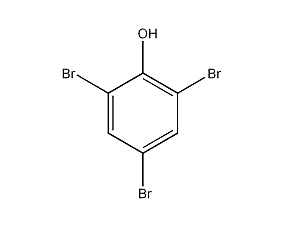
Structural formula
| Business number | 00ED |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H3Br3O |
| Molecular weight | 330.80 |
| label |
2,4,6-tribromophenol, Reactive flame retardants, Electronic coating raw materials and intermediates |
Numbering system
CAS number:118-79-6
MDL number:MFCD00002150
EINECS number:204-278-6
RTECS number:SN1225000
BRN number:776920
PubChem number:24862806
Physical property data
1. Properties: white powdery crystal, sweet taste.
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): 2.55
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 11.4
4. Melting point (ºC): 90-94
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 244
6. Flash point (ºC): 282-290
7. Solubility: Easily soluble in acetone, ether, benzene, methyl ethyl ketone, toluene, ethanol, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, petroleum ether, pyridine and caustic alkali solution, almost insoluble in water.
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 200mg/kg
Ecological data
Slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 51.20
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 136.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 373.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 56.3
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3):20.29
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 20.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 108
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with oxides, acid chlorides, and acid anhydrides. This product is toxic. Operators should wear anti-corrosion overalls, chemical-resistant gloves and chemical safety glasses.
Storage method
Stored sealed in a cool, dry place. Make sure the workspace has good ventilation. Store away from oxidizing agents. It needs to be protected from moisture and heat during storage and transportation.
Synthesis method
1. Add phenol to the reaction kettle, add water to dissolve it while stirring and raise the temperature to 60°C.Add bromine and continue stirring for 30 minutes after the addition is complete. Then cool to 40°C, filter, and wash the filter cake with water until neutral to obtain the crude product. Dissolve the crude product in ethanol at 70°C, add activated carbon to decolorize, filter, and mix an equal amount of water with the filtrate to precipitate needle-like crystals, which is the finished product. The yield is about 96%.
2.There are mainly three process routes for producing tribromophenol.
(1) Direct bromination method (phenolbromine water oxidation method) is currently the traditional process used in China – utilizing the dual characteristics of oxidation and substitution of bromine water , reacts with phenol to form a white precipitate of tribromophenol. The process is described below.
① Preparation: Dissolve phenol in water, slowly add bromine water (KBr as a co-solvent) equal to the chemical reaction while stirring, and control the temperature to 60°C , after the dropwise addition is completed, react for 30 minutes, cool to 40°C, filter, wash with dilute sodium bisulfite aqueous solution, then wash with water until neutral, and dry to obtain crude 2,4,6-tribromophenol.
②Refining: Dissolve the above crude crystals in hot anhydrous ethanol, and add activated carbon to decolorize , after filtration, mix an equal amount of water with the filtrate to precipitate a needle-shaped crystal product with a yield of 96%.
③ Recovery of hydrogen bromide Dissolve 0.2 mol of benzene in water and add 0.3 mol of bromine water dropwise under vigorous stirring. After the dropwise addition, slowly add 0.3 mol of bromine water. mol chlorine, filter after the reaction is complete, wash with dilute sodium bisulfite aqueous solution, then wash with water until neutral, and dry to obtain the product.
3.The bromine chloride method uses halogenated hydrocarbons as solvents and chlorine Instead of bromine, react with phenol. During production, bromine chloride must first be synthesized. Secondly, a large amount of hydrogen chloride will be produced during the reaction between bromine chloride and phenol solution, which can easily accumulate in the reaction system, thus affecting the reaction speed and product quality.
4.Oxidative bromination method This method uses an oxidizing agent to produce hydrogen bromide produced by the bromination reaction of phenol and bromine. (Hydrogen peroxide, chlorine) is oxidized to bromine, and then continues to participate in the reaction. This method is currently used more frequently at home and abroad.
Purpose
1. This product is a reactive flame retardant and an intermediate for the manufacture of other brominated flame retardants and flame retardant polymers. For example, 2,6-dibromophenylene ether produced by solution polycondensation or aqueous precipitation polycondensation is a newly developed flame retardant that can be used in engineering plastics such as nylon 66, thermoplastic polyester and modified polyphenylene ether. It can also be used for high-impact polystyrene and ABS resin. This product can also be used to prepare detoxification and antiseptic drugs such as bismuth tribromophenate.
2.Used as reactive flame retardant, suitable for epoxy resin, polyurethane, polycarbonate, phenolic resin, etc. It can also be used to prepare poly-2,6-dibromophenylene ether. This product is a new type of flame retardant and can be used in nylon 66, thermoplastic resin, etc. It can also be used as a catalyst for olefin polymerization; it is also a synthetic raw material for the organic bromine-containing additive flame retardant tris (2,4,6-tribromophenol) phosphate and bromophenol barium salt flame retardant. Suitable for unsaturated polyester resin, polyurethane and other plastics and chemical fibers. In addition, it is also used as a variety of pharmaceutical intermediates and as a fungicide for wood and paper.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

