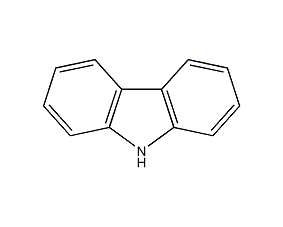
Structural formula
| Business number | 01X1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C12H9N |
| Molecular weight | 167.21 |
| label |
9H-carbazole, Benzazole, nitrogen fluorene, Azafluorene, iminodiphenylene, Diphenyleneimine, Dibenzopyrrole, 9-Azafluorene, Determination of nitrite, determination of formaldehyde |
Numbering system
CAS number:86-74-8
MDL number:MFCD00004960
EINECS number:201-696-0
RTECS number:FE3150000
BRN number:3956
PubChem number:24892756
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless monoclinic flake crystals with special odor
2. Density (g/mL, 17.5/4℃): 1.1035
3. Relative Vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 244.85
5. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kpa): 354.75
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): 108℃
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): 53.33kPa (kpa, 323ºC)
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (octanol/water) distribution Log value of coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Slightly soluble in petroleum ether and acetic acid, soluble in alcohol, ether, acetone, quinoline, pyridine and concentrated sulfuric acid.
Toxicological data
Harmful if swallowed
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 56.37
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 135.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 374.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 57.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 22.34
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 15.8
7. Number of heavy atoms: 13
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 170
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
None yet
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored in a cool place.
Synthesis method
(1) At present, the domestic production method of carbazole uses crude anthracene as raw material, which generally does not co-produce refined anthracene, and the economic benefits are poor. The method is to extract with sulfuric acid to form a carbazole sulfate salt solution, and then backflush with ammonia water to precipitate the carbazole. Jiangsu Dafeng Chemical Factory once used this method, but has now stopped production. The reasons are: (1) The product purity is low. Contains a large amount of acridine and other impurities, and the purity is less than 90%. (2) It cannot co-produce refined anthracene and is uncompetitive. (3) Equipment material requirements are high and corrosion is serious. (4) The discharge of waste water is large and the pollution is serious. The KOH melting method has been used to produce carbazole in foreign countries, but it has never been put into industrial production. Methods of synthesizing carbazole have also been tested abroad. The method is o-aminobiphenyl closed-loop dehydrogenation, and the raw material is ammonia or chlorobenzene. The advantage of this method is that the raw materials are easily available, but the disadvantage is that it is not competitive in the market because: (1) the synthesis route is long and the reaction steps are many. Each reaction step requires complex pre- and post-processing, and the separation equipment and operation costs are particularly high. (2) The conversion rate is low. Most reactions are accompanied by side reactions and the final conversion rate is low due to long routes. (3) The amount of waste treatment is large and the environmental protection costs are high. Judging from the current market share, the main source of carbazole is coal tar (anthracene oil). The world’s major carbazole manufacturers, such as RUTGERS of Germany, DEIA of the Czech Republic, and JORYU of Japan, are all the same, and they all co-produce anthracene and carbazole. Carbazole is industrially extracted from coal tar. The extracted raw material is the anthracene oil fraction in the continuous distillation of tar. The initial boiling point is 300°C. The distillation volume before 350°C is 95%. The output of anthracene oil accounts for 12-14% of the tar. After the anthracene oil is cooled and crystallized, and part of the oil is removed by vacuum filtration or filtration, it contains 25-30% of anthracene, 20-25% of carbazole, and about 30% of phenanthrene. Phenanthrene is easily soluble in oil. This characteristic is used to separate phenanthrene from anthracene and carbazole. There are two methods for separating anthracene and carbazole: 1. Distillation separation method uses the boiling point difference with carbazole (the boiling point of anthracene is 340.7°C, the boiling point of carbazole is 355°C), and an emulsification tower with a tower efficiency equivalent to 40 theoretical plates is used. Carry out distillation with a reflux ratio of 19:1. Cut the fraction with a top temperature of 310-344°C to obtain industrial anthracene containing an average of 85% of anthracene. Then cut the carbazole fraction with a temperature of 348-355°C to obtain about 85% carbazole. of industrial carbazole. 2. The potassium melting method takes advantage of the fact that the potassium melt of carbazole is insoluble in oil and forms a precipitate. The crude anthracene is heated and melted and then flake caustic potassium is added to separate the potassium compound of carbazole and put into a hydrolysis tank for hydrolysis. The generated crude carbazole is separated from the alkali solution through a centrifuge, washed with water and purged with steam to obtain crude carbazole. After the refined carbazole is dried, it is sublimated at 180-240°C, and then recrystallized with xylene to obtain commercial carbazole with a purity of 95-98%. In addition, carbazole can also be synthesized from o-aminobiphenyl.
(2) Carbazole can be extracted from coal tar and then separated by distillation; it can also be synthesized from o-aminobiphenyl and then recrystallized with xylene refined.
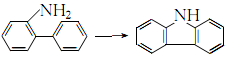
(1) Synthesis method: Using o-aminodiphenylamine as raw material, 1-phenyl-1,2,3-benzotriazole is obtained by treatment with nitrous acid. After heating, it loses nitrogen and generates carbazole.
(2) Sulfuric acid method Dissolve the crude anthracene with chlorobenzene or other solvents. The phenanthrene, fluorene and other substances in the crude anthracene are separated from anthracene and carbazole because they are insoluble. Add anthracene and carbazole to sulfuric acid. The reaction proceeds in the reaction medium, and carbazole reacts with sulfuric acid to form carbazole sulfate and separates from anthracene. After hydrolyzing carbazole sulfate, it is filtered and dried to obtain the finished product.
(3) Solvent-distillation method Dissolve the crude anthracene with the heavy benzene (160~200℃) fraction produced by coking, separate the phenanthrene, fluorene and other substances in the crude anthracene from the anthracene and carbazole, and separate Anthracene and carbazole are subjected to high-temperature distillation in a distillation tower. After one distillation, a product containing 85% to 90% of carbazole can be obtained, with a yield of 65%.
Purpose
1. Used in the manufacture of dyes, chemical reagents, explosives, pesticides, lubricants, rubber antioxidants, etc.
2.Used as an analytical reagent for the photometric determination of nitrite and methylene, and for the determination of lignin, hydrocarbons and Formaldehyde reagent. Also used in organic synthesis.
3. Used to prepare Haichang blue, sulfide reduction blue GNX, sulfide reduction deep blue 4RB, permanent violet RL, naphthol AS-IB, anthraquinone reduction dye and oxazine dye. Pesticide Insecticide Tetranitrocarbazole. Preparation of UV-sensitive photographic films, N-vinylcarbazole plastics, etc.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

