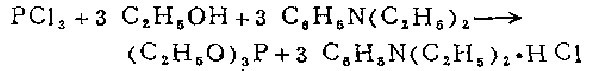
Purpose
1. This product is used as plastic stabilizer and plasticizer; it is also used as an intermediate for medicines and pesticides. It is used to produce the analgesic benzodiazepine, the pesticide fenithiocarb, etc.; it is also used as a plasticizer, stabilizer, additive for lubricants and greases.
2. Preparation of phosphorus acid cheese (Arbuzow reaction). Deoxidizer and desulfurizer. Deoxygenation of hydroperoxides, peroxydiaroyl peroxides, epoxides, isocyanates, and deoxygenation of 1 and 2-diones to produce alkynes. Reduction of nitrogen-containing functional groups. Desulfurization of episulfides, mercaptans, and disulfides. Reduction of α-keto acid to α-hydroxy acid. It reacts with α-halogenated aldehydes and ketones to form dialkyl vinyl phosphates (Perkow reaction).
3. Triethyl phosphite is widely used in organic synthesis and is often used as a reducing agent and nucleophile. The reactions in which it is directly involved have been given various names due to their importance.
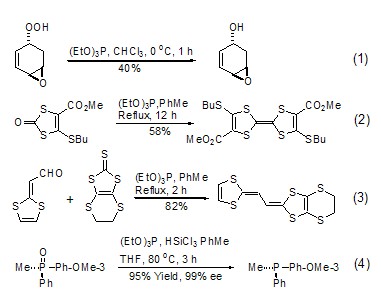
Triethyl phosphite is used as a reducing agent. During the reaction, the phosphorus atom itself is oxidized from +3 valence to +5 valence, and it also has the function of taking away oxygen atoms or sulfur atoms from another reactant. , generating the corresponding triethyl phosphate. For example: triethyl phosphite can reduce peroxy compounds to alcohols, and can selectively reduce one of them in the presence of two peroxy groups under controlled conditions (formula 1)[1]. 1,3-Dimercaptoketone can undergo coupling reaction in the presence of triethyl phosphite (Formula 2)[2]. Refluxing triethyl phosphite with aldehyde and 1,3-dimercaptothione can give the corresponding olefin (formula 3)[3]. According to literature reports, triethyl phosphite can also undergo oxygen exchange reactions with other phosphates (Formula 4)[4].
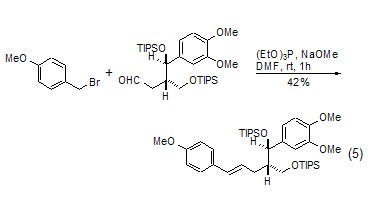
Triethyl phosphite-led One of the name reactions is the Arbuzov reaction[5]. Triethyl phosphite and halogenated hydrocarbon first undergo a nucleophilic substitution reaction, and at the same time, the halide ion causes the cleavage of the ethoxy group to generate a hydrocarbyl-substituted diethyl phosphonate derivative. When there is an electron-withdrawing group at the β-position of the halogen atom in a halogenated hydrocarbon, the product will generate phosphine ylide under the action of a strong base, and then undergo a “one-pot cooking” reaction with the aldehyde to obtain the Horner-Emmons reaction. product. This reaction plays an important role in the synthesis of complex natural products (Formula 5)[6].
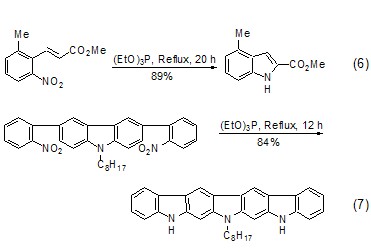
Triethyl phosphite-led Another well-known reaction is the Cadogan reaction [7], which is an important method for the synthesis of polycyclic nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds. When the aryl nitro functional group is heated with triethyl phosphite, the nitro group can be reduced to nitrene. Nibenine then attacks other olefinic bonds or aromatic rings in the molecule to generate polycyclic nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds. In the Cadogan reaction, triethyl phosphite generally serves as both reactant and solvent. For example: o-vinyl-substituted nitrobenzene and triethyl phosphite are co-thermally generated to form indole derivatives (Formula 6)[8,9]. The co-heating of o-aryl-substituted nitrobenzene and triethyl phosphite produces carboline derivatives (Formula 7)[10,11].

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

