[Background and Overview][1][2]
Hypertriglyceridemia (HTG) is a heterogeneous disorder of triglyceride protein synthesis or degradation. Chylomicrons and pre-β-lipoprotein are the highest triglycerides in the blood, which are closely related to the formation of atherosclerosis. The elevation of triglycerides is of great significance to the occurrence of coronary heart disease. The value of elevation of serum triglycerides is greater than that of cholesterol, especially in myocardial infarction. 82% of patients with myocardial infarction have hypertriglyceridemia, and high Only 47% had high cholesterol. Primary hyperlipidemia, obesity, arteriosclerosis, obstructive jaundice, diabetes, extreme anemia, nephrotic syndrome, pancreatitis, hypothyroidism, long-term hunger and high-fat diet can all increase the level. Triglycerides can be falsely elevated after drinking alcohol.
Hyperlipidemia mainly refers to elevated blood cholesterol and/or triglycerides. Hyperlipidemia is a manifestation of abnormal fat metabolism in the human body and is mainly divided into three categories: hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia and mixed hyperlipidemia. Lipemia. Mixed hyperlipidemia is a clinical type of hyperlipidemia, which refers to high serum total cholesterol and triglyceride levels, that is, total cholesterol. For such diseases, bezafibrate drugs on the market have good therapeutic effects.
Bezafibrate, chemical name 2-[4-[2-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]ethyl]phenoxy]-2-methylpropionic acid, is the Second-generation phenoxyacetic acid lipid-lowering drugs were developed by the German company Boehringer Mannheim. They were launched in West Germany and Switzerland in 1979 and were approved for production in my country in 2000. A large number of clinical studies have shown that it has obvious effects in reducing triacylglycerol and increasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and is mainly used in the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, and mixed hyperlipidemia. In recent years, studies have found that the combined use of simvastatin and bezafibrate in the treatment of patients with mixed hyperlipidemia is better than monotherapy in achieving major blood lipid parameters, and fibrates are peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. (PPARs) ligands. The effects mediated by PPARs mainly include lipid metabolism, immune response, etc. Therefore, the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis, obesity, diabetes, tumors, and inflammatory diseases are closely related to PPARs. PPARs It will most likely become a new target for the treatment of these diseases.
[Indications][3]
Bezafibrate can be used as a first-line lipid-lowering drug, suitable for hyperlipidemia caused by various causes, especially for patients with hyperlipidemia and diabetes.
[Specifications][3]
Tablets: 200mg each; extended-release tablets: 400mg each.
【Usage and Dosage】[3]
Oral administration: 200 to 400 mg each time, 3 times a day. After blood lipids are reduced, the dose is reduced and maintained.
[Pharmacological effects and mechanism of action] [4]
Bezafibrate is a fibric acid lipid-lowering drug. Bezafibrate Bezafibrate can lower cholesterol and inhibit the rate-limiting enzyme for cholesterol synthesis – methylhydroxyglutaryl-CoA reductase, reducing cholesterol synthesis; increasing the decomposition and metabolism of low-density lipoprotein, thereby making Cholesterol is lowered. It can also reduce triglycerides by inhibiting acetyl-CoA reductase, reducing triglyceride synthesis; activating lipoprotein lipase in the liver increases triglyceride clearance, thereby reducing triglycerides. It can increase serum high-density lipoprotein concentration and slightly reduce blood sugar levels by reducing the body’s insulin resistance.
[Pharmacokinetics][3]
Easily absorbed after oral administration, Tmax is 2 hours, t1/2 is 2 hours, PBP is 94% to 96%, and about half of the amount is excreted in the urine in its original form. , and the rest of the metabolites are excreted in the feces.
[Adverse reactions][4]
Bezafibrate has minor side effects. Long-term use may cause gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension, occasional rash, accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, liver pain, and elevated serum aminotransferases.
