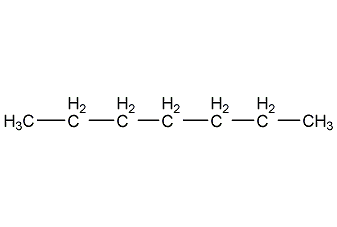
Structural formula
| Business number | 03VE |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H16 |
| Molecular weight | 100.20 |
| label |
n-heptane, Heptane fraction, Alkane C7, Dehydration solvent for organic synthesis |
Numbering system
CAS number:142-82-5
MDL number:MFCD00009544
EINECS number:205-563-8
RTECS number:MI7700000
BRN number:1730763
PubChem number:24854818
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless, transparent and volatile liquid. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -90.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 98.5[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.68[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 3.45[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 6.36 (25℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -4806.6[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 266[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 2.74[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 4.66 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): -4 (CC); -1 (OC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 215[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 6.7[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.05[14]
15. Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol, carbon tetrachloride, miscible In ether, chloroform, acetone, benzene. [15]
16. Viscosity (20℃, liquid, mPa·s): 0.409
17. Flash point (ºC): 233
18. Heat of fusion (kJ/mol): 14.059
19. Aniline point (ºC): 70.6
20. Thermal conductivity (25 ºC, liquid)/ [W/(m·K)]: 122.25×10-3
21. Heat of formation (25 ºC, liquid) / (kJ·mol): -224.54
22. Specific heat capacity (0ºC, constant pressure)/[kJ/(kg·K)]: 2.233
23. Critical density (g·cm-3 ): 0.234
24. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 428
25. Critical compression factor : 0.261
26. Eccentricity factor: 0.351
27. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 6.7638
28. Lennard-Jones parameter (K): 337.78
29. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 15.208
30. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 1.099×1010
31. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 78.490
32. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1 ): -4153.57
33. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -187.15
34. Gas phase standard entropy ( J·mol-1·K-1): 428.1
35. Gas phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): 8.3
36. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 165.2
37. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -4817.00
38. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ· mol-1): -224.22
39. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 328.57
40. Liquid phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): 1.23
41. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 224.78
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 222mg/kg (mouse vein)
LC50: 103g/m3 (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation No information available
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[17] EC50: 82.5mg/L (96h) (Water flea)
2. Biological Degradability [18] MITI-I test, initial concentration 100ppm, sludge concentration 30ppm, 100% degradation in 4 weeks.
3. Non-biodegradability[19] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pcs/cm3, the degradation half-life is 54h (theoretical).
4. Bioconcentration[20] BCF: 2000 (Theory)
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 34.47
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 144.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 310.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 21.6
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 13.66
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 19.2
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties are stable under normal temperature and pressure. Isomerization reaction can occur under the catalysis of aluminum trichloride. It reacts with halogen under the action of sunlight or ultraviolet light to generate halogen derivatives.
2. Stability[21] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[22] Strong oxidants, strong acids, strong bases, halogens
4. Polymerization hazards[23] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[24] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37℃. Keep container tightly sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. The n-heptane content in the platinum reforming raffinate (93-102°C) fraction reaches more than 57%. Use 5A molecular sieve gas phase to adsorb the n-alkanes in the base, and then use steam to desorb and separate the n-alkanes. . After nickel-catalyzed hydrogenation, a small amount of normal olefins is saturated and converted into normal alkanes, and the iodine value is reduced to less than 0.1g iodine/100g, which is qualified. Finally, standard n-heptane with a purity of 99.9% is obtained through distillation. Industrial grade n-heptane can also be purified by washing with concentrated sulfuric acid, methanol azeotropic distillation and other methods.
2. Hydrocarbon fraction of petroleum. May contain n-heptane, dimethylcyclopentane, 3-ethylpentane, methylcyclohexane and 3-methylcyclohexane.
3. Refining method: In addition to alkanes and cycloalkane compounds with similar boiling points, heptane also contains unsaturated compounds, moisture and benzene. Benzene can be removed in the same way as hexane. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are removed by washing with concentrated sulfuric acid. Calcium chloride, phosphorus pentoxide, metal sodium and potassium, etc. can be used to remove moisture. Molecular sieves can also be used as solid desiccants. Finally, it is fractionated and refined.
4. Purify industrial-grade n-heptane by washing with concentrated sulfuric acid, methanol azeotropic distillation and other methods.
5. Preparation method:
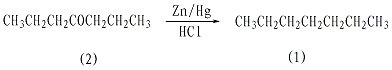
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, reflux condenser, and ventilation tube (extending into the bottom of the bottle), add 100g zinc-amalgam (1.53mol), 250mL concentrated hydrochloric acid, and 50mL water, and add 40g while stirring (0.35mol) heptanone-4(2), slowly add hydrogen chloride gas. If the reaction is too violent, the flow of hydrogen chloride gas can be suspended. After 2-3 hours, most of the zinc-amalgam reaction is completed, stop passing the hydrogen chloride, and leave it overnight. Remove the stirrer, etc., replace it with a steam distillation device, and perform steam distillation until the distilled liquid is transparent. Separate the upper oil layer, wash it twice with distilled water, dry it with anhydrous sodium sulfate and then distill it. Collect the fractions at 97-99°C to obtain 26 g of heptane ①(1), with a yield of 74%. Note: ① Most of the products of Clemmensen reduction reaction contain a small amount of unsaturated hydrocarbons. Add about 10% volume of concentrated sulfuric acid and shake thoroughly until the acid layer is colorless or only very light yellow. Separate the acid layer and wash it with 10% saturated sodium carbonate, water, anhydrous magnesium sulfate or anhydrous sodium. Drying and then fractionating (or distilling under reduced pressure) can obtain high-purity alkanes. [26]
Purpose
1. Used as analytical reagent, gasoline engine knock test standard, chromatographic analysis reference material, and solvent. This product can irritate the respiratory tract and has an anesthetic effect at high concentrations. It is flammable and the limit concentration to form explosive mixture in air is 1.0-6.0% (volume).
2. It can be used as an extraction solvent for animal and vegetable oils and quick-drying rubber adhesive. Solvents for the rubber industry. It is also used as a cleaning solvent in coatings, varnishes, quick-drying inks and printing industries. The pure product is used as the standard fuel for determining the octane number of gasoline.
3. Used as a standard and solvent for octane number determination, as well as for the preparation of organic synthesis and experimental reagents. [25]
Shock test standards, chromatographic analysis reference materials, solvents. This product can irritate the respiratory tract and has an anesthetic effect at high concentrations. It is flammable and the limit concentration to form explosive mixture in air is 1.0-6.0% (volume).
2. It can be used as an extraction solvent for animal and vegetable oils and quick-drying rubber adhesive. Solvents for the rubber industry. It is also used as a cleaning solvent in coatings, varnishes, quick-drying inks and printing industries. The pure product is used as the standard fuel for determining the octane number of gasoline.
3. Used as a standard and solvent for octane number determination, as well as for the preparation of organic synthesis and experimental reagents. [25]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

