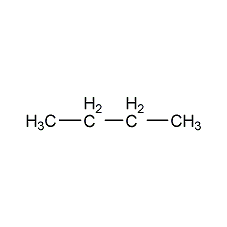
Structural formula
| Business number | 02UB |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H10 |
| Molecular weight | 58.12 |
| label |
Methylethylmethane, butane, diethyl, n-Butane, Diethyl, Methylethylmethane, Aliphatic hydrocarbons |
Numbering system
CAS number:106-97-8
MDL number:MFCD00009424
EINECS number:203-448-7
RTECS number:EJ4200000
BRN number:None
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless compressed or liquefied gas, with a slight unpleasant odor, pure and tasteless. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -138.4[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): -0.5[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.6 (0℃)[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 2.1[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 213.7 (21.1℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2637.8[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 153.2[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.79[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient :2.89[10]
11. Flash point (℃): -60 (CC) [11]
12 .Ignition temperature (℃): 287[12]
13. Explosion limit (%): 8.5[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.9[14]
15. Solubility: easily soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, and chloroform. [15]
16. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.3326
17. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 5.3835
18. Lennard-Jones parameter (K): 312.68
19. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 14.453
20. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.228
21. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 255
22. Critical compression factor: 0.274
23. Eccentricity factor: 0.1599
24. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 6.940×109
25. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 47.800
26. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1 ): -2876.4
27. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -126.8
28. Gas phase standard entropy ( J·mol-1·K-1): 309.91
29. Gas phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): -15.9
30. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 98.49
31. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2855.4
32. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ ·mol-1): -147.8
33. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 231.0
34. Liquid phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -15.2
35. Liquid phase standard heat Melting (J·mol-1·K-1): 139.79
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16] LC50: 658000ppm (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation None Information
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability[17] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3 When, the degradation half-life is 6.3d (theoretical).
4. Bioconcentration [18] BCF: 33 (theoretical)
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 20.58
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 94.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 191.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 16.7
5. Dielectric constant: 1.76
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 8.15
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 2
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[19] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[20] Strong oxidants, strong acids, strong bases, halogens
3. Polymerization hazards[21] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[22] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse dedicated to flammable gases. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 30℃. They should be stored separately from oxidants and halogens, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with leakage emergency response equipment.
Synthesis method
1. Separate oil field gas and wet natural gas by pressurizing, condensing and separating them to obtain liquefied petroleum gas containing propane and butane, which can then be separated by distillation to obtain butane.
2. Separate the C4 fraction from petroleum cracking and obtain the gas obtained by distillation at room temperature and under pressure in the refinery. After reforming; catalytic cracking; coking; thermal cracking; and the liquid gas obtained by hydrocracking, a large amount of C4 can be obtained The C4 fraction obtained by reforming, hydrocracking and atmospheric and vacuum distillation is mainly butane (n-butane and isobutane). The C4 fraction produced by the ethylene unit also contains butane. For example, the yield of butane in the naphtha medium-depth cracking product is 0.19% (weight), accounting for 6.5% of the C4 fraction. The tail gas from the catalytic cracking unit is fractionated to separate the C3 fraction; isobutylene and C5 fraction are sent from the bottom of the tower to the front acetonitrile extraction distillation tower, and more than 90% of n-butane is obtained from the top of the tower.
3. Using industrial crude butane (C4H1080%~90%) as raw material and molecular sieve as adsorbent for adsorption purification, n-butane with a purity of 98% can be obtained. Using distillation to remove light components, the purity of the product can reach over 99.99%.
Purpose
1. Mixed with propane as liquefied petroleum gas, it is widely used for home heating, cooking and industrial heating. In addition, it is widely used as raw material for organic synthesis. For example, butene and butadiene can be produced through dehydrogenation; isobutane can be produced through isomerization; maleic anhydride, acetic acid, acetaldehyde, etc. can be produced through catalytic oxidation; halogenated butane can be produced through halogenation; Nitrobutane can be produced by nitrification; carbon disulfide can be produced by catalysis at high temperatures, and hydrogen can be produced by steam conversion. Butane can also be used as a motor fuel blend to control volatile matter; it can also be used as a deasphalting agent for heavy oil refining; a solvent for wax precipitation in oil wells; an overflow agent for secondary oil recovery; a resin foaming agent; and the conversion of seawater into fresh water. Refrigerants; and olefin Ziegler polymerization solvents, etc.
2. Used in organic synthesis and ethylene manufacturing, as raw material for synthetic rubber and high-octane liquid fuel, as household fuel, solvent, refrigerant, and for instrument calibration, etc. [23]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