[Drugs for pregnant and lactating women][6]
The safety of bezafibrate during pregnancy has not been established, so its use by pregnant women is not recommended. It is unknown whether bezafibrate is excreted into breast milk, so lactating women should not take it.
【Pediatric Medication】[6]
There are currently no experimental studies to confirm the efficacy and safety of bezafibrate in children, so it should not be used.
[Drug for the elderly][6]
The elderly should adjust the dosage according to their liver and kidney function status. If there is poor renal function, the dosage of bezafibrate must be appropriately reduced.
[Drug Interaction][6]
1) Bezafibrate can significantly enhance the effect of oral anticoagulants. When used together with bezafibrate, attention should be paid to reducing the dose of oral anticoagulants, and frequent monitoring of prothrombin time to adjust the dose of anticoagulants. Its mechanism of action is still uncertain, but it may be because bezafibrate can replace warfarin from its protein binding site, thereby enhancing its effect.
2) When bezafibrate is combined with other drugs with high protein binding rates, they can also be removed from protein binding.Replacement at this point will lead to enhanced effects, such as tolbutamide and other sulfonylurea hypoglycemic drugs, phenytoin, furosemide, etc. If the above drugs are taken during hypolipidemic treatment, the hypoglycemic drugs and other drugs should be adjusted dosage.
3) The combined use of clofibric acid derivatives and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, such as lovastatin, to treat hyperlipidemia will increase the risk of severe muscle toxicity and can cause myalgia and rhabdomyolysis. , increased blood creatine phosphokinase and other myopathies, joint use should be avoided as much as possible.
4) Bezafibrate is mainly excreted by the kidneys. When combined with immunosuppressants such as cyclosporine, it can increase the blood concentration and renal toxicity of the latter, which may lead to the risk of worsening renal function. The dose should be reduced or discontinue medication. Caution should also be exercised when bezafibrate is used concomitantly with other nephrotoxic drugs.
5) Bezafibrate can increase the effect of hypoglycemic drugs.
[Notes][4]
1. Pregnant women, lactating women, and those with severe liver and kidney dysfunction are prohibited from taking this product. Use with caution by children.
2. Liver function should be checked regularly during medication. If transaminases are found to be elevated, medication should be stopped immediately.
【Synthesis】[1][5]
Method 1: p-hydroxybenzaldehyde, hydrochloride, chloride, and chloroform are used as the main raw materials, and bezafibrate is synthesized through acylation, condensation, and other processes:
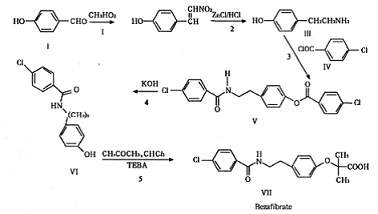
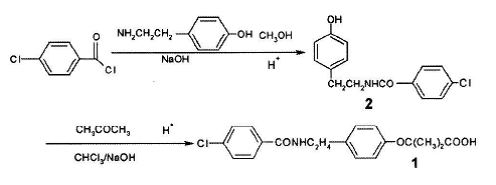
Method2:Use p-chlorobenzoyl chloride and p-hydroxyphenylethylamine as raw materials to first synthesize N-p-hydroxyphenylethyl -4-Chlorobenzamide is then condensed with acetone and chloroform in toluene under phase transfer catalysis to obtain bezafibrate:
[Main reference materials]
[1] Wu Jie, Gu Xu, Li Dong, Ding Aizhong, & Dai Xiaoyang. (2010). Improvement of the synthesis process of the lipid-lowering drug bezafibrate. Chinese Journal of New Drugs, (4), 311-312.
[2] Cao Cheng; Gao Yu. A kind of bezafibrate tablets and its preparation method CN201711250933.6, application date 2017-12-01.
[3] Handbook of Commonly Used New Drugs.
[4] General Practitioner Drug Manual.
[5] Synthesis research of bezafibrate.
[6] Instructions for bezafibrate tablets.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

