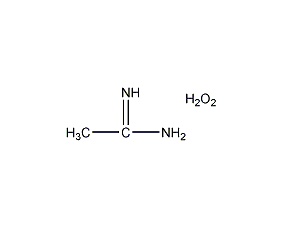
Structural formula
| Business number | 03J8 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CH6N2O3 |
| Molecular weight | 94.07 |
| label |
Carbamide perhydrate, Carbamide-Peroxide, Urea hydrogen peroxide adduct, UHP, Percarbamide, aliphatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:124-43-6
MDL number:MFCD00013119
EINECS number:204-701-4
RTECS number:None
BRN number:3680414
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Character: white crystal
2. Melting point (℃): 90~93
3. Solubility: easily soluble in water, ethanol, ethylene glycol and dichloride in organic solvents such as methane.
Toxicological data
None
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
None
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 4
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 110
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 29
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 2
Properties and stability
1. Basic properties: The aqueous solution has the properties of both urea and hydrogen peroxide, and can slowly release oxygen in the water. Compared with inorganic peroxides such as sodium percarbonate, its performance is superior, and it has the advantages of high active oxygen content, large solubility in water, good stability, and soluble in organic solvents.
2. Moist reagents will decompose into water and oxygen above 40 oC, which are corrosive and oxidizing. It is recommended to store them in a dry and cool place.
Storage method
Store in a dry, clean, well-ventilated warehouse with a room temperature of 15°C to 25°C. Keep away from fire, heat sources and direct sunlight, and pay attention to moisture and rain.
Synthesis method
1. There are two types of processes: wet process and dry process. The dry process requires a higher concentration of hydrogen peroxide (about 85 (wt)%), and has complex equipment, harsh technical conditions, high energy consumption, and poor product stability. and other shortcomings. Most percarbamide is prepared by a wet process, that is, low-concentration hydrogen peroxide is reacted with a saturated or supersaturated urea solution, a certain amount of stabilizer is added and the reaction temperature is controlled, the product is filtered and dried, and the mother liquor is recycled.
2. Prepared by recrystallization of urea in 30% aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution [1].
Purpose
1. In the medicine and pharmaceutical industry, urea peroxide can be used as an efficient, safe and convenient solid disinfectant, and it can also be used as an aqueous solution. Compared with hydrogen peroxide and peracetic acid, it has the advantages of strong bactericidal power, wide bactericidal spectrum, low concentration, and no residual poison. It can also inhibit the growth of bacteria and mold, and the residue is non-irritating. Used in cancer treatment to fight liver ascites, etc. In the daily chemical industry: urea peroxide can be used as a bleaching agent, straightening agent, perm, and hair dyeing neutralizer for human and animal hair. Especially when added to toothpaste, it can perform functions that ordinary toothpaste cannot. Function: Reduce dental plaque and bacteria, reduce periodontal disease and dental caries. At the same time, it can harden tooth enamel and exert a strong inhibitory effect on dental caries. In addition, urea peroxide can be used as a bleaching agent in neutral detergents. In agriculture and aquaculture: In aquaculture, urea peroxide can be used as an oxygenator, disinfectant and first-aid agent in the case of lack of oxygen in fish ponds. It can also be used as a disinfectant and oxygen supply agent for small poultry feed. It can also be used as an oxygen-rich ripening agent for fruits and vegetables. In the textile and paper industry: Urea peroxide can be used as a bleaching agent for cotton, wool, rayon, and flax fibers. Softener, antistatic agent and decolorizing agent for polyamide fibers. It is also used in the papermaking industry as a bleaching agent, ore flotation improver, etc.
2. Urea hydrogen peroxide complex (UHP) is a complex produced by the strong hydrogen bonding between urea and hydrogen peroxide. It converts unstable hydrogen peroxide into an easy-to-handle, safe, room-temperature-stable solid that is inexpensive. UHP shows different oxidizing abilities under different solvents and catalysts, and is an important oxidizing reagent in organic synthesis. A recently published paper briefly introduced the application of UHP in synthesis[2].
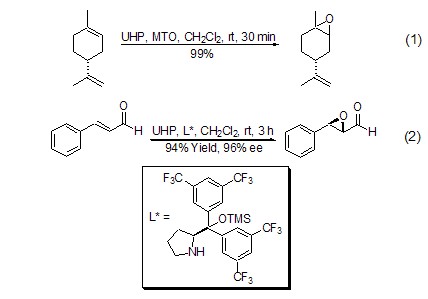
UHP has the properties of hydrogen peroxide and is often used in the epoxidation reaction of double bonds, and has a high degree of regio- and stereoselectivity as well as a high conversion rate. UHP combined with acid anhydrides (such as acetic anhydride, maleic anhydride) can generate organic peroxyacids in situ. This method can replace the use of high concentrations of organic peroxyacids. For the epoxidation reaction of α,β-unsaturated ketone and benzoquinone, the catalysis of a base is generally required, such as K2CO3[3]. The combination of UHP and methylrhenium trioxide (MTO) enables the epoxidation reaction of olefins with excellent regio- and stereoselectivity (Formula 1)[4]. For the asymmetric oxidation of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes, UHP shows better stereoselectivity and conversion rate than other oxidants (Formula 2)[ 5].
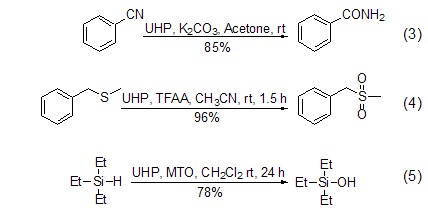
Since the oxidation properties of UHP can be easily controlled, it can be used to convert a variety of functional groups, such as converting cyano groups into amides, oximes into nitro groups, aldehydes into acids, etc. (Formula 3, Formula 4)[6]. Another important use of UHP is the oxidation reaction of heteroatoms such as N, S, P, I[2,6] and Si (Formula 5)[7] . In most cases its selectivity is better than hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution.
UHP same Like organic peracids, it can also complete the Baeyer-Villiger rearrangement reaction and has high stereoselectivity (Formula 6)[8].

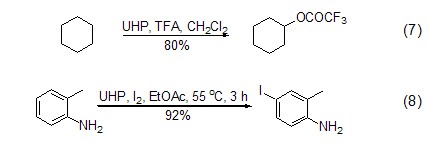
Recent literature reports that UHP can also Achieve oxidation of inactive C-H bonds to form hydroxyl or ester groups (Formula 7)[9]; UHP combined with I2 can conveniently and effectively realize the oxidation of aryl groups Iodination (Formula 8)[10].

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

