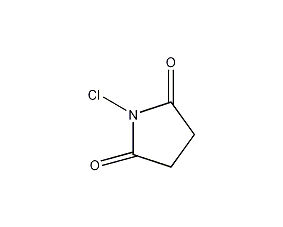
Structural formula
| Business number | 03LE |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H4ClNO2 |
| Molecular weight | 133.53 |
| label |
N-chlorosuccinimide, N-chlorosuccinimide, Succinyl chloride, Succinimide chloride, Chlorosuccinimide, Chlorodiacetimide, NCS, Chlorinating agent |
Numbering system
CAS number:128-09-6
MDL number:MFCD00005511
EINECS number:204-878-8
RTECS number:UY1013500
BRN number:None
PubChem number:24852348
Physical property data
1. Appearance: white powder or crystal
2. Melting point (oC): 150~152
3. Solubility: 1g N -Chlorosuccinimide is dissolved in about 70ml of water, 150ml of ethanol or 50ml of benzene, and slightly soluble in ether, chloroform and carbon tetrachloride.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Oral LDLO in rats: 1gm/kg; Intravenous LDLO in rats: 200mg/kg
2. Other multiple dose toxicity: Oral TDLO in rats: 15gm/kg kg/40D-I; rabbit oral TDLO: 5800mg/kg/5W-I
3. Oncogenicity: mouse subcutaneous TDLO: 840mg/kg/70W-I
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 27.46
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 88.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 236.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 50.4
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.88
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.2
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 3
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 37.4
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 129
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Sensitive to moisture and should be stored in a desiccator. During use, avoid inhalation or sticking to the skin, and generally operate in a fume hood with good ventilation.
Corrosive substances. Harmful if swallowed and may cause burns. In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical treatment. Wear suitable gloves and protective glasses or face shield.
Storage method
Store in dry containerInside.
Synthesis method
Dissolve 4.96g (0.05mol) succinimide in a mixed solvent of 17ml acetic acid and 15ml water, add 5.6g (0.05mol) tert-butyl hypochlorite (see page 43 of this book) under stirring, and then Let stand at 0°C for 1 hour. Precipitate out, filter, and dry the solid in vacuum to obtain 2.07 g, with a yield of 31.3%. Melting point 149~150℃.
Purpose
1. An important chlorinating agent that can chlorinate aromatic aldehydes without affecting the aromatic ring. In the chlorination of aniline and N-alkyl aniline (ortho-based), a-aminopyridine chlorination, a-phenylthioamide dehydrochlorination and degradation chlorination, and cyclopentadiene monochlorination reaction The yield is higher than using chlorine gas, tert-butyl hypochlorite, chloramine T, etc. As an oxidizing agent, diols can be oxidized to lactones, primary (secondary) alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes (ketones), B-hydroxyketones can be oxidized to B-diketones, etc. It can selectively break the peptide bond formed by tryptophan under acidic conditions. It can also be used for the synthesis of allylamine, B, R-unsaturated amino acids and their derivatives.
2. Pharmaceutical intermediates. It is often used in the synthesis of antibiotics, such as benzyl cephalosporin, and can also be used to prepare rubber additives.
3.N-Chlorosuccinimide (NCS) is a relatively convenient electrophilic addition and electrophilic substitution reagent, often used for sulfides, sulfones and Chlorination of ketones can also be used to synthesize N-amine chloride.
Chlorination reaction of α-position of carbonyl compounds Under the action of lithium or other reagents, NCS can make α of carbonyl compounds Chlorination at the -position (formula 1)[1~3].
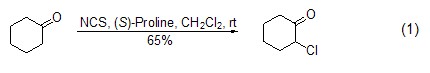
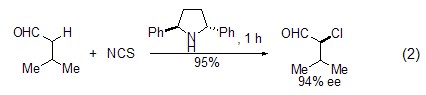
If in the presence of a chiral catalyst Under this condition, NCS can undergo asymmetric chlorination at the α-position of the carbonyl compound (formula 2)[4,5].
Catalysis of sulfoxide Reduction Under the catalysis of NCS, sulfoxide can be reduced to thioether compounds (formula 3)[6].
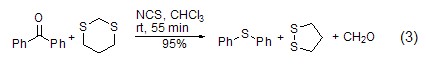
Oxidation reaction
strong> NCS can also be used as an oxidizing agent to convert unsaturated bonds into corresponding saturated bonds. For example, enol ester undergoes cyanation reaction under the oxidation of NCS to generate saturated cyanide amine (formula 4)[7].

Chlorine of aromatic compounds Chlorination NCS can chlorine aromatic compounds (Formula 5) [8], thiophene compounds (Formula 6) [9] and nitrogen heterocyclic compounds (Formula 7)[10,11].
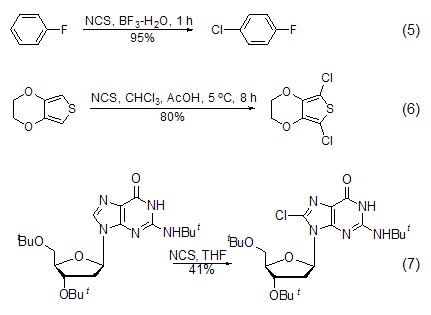
N Synthesis of -chloroamino compounds Under the action of NCS, secondary amines can be converted into N-chloroamino compounds (formula 8)[12].
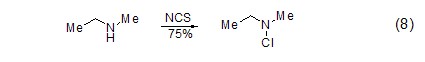
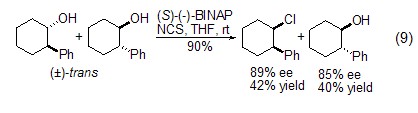
Chlorine of alcoholic hydroxyl group In addition to N-chlorination of amines, NCS can also undergo chlorination at the hydroxyl site with alcohol compounds. In the presence of a chiral catalyst, NCS can selectively react with a certain configuration of chiral alcohols, thereby achieving the resolution of alcohols (Formula 9)[13].
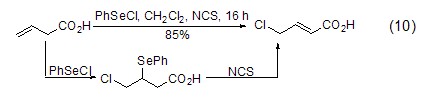
Reaction with alkenes Under the action of a catalyst such as PhSeCl, NCS can also chlorinate olefins. After the reaction undergoes electrophilic addition to obtain chloride, the catalyst is restored to obtain the final product (Formula 10)[14].

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

