Background and overview[1]
4-Nitrosoresorcin monomethyl ether is an organic intermediate that can be prepared from 3-methoxyphenol in one step.
Preparation[1]
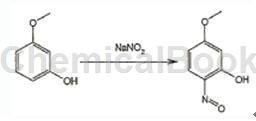
3-Methoxyphenol (4.96g, 0.04mol) was dissolved in 50mL propionic acid, cooled to -10°C, 0.5 mL propionic anhydride was added dropwise, and sodium nitrite (2.90g, 0.042mol) was added in 4 batches. , a brown solid precipitated, reacted for 1 hour, poured into 250 mL of water, filtered, washed with water, and dried to obtain 4.03g of 4-nitrosoresorcin monomethyl ether as a brown solid.
Application[1]
WO2008125014 reported that 4-nitrosoresorcinol monomethyl ether can be used to prepare small molecule compounds with p38 MAPK inhibitory activity to treat diseases mediated by cytokines (TNF-o, IL-1, etc.), Risk factors or conditions, such as psoriatic arthritis, Reiter’s syndrome, gout, traumatic arthritis, rubella arthritis, acute synovitis, rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid spondylitis, osteoarthritis inflammation, gouty arthritis and other joint diseases, sepsis, septic shock, endotoxic shock, Gram-negative, sepsis, toxic shock syndrome, cerebral malaria, meningitis, ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic Stroke, neurotrauma/closed head injury, asthma, adult respiratory distress syndrome, chronic pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, silicosis, pulmonary sarcoidosis, bone resorptive diseases, osteoporosis, restenosis, heart and brain and kidney re-stenosis Perfusion injury, congestive heart failure, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), blood test formation, glomerulonephritis, chronic renal failure, diabetes, diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, graft-versus-host reaction, allograft Graft rejection, Inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s disease, Ulcerative colitis Neurodegenerative diseases, Muscle degeneration, Diabetic retinopathy, Macular degeneration, Tumor growth and metastasis, Angiogenic diseases, Influenza-induced pneumonia, Eczema, Contact dermatitis, psoriasis, sunburn or conjunctivitis, etc.
Main reference materials
[1] (WO2008125014) Urea compounds, their preparation methods and their medicinal uses

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

