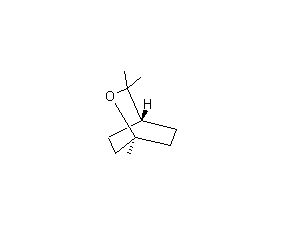
Structural formula
| Business number | 050Q |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H18O |
| Molecular weight | 154.24 |
| label |
1,8-cineole, Aminophyllin, 1,8-Cineole, Eucalyptol, 1,8-Epoxy-p-menthane, 2-Oxa-1,3,3-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.2]octane, food additives, Ether and acetal solvents |
Numbering system
CAS number:470-82-6
MDL number:MFCD00167977
EINECS number:207-431-5
RTECS number:OS9275000
BRN number:105109
PubChem number:24857559
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and transparent liquid, with a pungent odor similar to camphor, and a note similar to eucalyptus oil and lavender oil.
2. Relative density (g/mL, 15.5/15.5ºC): 0.9294
3. Relative density (g/mL, 20/4ºC): 0.9267
4. Melting point (ºC): 1.5
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 176.4
6. Refractive index (15ºC): 1.4584
7. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.4586
8. Flash point (ºC, closed): 50
9. Vapor pressure (kPa, 15ºC): 0.13
10. Vapor pressure (kPa, 54ºC): 1.33
11. Heat of combustion (KJ/kg): 6110
12. Solubility: insoluble in water, able to mix with Miscible with ethanol, chloroform, glacial acetic acid, volatile oils or non-volatile oils.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 2480mg/kg, lethargy or coma;
Mouse subcutaneous LD50: 1070mg/kg, peripheral nerves and sensation – spastic paralysis or no feeling , altered behavior – convulsions or epilepsy;
Mouse transmuscular LD50: 1gm/kg, no details except lethal dose;
Dog subcutaneous LDLo: 1500mg/kg, Skin and appendages – dermatitis, other (after systemic exposure);
Guinea pig LDLo: 2250 mg/kg, behavior – lethargy (common depressive activity), respiratory irritation.
2. Reproductive toxicity: Rat DOSE subcutaneous TDLo: Female after 19-22 days of pregnancy: 2gm/kg SEX/DURATION, which affects the biochemistry and metabolism of newborns.
3. Mutagenicity data: sister chromatid exchangeTEST system: rodent-hamster ovary: 200mg/L
4. A small amount can cause skin rashes in people who are sensitive to poisons , 3~30mL is fatal, and symptoms include suffocation, dizziness, vomiting, confusion, and convulsions. Excessive use can damage the central nervous system.
Ecological data
Usually not hazardous to water. Do not use materials without government permission.Into the surrounding environment.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 45.87
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 167.1
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 399.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 32.4
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 18.18
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 9.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 164
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Use and store according to specifications. It will not decompose and avoid contact with oxides.
2. Chemical properties: It is an extremely stable compound. It does not decompose under normal pressure distillation and does not interact with reducing agents. Reacts with hydrogen bromide to form the adduct C8H18O·HBr (m.p. 56~57℃). When oxidized with potassium permanganate, cineoleic acid (m.p. 204~206℃) is generated. Addition products can also be generated with phenols and phosphoric acid.
3. Found in flue-cured tobacco leaves, burley tobacco leaves, and oriental tobacco leaves.
4. Naturally found in eucalyptus globulus oil, rosemary oil, camphor oil, bay leaf oil, etc.
Storage method
Save in a sealed container at 2-8°C, placed in a ventilated, dry place, and avoid contact with other oxides.
Synthesis method
1. Cineole is widely present in natural aromatic oils and is the main component of eucalyptus oil. Cineole can be isolated from aromatic oils. For example, fractionate eucalyptus oil, collect the 175-180°C fraction, and refine it slightly. If you need to manufacture products with higher purity, the cineole obtained by fractionation from aromatic oil can be cooled and dried by passing it through HCI. Separate the hydrochloric acid and cineole crystals, use hot water to decompose the crystals, and then distill them to obtain pure cineole. The synthesis method is to convert terpine into acid and then dehydrate it.
2. From eucalyptus oil, eucalyptus globulus oil and other essential oils containing more eucalyptol, the 170-180℃ distillate is obtained by freezing or fractionating under freezing.
Refining method: After recrystallizing the adduct formed by cineole, resorcinol, catechol, etc. with petroleum ether, it is refined by steam distillation. You can also dilute cineole with an equal volume of petroleum ether, then saturate it with hydrogen bromide, filter out the precipitate, wash it with a small amount of petroleum ether and put it into water for stirring, and cineole can be regenerated.
3. Tobacco: BU, 9; OR, 26; FC, 18.
Purpose
1. GB 2760-96 stipulates that food spices are allowed to be used. Mainly used in cough drops, artificial mints, etc. 2. is one of the inherent components of lavender oil and spike lavender oil. It is the preparation of this A must-have fragrance for essential oils. Appropriate amounts can be used in herbal flavors such as lavender, fresh mowing and fragrant spices to increase the freshness. Used in medicated soaps, sprays or cosmetic essences and other hygiene products, such as toothpaste, etc., to have a bactericidal effect. It can be used as a masking agent for bad odor in industrial products. Also used in food flavors. 3. Used in the preparation of oral flavors and the manufacture of pharmaceutical products, as a food additive , Japan’s “Official Convention on Food Additives” stipulates that the purity of cineole is above 85% and cannot be used for purposes other than flavoring.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

