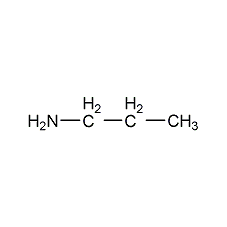
Structural formula
| Business number | 02UN |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H9N |
| Molecular weight | 59 |
| label |
propylamine, 1-aminopropane, Propylamine, 1-Aminopropane |
Numbering system
CAS number:107-10-8
MDL number:MFCD00008205
EINECS number:203-462-3
RTECS number:UH9100000
BRN number:1098243
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless hygroscopic liquid with strong ammonia smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -83[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 48.5[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.719[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.0[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 32.9 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2363.0[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 233.8[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.74[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.15 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): -37[11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 317.8[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 10.4[13]
14. Explosion lower limit (% ): 2.0[14]
15. Solubility: Miscible with water, miscible in ethanol and ether, soluble in acetone, benzene and chloroform. [15]
16. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.3885
17. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 0.353
18. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 31.36
19. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 29.75
20. Heat of generation (KJ/kg , 25ºC, liquid): -101.57
21. Heat of generation (KJ/kg, 25ºC, gas): -70.21
22. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 25ºC, constant pressure): 2.70
23. Vapor pressure (kPa, 4.5ºC): 14.13
24. Vapor pressure (kPa, 32.2ºC): 52.93
25.pKa (25ºC, water): 10.568
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 370mg/kg (rat oral); 400mg/kg (rabbit dermal )
LC50: 2310ppm (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation [17] Rabbit eye : 720μg (24h), severe irritation.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity [18] Rats inhaled 968mg/m3, 7 hours a day, After a total of 50 days, 1/10 died, and the growth of other animals was retarded; 1936 mg/m3 caused the animals to lose weight, cause corneal opacity, and 10/10 died.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability[19] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3 When, the degradation half-life is 12h (theoretical).
4. Other harmful effects [20] This substance is harmful to the environment, special attention should be paid to its use on water.� pollution.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 19.48
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 81.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 180.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 23.8
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 7.72
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 7.2
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties are similar to methylamine. Its aqueous solution is alkaline and reacts with nitrous acid to release nitrogen and generate propanol and propylene.
2. Stability[21] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[22] Acids, acid anhydrides, acid chlorides, strong oxidants
4. Polymerization hazards[23] No polymerization p>
Storage method
Storage Precautions[24] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 29°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, etc., and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Propylamine can be prepared by reacting n-propanol with ammonia, hydrogenating propionitrile or acrylonitrile, or reducing and ammoniating propionaldehyde. The reaction yields a mixture of mono-n-propylamine, di-n-propylamine and tri-n-propylamine. Each pure component is obtained by fractionation. The method of reacting n-propanol with ammonia is an industrial method. 1. The n-propanol method uses n-propanol as raw material, reacts under the action of the catalyst nickel-copper-alumina (Ni-Cu-Al2O3) at a temperature of 190±10°C, and dehydrogenates to produce propionaldehyde, which is added with ammonia. The product is dehydrated to obtain imine, which can be further hydrogenated to obtain the product n-propylamine by controlling the ratio of propanol and ammonia. However, dipropylamine and tripropylamine are also generated (see “Tripropylamine”).
2. Nitropropane method: low-pressure catalytic hydrogenation of nitro-n-propane to obtain n-propylamine.
Purpose
1. Organic synthetic raw materials, used as finishing agents for drugs, coatings, pesticides, rubber, fibers, textiles and resins, etc. It is used in medicine to synthesize propafenone, prilocaine hydrochloride, etc.
2. Used as organic synthesis intermediates, experimental reagents and solvents. [25]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

