Background and overview[1]
Lobenzaritdisodium, whose chemical name is disodium N-o-carboxyphenyl-4-chloro-2-aminobenzoate, is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug developed by Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. . This product has antipyretic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory and immune-regulating effects, and is clinically used to treat chronic rheumatoid arthritis. The synthesis method reported in the literature is to dissolve 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid and anthranilic acid in isoamyl alcohol or N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) solvent, add potassium carbonate and copper powder to perform Ullmann reaction, After the reaction is completed, add water, decolorize with activated carbon, evaporate the solvent, and acidify to obtain crude chlorbenzaride, which is then refined multiple times with tetrahydrofuran, methanol or ethanol to obtain a refined product of the crude chlorbenzaride. The crude chlorbenzaride is then mixed with an appropriate amount of sodium bicarbonate or sodium hydroxide to form a salt. Part of the water is evaporated and ethanol is added to precipitate chlorbenzaride disodium. The total yield is 63.7%. Due to the cumbersome synthesis and refining operations of chlorbenzaride, when chlorbenzaride reacts with an appropriate amount of sodium bicarbonate or sodium hydroxide to form a salt and then adds ethanol to precipitate the product chlorbenzaride disodium, colloids are prone to form and are difficult to filter. The above factors are not conducive to industrial production.
Apply[2-3]
Lobenzaritdisodium, also known as carboxyphenyl chlorophthalamine and diphenylamine derivatives, is clinically used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. It is more effective than indomethacin and can be quickly absorbed by the digestive system when taken orally. , and has little irritation to the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, its bioavailability is relatively high, so clobenzaride disodium is a non-steroidal antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug with good development prospects. The drug Chlorbenzaride can improve the body’s immunity and has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. It is clinically used to treat chronic rheumatoid arthritis, and its effects on various inflammation models of chronic rheumatoid arthritis: ① It can inhibit the occurrence of various symptoms (secondary inflammation) of adjuvant arthritis in rats. ② It can prevent spontaneous nephritis (proteinuria, renal tissue lesions, etc.) in NZB/WF1 mice and significantly extend their survival. It can inhibit the production of thymocyte-disordered natural autoantibodies and the emergence of anti-DNA antibodies and anti-nuclear antibodies. ③ It can prevent polyarthritis, nephritis (glomerular and other tissue changes, rabbit disease complex deposition, joint inflammation, etc.) in mice. , synovium, cartilage tissue lesions). Effect on the antibody production system: It can restore the reduced inhibitory T cell activity of NZB/WF1 mice with hereditary immune insufficiency and mice treated with colchicine. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, etc.: Carrageenan shows no inhibitory effect on acute inflammation such as plantar edema and granuloma (rats), and has no analgesic effect on pain caused by acetic acid twisting method and hot plate method (mice) . It also has no inhibitory effect on PGE2 biosynthesis (rat, in vitro), and has no effect on allergic reactions such as PCA reaction (rat, guinea pig) and complement activation reaction (in vitro).
Preparation[1]
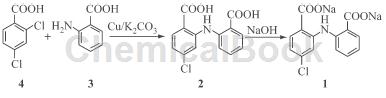
1) Synthesis of chlorbenzaride (2)
Add isoamyl alcohol (180mL), 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid (9.5g, 0.05mol) and anthranilic acid (21.0g, 0.15mol) into a 250mL three-necked flask, and dissolve Then add 20g potassium carbonate, 1g copper powder and 0.2g iodine, reflux the reaction in an oil bath at 125-130℃ for 6 hours. Pour the reaction solution into 200mL water, stir, filter, and let the filtrate stand.
Separate the isoamyl alcohol phase (recycle it after distillation), adjust the pH of the water phase to 2-3 with 3 mol/L hydrochloric acid, and precipitate. Filter, and wash the filter cake twice with cold water to obtain the crude product of compound 2.
2) Refining of chlorbenzaride
After the above crude product was dissolved and clarified with 20% (mass fraction, the same below) sodium carbonate solution, 2% (mass fraction) activated carbon was added, decolorized at 80°C for 30 minutes, then suction filtered, and the filtrate was 3 mol /L hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH to 2 to 3 and precipitate out. Filter, wash the filter cake with water, and then recrystallize with 95% (mass fraction, the same below) ethanol to obtain 12.3g of refined product, yield 84.2%, mp336~338°C, consistent with the literature value [4], and TLC detection is single Spots (developing agent: CHCl3:CH3COOH=20:1).
1HNMR(DMSO-d6)δ/×10-6: 12.04(2H, brs, COOH), 7.84(2H, d, J=8.0Hz, Ar-H), 7.35(1H, d, J=8.0Hz, Ar-H), 7.29 (1Hd, J=1.5Hz, Ar-H), 7.19 (1H, t, J=7.5Hz, Ar-H), 6.77 (1H, t, J= 7.5Hz, Ar-H), 6.67 (1H, dd, J=8.8Hz, 1.5Hz, Ar-H).
3) Synthesis of chlorbenzaride disodium
Chlorbenzaril (10g, 0.034mol) was dissolved and clarified with 10% (mass fraction, the same below) sodium hydroxide solution, then 2% (mass ratio) of activated carbon was added, and decolorized at 80°C After 30 minutes, filter, concentrate under reduced pressure until crystals precipitate, cool and crystallize, filter, wash with a small amount of cold water, and dry at 70°C to obtain 10g of clobenzaride disodium, yield 86.9%, mp386°C (dec).
Determination of related substances[4]
Establish a method for determining the content of related substances in chlorbenzaride disodium tablets. Fang used high-performance liquid chromatography to determine impurity A (anthranilic acid) and impurity B (2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid) and other related substances in three batches of samples. The chromatographic column is TianHeC18, the mobile phase is acetonitrile-potassium dihydrogen phosphate solution (pH 3.2) (50:50), the flow rate is 1.0ml/min, the detection wavelength is 222nm, and the column temperature is 30°C. Results: The linear range of the detection mass concentration of clobenzaride disodium was 0.2608 ~ 2.608 μg/ml (r=0.9994), the average recovery rate was 99.85%, RSD=0.22% (n=9). The detection limits of chlorbenzaride disodium, impurity A, and impurity B are 0.20 respectively.224, 0.3744, 0.8384ng. This method is sensitive and accurate and can be used as a method for the determination of related substances in clobenzaride disodium tablets.
Main reference materials
[1] Improvement of post-treatment process in the synthesis of chlorbenzaride disodium
[2] Preparation of chlorbenzaride disodium tablets
[3] CN201610814031.X A method for synthesizing chlorbenzaride drug intermediate N-o-carboxyphenyl-4-chloro-2-aminobenzoic acid
[4] Determination of related substance content in chlorbenzaride disodium tablets by HPLC method

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

