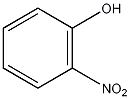
Structural formula
| Business number | 0201 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H5NO3 |
| Molecular weight | 139.11 |
| label |
2-nitrophenol, 2-Nitrophenol, o-Nitrofenol, Acid-base indicator |
Numbering system
CAS number:88-75-5
MDL number:MFCD00011688
EINECS number:201-857-5
RTECS number:SM2100000
BRN number:775403
PubChem number:24862096
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: light yellow crystal with aromatic odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 45[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 214.5 ~216[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.495[4]
5. Saturation Vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (49.3℃)[5]
6. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): -2880.4[6]
7. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.79[7]
8. Solubility: soluble in hot water, easily soluble in ethanol and ether ,benzene. [8]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[9] LD50: 334mg/kg (rat oral)
2. Irritation No information available
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[10]
LC50: 100mg/L (48h) (medaka) ;210mg/L (24h) (water flea)
TLm: 46.3~67mg/L (96h) (bluegill sunfish)
IC50: 4.3~27mg/L (72h ) (algae)
2. Biodegradability[11]
Aerobic organisms Degradation (h): 168~672
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 168~672
3. Non-biodegradability[12 ]
Aqueous photolysis half-life (h): 230~408
Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 7~ 71
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 34.67
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 99.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 277.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 60.2
5. Dielectric constant: None available
6. Polarizability ( 10-24cm3): 13.74
7. Single isotope mass: 139.026943 Da
8. Nominal mass: 139 Da
9. Average mass: 139.1088 Da
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 4
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 66
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 131
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. CovalentNumber of key units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[13] Stable
2. Incompatible materials [14] Strong oxidizing agent, strong reducing agent, strong alkali
3. Conditions to avoid contact[ 15] Heating
4. Polymerization hazard[16] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[17] Nitrogen oxides
Storage method
Storage Precautions[18] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Hydrolysis method: Obtained from o-nitrochlorobenzene by hydrolysis and acidification with sodium hydroxide solution. Add 1850-1950L of sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 76-80g/L into the hydrolysis pot, and then add 250kg of molten o-nitrochlorobenzene. When heated to 140-150℃ and the pressure is about 0.45MPa, keep it for 2.5h, then raise the temperature to 153-155℃ and the pressure to about 0.53MPa, and continue to keep it warm for 3h. After the reaction is completed, cool to 60°C. Add 1000L water and 60L concentrated sulfuric acid into the crystallization pot in advance, then press into the above-mentioned hydrolyzate, and slowly add sulfuric acid until the Congo red test paper turns purple, add ice and cool to 30°C, stir, suction filter, and spin out with a centrifuge After removing the mother liquor, 210kg of o-nitrophenol with a content of about 90% was obtained. The yield is about 90%. Another preparation method is to nitrate phenol into a mixture of o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol, and then steam distillation of o-nitrophenol. The nitrification reaction is carried out at 15-23°C, and the maximum temperature shall not exceed 25°C.
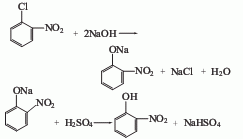
2. Phenol nitration method From phenol It is nitrated with nitric acid into a mixture of o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol, and then separated by steam distillation.
Purpose
1. Used as an intermediate in organic synthesis of medicines, dyes, rubber additives, photosensitive materials, etc. Used for the production of sulfur dyes (sulfide grass green GN, sulfide reduction black CL, sulfide reduction black CLB, sulfide red brown B3R, sulfide reduction blue RNX, etc.). Preparation of medicines phenacetin, paracetamol, developer Mitol and pesticides organophosphorus insecticides parathion, methyl parathion, etc. It can also be used as a single-color pH indicator.
2. Mainly used as dyes, pharmaceuticals and organic synthesis intermediates. It can be used as rubber antioxidant, developer, single-color pH indicator, photosensitive material, etc.
3. Used as organic synthesis intermediates, indicators, and analytical reagents. [19]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

