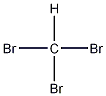
Structural formula
| Business number | 01JA |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CHBr3 |
| Molecular weight | 252.73 |
| label |
Bromoform, Methyl tribromide, Tribromomethane, Formyltribromide, Aliphatic halogenated derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:75-25-2
MDL number:MFCD00000128
EINECS number:200-854-6
RTECS number:PB5600000
BRN number:1731048
PubChem number:24863014
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless heavy liquid with a chloroform-like smell. [1]
2. Melting point (ºC): 6~9[2]
3. Boiling point (ºC) : 149.5[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 2.89[4]
5. Relative Vapor density (air=1): 8.7[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.75 (25ºC)[6]
7. Critical pressure (MPa): 6.09[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.38[8]
9. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform, benzene, etc. [9]
10. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 18~50ºC, constant pressure): 0.519
11. Electrical conductivity ( S/m, 25ºC): <2×10-8
12. Vapor pressure (kPa, 22ºC): 0.67
13. Vapor pressure ( kPa, 48ºC): 2.67
14. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1): 0.00091
15. Refractive index at room temperature (n20 ): 1.5976
16. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.5956
17. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 8.153
18. Lennard-Jones parameter (K): 162.2
19. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5 sup>: 21.726
20. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 6.810×109
21. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 49.980
22. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 330.70
23. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 70.98
24. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K– 1): 129.9
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[10]
LD50: 933mg/kg (rat oral); 414mg/kg (rat intraperitoneal ); 1072mg/kg (orally administered to mice)
LC50: 12100mg/m3 (inhaled to mice, 2h)
2. Irritation No data available
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity [11] Rat inhalation 0.25mg/L, 4 hours a day , 2 months later, abnormal liver and kidney function.
4. Mutagenicity [12] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 50μl/dish. Sister chromatid exchange: human lymphocytes 80 μmol/L. DNA damage: human lung 100 μmol/L (3h).
5. Teratogenicity[13] Mice were orally administered the lowest toxic dose (TDLo) 200mg/kg for many generations, causing hepatobiliary and Developmental malformations of the genitourinary system.
6. Carcinogenicity[14] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G3, insufficient evidence of carcinogenicity to humans and animals.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[15] LC50: 40.4mg/L (48h) (medaka)
2. Biology Degradability[16]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 672~4320
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 2688 ~17280
3. Non-biodegradability[17]
Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 1299~ 12989
First-order hydrolysis half-life (h): 6.02×106
4. Bioaccumulation [18] BCF: 7.1~21 (carp, exposure concentration 100mg/L, exposure time 6 weeks); 7.7~19 (carp, exposure concentration 10mg/L, exposure time 6 weeks)
5. Other harmful effects[19] It decomposes when exposed to alkali, but it is a highly persistent compound in water and will not be biodegraded. Especially if it stays in drinking water for a long time, it will cause harm.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 29.83
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 84.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 225.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 49.8
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 11.82
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 2.8
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[20] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[21] Strong oxidants, active metal powders
3. Conditions to avoid contact[22] Light
4.Polymerization hazard[23] No polymerization
5. Diversity products[24] Bromine Hydrogen
Storage method
Storage Precautions[25] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature does not exceed 32°C and the relative humidity does not exceed 80%. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, active metal powders, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Under alkaline conditions, acetone reacts with sodium hypobromite to obtain tribromoacetone, which will continue to decompose under alkaline conditions to obtain crude product. After distillation, washing, filtering and drying, the finished product is obtained. 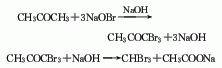
Purpose
1. It can be used as dye intermediates, disinfectants, analgesics, anesthetics, refrigerants, mineral processing agents, precipitants, solvents and anti-explosion liquid components.
2. Used as solvent, refractive index liquid and specific gravity liquid.
3. Used as solvent and organic synthesis intermediate. [26]
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/nt-cat-a-240-catalyst-cas1739-84-0-newtopchem/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/38895extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-bl-13-niax-catalyst-a-133-niax-a-133/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1909extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/low-odor-catalyst-dabco-amine-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/808extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/73.jpgextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44944extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44658extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/30.jpg

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

