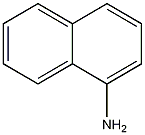
Structural formula
| Business number | 03PJ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H9N |
| Molecular weight | 143 |
| label |
α-Naphthylamine, α-amino naphthalene, α-Naphthylamine, 1-Aminonaphthalene, Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:134-32-7
MDL number:MFCD00004016
EINECS number:205-138-7
RTECS number:QM1400000
BRN number:386133
PubChem number:24897885
Physical property data
1. Properties: The pure product is colorless crystal or block, has a foul odor, and is easy to sublimate. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 50[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 300.8 [3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.13[4]
5. Relative vapor density (Air=1): 4.93[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (104.3℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -5281.4[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.25[8]
9. Flash point (℃): 157.2 (CC) [9]
10. Ignition temperature (℃): 460 [10]
11. Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether and chloroform. [11]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[12] LD50: 680mg/kg (rat Oral); 96mg/kg (mouse abdominal cavity)
2. Irritation No data available
3. Mutagenicity [13] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 10μg/dish. DNA repair: E. coli 25mg/L. DNA damage: 2790 μmol/kg in rat abdominal cavity. Unprogrammed DNA synthesis: rat liver 700 μmol/L. Cytogenetic analysis: hamster fibroblasts 60mg/L (48h)
4. Carcinogenicity [14] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: Group 3 , the available evidence cannot be used to classify human carcinogenicity.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[15] LC50: 25mg/L (48h) ( Medaka)
2. Biodegradability[16]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 672~4320
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 2688~17280
3. Non-biodegradability[17]
The half-life of photooxidation in water (h): 62.4~3480
The half-life of photooxidation in air (h): 0.292~2.92
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 48.33
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 125.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 336.9
4. Surface tension (3.0 dyne/cm): 51.4
5. Polarizability (0.5 10-24cm 3): 19.16
Compute chemical data
1. Hydrophobic parameter calculation reference�(XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Rotatable chemical bonds Number: 0
5. Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 133
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the atoms Number of stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of stereocenters of atoms: 0
13. Determined number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[18] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[19] Acids, acid anhydrides, strong oxidants
3. Polymerization hazards[20] No polymerization
4. Decomposition products[21] Ammonia
Storage method
Storage Precautions[22] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reduction of 1-nitronaphthalene (see C10H7NO2, [86-57-7]). Raw material consumption (kg/t) Refined naphthalene 1116 Nitric acid (96%) 561 Sulfuric acid (92.5%) 312 Alkali sulfide (60%) 703 Sulfur (99%) 211
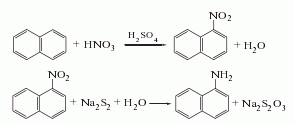
2. Add the same amount of sodium sulfide and sulfur to 90℃ water to obtain a concentration of 4.3 ~4.4mol/l sodium disulfide solution. Then add small amounts in small portions over several hours to the nitronaphthalene that has been heated to 100°C in advance. After the addition is completed, continue boiling for 4.5 hours:
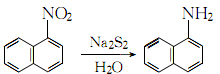
After letting it stand, separate the sodium thiosulfate solution in the lower layer, and wash the upper layer product twice with hot water at 55-65°C. Distill at 8.0kPa. Collect the fractions with a freezing point higher than 45.5°C and pour them into xylene to make them loose crystals. Filter them and centrifuge them to dryness. Then wash them once with xylene. After drying, the reagent 1-naphthylamine is obtained. .
Purpose
1. This product is an intermediate for various dye products such as direct dyes, acid dyes, ice dyes and disperse dyes. It is also the main raw material for various rubber antioxidants. 1-naphthol is produced from 1-naphthylamine. It is an important intermediate of the pesticide carbaryl. 1-Naphthylamine can be absorbed through the skin and produce methemoglobin, causing poisoning of the prepared solution and urinary system diseases; chronic poisoning can cause bladder cancer. The maximum allowable concentration in the air is 0.001mg/L.
2. Used as a reagent for detecting nitro compounds by thin layer chromatography. Used as UV derivatization reagent for aldehydes and ketones. It is also used as an acid-base fluorescent indicator with a pH value of 3.4 (no fluorescence) to 4.8 (blue).
3. Dye intermediates. Used to prepare direct dyes, acid dyes, ice dyes and disperse dyes, etc., such as direct light fast blue B2RL, direct light fast gray 3B, naphthol AS-BO, naphthol AS-KN, weak acidic soybean red 5BL, weak acid Dyes such as dark blue GR, weakly acidic dark blue 5R, weakly acidic black BR, etc.
4. Used as dye intermediates and in the pharmaceutical industry. [23]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

