Background and overview[1]
2,6-diazaspiro[3.3]heptane-2-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester oxalate is a A kind of azaspirocyclic compound, often used as an intermediate in drug synthesis. There are reports in the literature that it can bind to Autotaxin and act as an Autotaxin inhibitor.

Preparation[1]
(1) 1-benzoylazetidine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester (compound 1 -1) Preparation.
Take a 250mL single-neck bottle, add azetidine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester (10g, 86.9mmol), dissolve DCM (100mL), add triethylamine (14.5mL, 104.2mmol, 1.2 equivalents), placed at 0°C, slowly added BzCl (11.1 mL, 95.6 mmol, 1.1 equivalents), stirred at room temperature overnight, and monitored by TLC. After the reaction is completed, cool to room temperature, add saturated NaHCO3 solution and DCM for extraction, wash with saturated brine, dry with anhydrous sodium sulfate, spin to dryness, and pass through a column to obtain 18.5g of yellow liquid with a yield of 96.8%. ESI-MS m/z: 220.1(M+H)+.
(2) Preparation of 1-benzoylazetidine-3,3-dicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester (compound 1-2).
Place compound 1-1 (10g, 45.6mmol) in a 250mL two-neck flask, exchange argon, add THF, place it at -78°C, and slowly add LDA (34.2mL, 68.4mmol, 1.5 equivalent) , stir for 2 h, slowly add methyl chloroformate (7.0 mL, 91.2 mmol, 2 equivalents), slowly raise the temperature to -70°C, and stir for 1 h. After the reaction is completed, add saturated ammonium chloride solution and EA for extraction, wash with saturated brine, dry with anhydrous sodium sulfate, spin dry, and pass through the column. 9g of yellow liquid was obtained, with a yield of 71%. ESI-MS m/z: 278.1(M+H)+.
(3)(1-Benzylazetidine-3,3-diyl)dimethanol (compound 1-3 ) preparation.
Take a 250mL two-neck bottle, add lithium aluminum hydride (4.9g, 130mmol, 4 equivalents), protect it with argon, add anhydrous THF, place it at 0°C, stir for 15min, and slowly add compound 1 dropwise -2 (9g, 32.5mmol) solution in THF, raised to room temperature, stirred for 15min. Place at 85°C, reflux and stir overnight. The reaction solution was slowly added dropwise to the saturated ammonium chloride solution, filtered through diatomaceous earth, the filtrate was separated into layers, the aqueous layer was extracted three times with EA (100 mL), and washed with saturated brine. Extract once with iPrOH/DCM (20%) solution, wash with saturated brine, combine the organic layers, dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and evaporate to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain 4.5 g of crude product, with a crude yield of 67.2%. used directly in the next step.
(4)(1-Benzylazetidine-3,3-diyl)bis(methylene)bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate) (compound 1-4 ) preparation.
Take a 100mL single-neck bottle, add compound 1-3 (4g, 19.3mmol), dissolve DCM, add TEA (10.7mL, 77mmol, 4 equivalents) and DMAP (catalytic amount), slowly add TsCl ( 12g, 77mmol, 4 equivalents), stir at room temperature overnight. Add water and DCM for extraction, wash with saturated brine, dry with anhydrous sodium sulfate, spin dry, and pass through the column (PE:EA=5:1). 6.5g of yellow liquid was obtained, with a yield of 65.3%.
Preparation of (5) 2-benzyl-6-toluenesulfonyl-2,6-diazaspiro[3.3]heptane (compound 1-5).
Place compound 1-4 (6.5g, 19mmol) in a 250mL single-mouth bottle, add p-toluenesulfonamide (3.9g, 22.8mmol, 1.2 equivalents) and potassium carbonate (6.6g, 47.5mmol, 2.5 equivalent), heat at 100°C and stir overnight. TLC showed that the raw material reaction was completed. Use an oil pump to spin off the DMF, add EA and water, wash with saturated brine, dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate, spin to dryness, and pass through the column (PE:EA=4:1). 4.0g of yellow liquid was obtained.
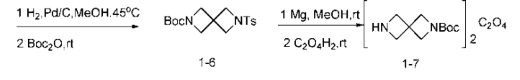
Preparation of (6) 6-tosyl-2,6-diazaspiro[3.3]heptane-2-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (compound 1-6).
Take a 500mL single-mouth bottle, add compound 1-5 (9.5g, 27.8mmol) dissolved in methanol (150mL), add formic acid (3mL), and add 10% palladium on carbon (3g, 2.78mmol) , 10 mol%), exchange with hydrogen, place at 45°C, and stir for 2 days. Cool to room temperature, filter through diatomaceous earth, rinse with methanol, add Boc anhydride (6.5 mL, 27.7 mmol, 1 equivalent), stir at room temperature for 1.5 h, rotary evaporate to remove the solvent, and pass through the column (PE:EA=2:1) to obtain 7g Colorless crystals, 72%.
The characterization data of compound 1-6 are: 1H NMR (400MHz, Chloroform-d, δppm): 7.70 (d, J=8.2, 2H), 7.36 (d, J=8.2, 2H) , 3.84(s, 4H), 3.83(s, 4H), 2.45(s, 3H), 1.38(s, 9H).
(7) Preparation of 2,6-diazaspiro[3.3]heptane-2-carboxylic acid tert-butyl oxalate (compound 1-7).
Take a 500mL single-neck bottle, add compound 1-6 (7g, 20mmol), dissolve it in methanol (200mL), add magnesium chips (3.84g, 0.16mol, 8 equivalents), and stir at room temperature. As the magnesium chips dissolved, the reaction solution gradually turned into a white viscous state, and TLC showed that the reaction of the raw materials was complete. The solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, diethyl ether (150 mL) was added, stirred at room temperature for 1 h, filtered through diatomaceous earth, the filtrate was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and an ethanol solution (3 mL) of anhydrous oxalic acid (0.89 g, 9.9 mmol, 0.5 equivalent) was added dropwise. A white precipitate appeared immediately and was filtered under reduced pressure to obtain 3.2g of colorless solid, 82%.
The characterization data of compound 1-7 are: 1H NMR (400MHz, CD3OD+D2O, δppm): 4.90 (s, 2H), 4.20 (s, 4H), 4.09 (s, 4H), 1.42(s,9H).
References
[1] [Invented in China, authorized by China] CN201710098384.9 Azaspirocyclic compounds and their preparation methods and applications


 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

