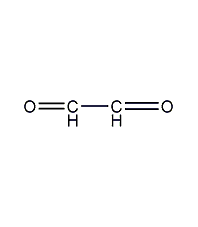
Structural formula
| Business number | 02UZ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H2O2 |
| Molecular weight | 58 |
| label |
Oxalaldehyde, Glyoxal aqueous solution, 30%, Glyceral, Oxalaldehyde, biformyl, Ethanedial |
Numbering system
CAS number:107-22-2
MDL number:MFCD00006957
EINECS number:203-474-9
RTECS number:MD2700000
BRN number:1732463
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: yellow prismatic or irregular flakes, turning white after cooling.
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): 1.27
3. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.14
4. Melting point (ºC): 15
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 51
6. Boiling point (ºC, kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index (n20D): 1.409
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (ºC): Undetermined
10. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -860.88
11. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -211.96
12. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol -1·K-1): 272.51
13. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): – 189.7
14. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 60.9
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V) : Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Easy Soluble in water, alcohol and ether. It is unstable, so it is generally used as an aqueous solution with a concentration of 40% to 41%. The solution is a colorless light yellow transparent liquid with a relative density of 1.260 to 1.310. It has strong reducibility. Contact with air can cause explosion. Strong polymerization occurs when exposed to water. Reacts strongly with chlorosulfonic acid, ethyleneimine, nitric acid, fuming sulfuric acid, and sodium hydroxide. Emit toxic and irritating smoke when burning.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: mouse intraperitoneal LD50: 200 mg/kg
Rat oral LD5O: 20200 mg/kg, 30% aqueous solution
Rabbit transdermal LD5O: 6600 mg/kg, 30% aqueous solution
Ecological data
This substance is harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to atmospheric pollution. Strongly irritates skin and mucous membranes. May be harmful if inhaled, ingested or absorbed through skin. Its vapor or smoke is irritating to eyes, skin, mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 11.68
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 56.1
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 129.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 28.2
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 4.63
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.4
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 34.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 25
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid air, light and heat. Avoid contact with strong oxidants and strong alkali.
2.It is moderately toxic and strongly irritates skin and mucous membranes. Mouse oral LD50600~1000mg/kg. The workplace should be ventilated, equipment should be sealed, and operators should wear protective equipment.
3. Exist in tobacco leaves and smoke.
4. The mixture with air will explode!
5. Moderately irritating to skin and mucous membranes.
Storage method
1. Products are usually diluted before storage. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 30℃. The packaging must be sealed and must not come into contact with air. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
2. Packed in plastic barrels, 25kg per barrel. Protect from sunlight during storage.
Synthesis method
The main industrial production methods include ethylene glycol gas phase catalytic oxidation method and acetaldehyde nitric acid oxidation method. 1. Glyoxal phase catalytic oxidation method: ethylene glycol and air are catalytically oxidized in the presence of a copper catalyst at 250-300°C to generate glyoxal: the active component of the catalyst is copper oxide (containing Cu03-8%), and the carrier It is made of alumina or corundum, aluminum sand, impregnated and roasted with copper nitrate. The service life is up to one year and can be regenerated by burning method. After ethylene glycol is preheated and vaporized, it is mixed with circulating gas and enters the catalytic reactor. The amount of fresh air is controlled to prevent the deep oxidation of ethylene glycol, and a nitrogen flow is used to bring in halogen compounds as an inhibitor of deep oxidation. The reaction is at 275 ℃, 0.74MPa pressure, the reaction product is quenched with water, and the concentration obtained by absorption is the finished product. The conversion rate of ethylene glycol in one pass is 80-85%. 2. The acetaldehyde nitric acid oxidation method uses copper nitrate as the catalyst and nitric acid for liquid phase oxidation: under the conditions of stirring and sufficient cooling, prepare acetaldehyde and nitric acid into a solution of about 50% each, and copper nitrate into a 40% solution. solution, sodium nitrite is made into a 5% solution. First add a small amount of nitric acid solution and acetaldehyde solution into the reaction pot, then add sodium nitrite solution, heat it slightly until brown-red gas is generated, naturally raise the temperature to 30°C, and start to drop a small amount of nitric acid solution and acetaldehyde solution at the same time, about After 4 hours of addition, the reaction temperature is controlled at 40-45°C. The escaped acetaldehyde gas is absorbed by water and added to the reaction pot, and the reaction continues for 3 hours. The ingredients of acetaldehyde in the reaction are excessive (mol ratio, nitric acid: acetic acid = 1:2). After the reaction is completed, acetaldehyde is recovered by heating to 98°C. Then add activated carbon to decolorize, cool, filter, and wash with water. Combine the filtrate and washing liquid, steam out the organic acid below 70°C (21.33kPa), repeatedly add water and steam until the acidic cation exchange resin and weakly basic anion exchange resin in the distillate remove impurities. The exchange liquid and eluent are hydraulically concentrated to obtain glyoxal with a qualified concentration. Based on acetaldehyde, the yield is about 32%.
![]()
Purpose
1. Insoluble adhesive agent used for gelatin, animal glue, polyethylene and starch, etc. It can also be used as shrinkage inhibitor for rayon, paint raw materials, pharmaceutical raw materials and insoluble dye raw materials and organic synthesis
2.It can be used as a bactericide in water-based oil well fracturing fluids, a cross-linking agent for cellulose, etc. In the textile printing and dyeing industry, it is used as an anti-shrinkage and anti-wrinkle finishing agent for fabrics; in the leather industry, the primers of glyoxal and isobutyraldehyde semicarbazone can be used as tanning agents for cowhide; in the pharmaceutical industry, glyoxal and The condensation of amines produces 2-hydroxypyrazine, which is used as a raw material for sulfa drugs and pesticides. In coatings and adhesives, cross-linking with polymers can improve the water resistance of copolymers. Acryloyl copolymer is cross-linked with glyoxal and can be used as fiberglass board.
Alkenal copolymer is cross-linked with glyoxal and can be used as fiberglass board.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

