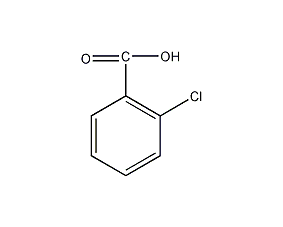
Structural formula
| Business number | 03AB |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H5ClO2 |
| Molecular weight | 156 |
| label |
Pesticide intermediates; aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:118-91-2
MDL number:MFCD00002412
EINECS number:204-285-4
RTECS number:DG4976000
BRN number:907340
PubChem number:24848210
Physical property data
1. Properties: white coarse powder, easy to sublimate.
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): 1.544
3. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.544
4. Melting point (ºC): 142
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 285
6. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.5355
7. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -325.0
8. Flash point (ºC): 173
9 . Crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -404.5
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/ mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water ( Log value of the partition coefficient (octanol/water): Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/ V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in methanol, absolute ethanol, and ether.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 6460mg/kg
Rabbit oral LD50: >500mg/kg
Ecological data
This substance is harmful to the environment and can cause pollution to water bodies and the atmosphere. Organic acids can easily form acid rain during atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physical changes. Therefore, when the pH value drops below 5, it will cause serious harm to animals and plants, and the reproduction and development of fish will be seriously affected. Metals in the soil and water sediments in the watershed can be dissolved into the water and poison the fish. Acidification of water bodies will also lead to changes in the composition and structure of aquatic organisms. Acid-resistant algae and fungi will increase, while root plants, bacteria and vertebrates will decrease, and the decomposition rate of organic matter will decrease. Acidification will seriously lead to the reduction or death of fish in lakes and rivers.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 38.07
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 113.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 305.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 51.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 15.09
Compute chemical data
1. Hydrophobic parameter calculation reference value (XlogP): 2.1
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 37.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 136
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters Quantity: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with strong oxidants and strong alkali.
2.This product is toxic. For its toxicity and protection, please refer to benzoic acid. Mice were injected subcutaneously with LD501200mg/kg.
Storage method
Stored sealed in a cool, dry place. Make sure the workspace has good ventilation. Store away from oxidants, alkali, fire sources, and heat sources.
Packaged in sack-lined plastic bags. 50kg per bag. Store and transport according to regulations on toxic chemicals.
Synthesis method
1. Use phthalic anhydride as raw material to carry out amidation and degradation reactions with sodium hydroxide and ammonia to prepare anthranilic acid, then diazotize with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid, and then replace with cuprous chloride and hydrochloric acid The crude o-chlorobenzoic acid is obtained, and the finished product is obtained after refining.
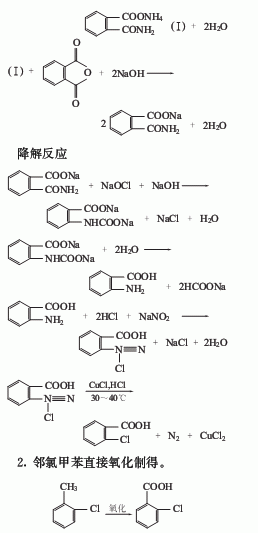
3. Chlorination of o-chlorotoluene Produced by hydrolysis.
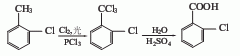
2. The preparation methods are as follows Two kinds.
O-chlorotoluene chlorination hydrolysis method
O-chlorotoluene is placed in a reaction kettle, illuminated with ultraviolet light, the reaction temperature is 100°C, chlorine gas is introduced to carry out the chlorination reaction, and the depth of the chlorination reaction is deepened to generate α , α, α, 2-tetrachlorotoluene, or using o-chlorotoluene as raw material and azobisisobutyronitrile as catalyst for chlorination, α, α, α, 2-tetrachlorotoluene can also be obtained, and then the above The product is moved into the hydrolysis kettle, and a little acid is added to hydrolyze it to produce o-chlorobenzoyl chloride. If the hydrolysis depth is large, 2-chlorobenzoic acid can be obtained.
Anthranilic acid diazotization method
Using anthranilic acid as raw material, adding hydrochloric acid and sodium nitrite for diazotization, and then adding Cu2 to the diazo liquid A solution of Cl2 dissolved in hydrochloric acid is added with stirring, and post-processed to obtain o-chlorobenzoic acid.
Purpose
As an intermediate for dyes and pesticides, it is used as a raw material for making chlorpromazine and anti-inflammatory spirit in medicine. It is also used as a preservative for glues and paints and as a raw material for organic synthesis.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

