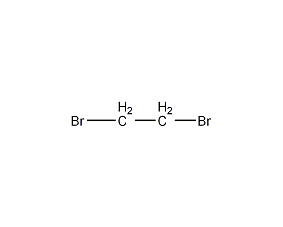
Structural formula
| Business number | 02U7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H4Br2 |
| Molecular weight | 187.86 |
| label |
Ethylene dibromide, 1,2-dibromoethane, Ethylene dibromide, Symmetric dibromoethane, 1,2-Dibromethane, Ethylene dibromide, sym-Dibromoethane, Ethylene bromide, EDB, Aliphatic halogenated derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:106-93-4
MDL number:MFCD00000233
EINECS number:203-444-5
RTECS number:KH9275000
BRN number:None
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and sweet liquid with chloroform smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 9.97[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 131 ~132[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 2.17[4]
5. Relative Vapor density (air=1): 6.48[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 2.32 (30℃)[6]
7. Critical pressure (MPa): 7.15[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.96[8]
9. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, miscible in most organic solvents. [9]
10. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 0.01613
11. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 190.9
12. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 10.84
13. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid): 80.805
14. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, liquid): 1217.9
15. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), constant pressure): 0.72
16. Conductivity (S/m, 25ºC ): 1.28×10-11
17. Solubility (%, water, 25ºC): 0.54
18. Volume expansion coefficient (K -1, 15~30ºC): 0.000958
19. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 2.1791
20. Refractive index at room temperature (n 20): 1.5387
21. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 20.656
22.van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 6.860×109
23. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 49.260
24. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -37.5
25. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 329.74
26. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -9.17
27. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ ·mol-1): -79.2
28. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 223.30
29. Liquid phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -17.6
30. Liquid phase standard heat Melting (J·mol-1·K-1): 131.8
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[10]
LD50: 108mg/kg (rat oral);300mg/kg (rat transdermal); 300mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 14300mg/m3, (rat inhalation, 30min)
2. Irritation[11] Rabbit transdermal: 1%, 14 days, severe irritation.
3. Mutagenicity[12] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 500nmol/dish; Escherichia coli 20μl/dish. Sister chromatid exchange: human lymphocytes 10nmol/L. Micronucleus test: human lymphocytes 1mmol/L. DNA suppression: human lymphocytes 5ml/L. Mammalian somatic mutations: human lymphocytes 5mg/L.
4. Teratogenicity[13] The lowest toxic dose of inhalation (TCLo) in rats 6~15 days after pregnancy 32ppm (23h), causing developmental malformations of the musculoskeletal system.
5. Carcinogenicity[14] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G2A, possible human carcinogen.
6. Others[15] The lowest toxic concentration for rats inhaled (TCLo): 80ppm (24h), causing The fetal rat dies. The lowest toxic concentration when inhaled by rats (TCLo); affects testicles, epididymis, vas deferens, gonads, urethra and male fertility index.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[16] LC50: 18mg/L (48h) (bluegill sunfish)
2. Biodegradability[17]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 672~4320
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 48~360
3. Non-biodegradability[18]
Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 257~2567
First-level hydrolysis half-life (h): 19272
4 .Other harmful effects[19] This substance is harmful to the environment and special attention should be paid to mammals and birds.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 26.77
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 87.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 216.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 36.4
5. Polarizability: 10.61
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 6
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Partially decomposes under the action of light. Reacts with strong base to generate vinyl bromide.
2. The vapor is toxic and can cause anesthesia at high concentrations. It can cause pulmonary edema and death under general anesthesia. The lowest poisoning concentration in the air is 25×10-6. The lethal concentration by inhalation is 1000×10-6. Carcinogenic to rodents. The maximum allowable concentration in the air is 130×10-9. The steam irritates the respiratory tract and damages the liver and kidneys. Liquid contact with skin can cause ulcers. When contaminated, take off your coat immediately and dry your skin. The production site is required to be well ventilated and equipped with gas masks and protective clothing.
3. It has a moderate anesthetic effect and is easily absorbed by the skin. Its vapor can irritate the eye mucosa and upper respiratory tract. It has little anesthesia, but can cause dullness, depression, and vomiting. Taking 40g can cause death. Chronic poisoning can cause symptoms such as eyeball conjunctivitis, bronchitis, laryngitis, loss of appetite, depression and other symptoms. Potential carcinogen. The olfactory threshold concentration is 199.94mg/m3. The maximum allowable concentration in the workplace is 192.25 mg/m3.
4. Stability[20] Stability
5. Incompatible substances[21] Alkali metals, strong oxidants
6. Conditions to avoid contact[22] Light and heat
7. Polymerization hazard[23] No polymerization
8. Decomposition products[24] Hydrogen bromide
Storage method
1. Storage precautions [25] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkali metals, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
2. The storage and transportation conditions and protection requirements are the same as (1) methyl bromide, and avoid contact with aluminum, magnesium, potassium, sodium, etc. or contact with strong alkali and chlorine-rich substances. The Joint International Air Transport Regulations are Article 727 Poison B.
Synthesis method
1. Ethylene bromination method: Industrial production uses non-catalytic addition of ethylene and bromine. The reaction rate increases as the reaction temperature increases. The presence of water vapor can accelerate the reaction. The exhaust gas contains excess ethylene and HBr. The HBr is removed by washing with water in the scrubber, and the excess ethylene is recovered.
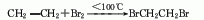
2. Ethane bromination method .

3. Ethylene glycol and hydrogen bromide Acid reaction method.
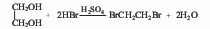
Purpose
1. Used as a solvent in organic synthesis, pesticides, medicine, etc. It is used as a fuel additive for automobiles and aviation, a non-flammable solvent for celluloid, a fungicide for grains and fruits, and a pesticide for wood.
2. Used as a solvent, used in organic synthesis, manufacturing pesticides, pharmaceuticals, etc. [26]
.gif” alt=”” />
2. Ethane bromination method.

3. Reaction method of ethylene glycol and hydrogen bromide.
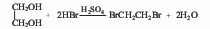
Purpose
1. Used as a solvent in organic synthesis, pesticides, medicine, etc. It is used as a fuel additive for automobiles and aviation, a non-flammable solvent for celluloid, a fungicide for grains and fruits, and a pesticide for wood.
2. Used as a solvent, used in organic synthesis, manufacturing pesticides, pharmaceuticals, etc. [26]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

