Background and overview[1] [2]
Fenbendazole, also known as benzimidazole, has a chemical name of 5-phenylthiobenzimidazole-2-methylcarbamate and was developed by Hoechst in the 1970s. Fenbendazole can repel parasites such as roundworms, hookworms, whipworms, some tapeworms, and Strongyloides in the gastrointestinal tract of animals. It has the advantages of wide anthelmintic spectrum, safety, low toxicity, and good palatability.
Although it has been used for more than 40 years, fenbendazole is still the preferred anthelmintic drug in modern animal husbandry. The annual global demand for fenbendazole is more than 1500t. The main domestic manufacturers include Jiangsu Baozhong Baoda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Changzhou Yabang Qihui Pharmaceutical Chemical Co., Ltd., etc. Fenbendazole is a white or off-white powder, odorless, tasteless, insoluble in water, soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide and glacial acetic acid. It is currently one of the most commonly used and ideal anthelmintic drugs for animals. It is effective against nematodes, flukes, and tapeworms in animals; a single preparation, such as powder and tablets of fenbendazole, can effectively treat parasitic diseases in livestock and poultry. However, because the drug is difficult to dissolve in water, the bioavailability of oral medication is relatively low. Low. In veterinary clinical use, the dosage and course of treatment must be increased. It is inconvenient to use and the cost is relatively high. It does not have the characteristics of high efficiency, long-term effect, and environmental protection of ideal anthelmintic drugs.
Synthesis[1]
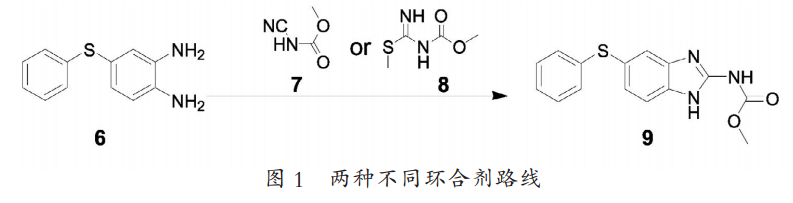
After decades of continuous accumulation and selection, the synthesis route for large-scale production of fenbendazole has been basically fixed, and no major changes are possible in the short term. According to the different cyclizing agents used, it can be divided into: S-methylisothiourea process and methyl cyanide carbamate process (as shown in Figure 1). There are some other synthetic routes reported in the literature, but they are only for research and discussion, and cannot achieve industrial production. As a widely used veterinary drug, only by continuously improving its production process and achieving environmentally friendly and low-cost production can its market competitiveness be improved.
Microcrystal preparation[2]
This embodiment provides a method for preparing fenbendazole microcrystals, which includes the following steps:
Preparation of fenbendazole ethanol mixture: Dissolve quantitative fenbendazole raw materials in the ethanol solution to prepare a fenbendazole ethanol mixture with a fenbendazole concentration of 60 mg/mL; form hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose aqueous solution: Dissolve a certain amount of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose in water to form a hydroxypropylmethylcellulose aqueous solution with a concentration of 4 mg/mL; crystallization: respectively at 4℃, 20℃, and 40℃. Slowly add the fenbendazole ethanol solution to the hydroxypropylmethylcellulose aqueous solution in a volume ratio of 1:10 to the hydroxypropylmethylcellulose aqueous solution to form fenbendazole supersaturation Solution; use a magnetic stirrer to stir the fenbendazole supersaturated solution at a speed of 900 r/min for 15 minutes to precipitate crystals and form a fenbendazole microcrystalline suspension;
Separation and drying: Use a vacuum pump to perform suction filtration and separation treatment on the fenbendazole microcrystalline suspension to obtain fenbendazole microcrystalline semi-finished product; vacuum dry the fenbendazole microcrystalline semi-finished product at 50°C The finished product of fenbendazole microcrystals was obtained in 12 hours. Wherein, the method for measuring the average particle size of the fenbendazole microcrystals is: take an appropriate amount of the finished fenbendazole microcrystals, add a small beaker containing an appropriate amount of distilled water, disperse ultrasonically for 20 minutes, and dip it with a glass rod. The dispersed sample suspension is placed on a glass slide, covered with a cover slip and observed under an electron microscope.
Preparations[3]
1. Preparation method of 5% fenbendazole high-dissolution preparation
Raw materials and excipients: 50 kg of pharmaceutical grade fenbendazole API, 150 kg of food grade solvent triethanolamine, 50 kg of food grade emulsifier Tween-80, 250 kg of food grade silica, 500 kg of starch.
Main equipment: 500L dissolving tank with stirring, one 2000L mixer.
In the first step of preparation, place 150 kg of food-grade solvent triethanolamine in a 500L dissolving tank, add 50 kg of pharmaceutical-grade fenbendazole API, and start stirring at 30-60 rpm. At the same time, the temperature is slowly heated to about 160 degrees through the interlayer heating of the dissolving tank and maintained for 30-60 minutes until all the raw materials are dissolved and the solution is clear.
The second step of preparation is to prepare 50 kilograms of food-grade emulsified food.�Add into the above solution and keep stirring for 10-20 minutes to disperse the emulsifier evenly.
The third step of preparation is to use a 2000L mixer, add 250 kg of silica and 500 kg of corn starch, and mix for 5 minutes. Then, in the mixed state, slowly add the solution prepared in the second step to the mixer through pump pressure, so that the addition is completed in 10-15 minutes. And after completion, keep the mixing state for 10-15 minutes to obtain 1000 kilograms of 5% fenbendazole solid pharmaceutical preparation.
2. Preparation method of 10% fenbendazole high dissolution preparation
Raw materials and excipients: 100 kg of pharmaceutical grade fenbendazole API, 300 kg of food grade solvent triethanolamine, 100 kg of food grade emulsifier Tween-80, 500 kg of food grade silica.
Main equipment: 1000L dissolving tank with stirring, one 2000L mixer.
In the first step of preparation, place 300 kg of food-grade solvent triethanolamine in a 500L dissolving tank, add 100 kg of pharmaceutical-grade fenbendazole API, and start stirring at 30-60 rpm. At the same time, the temperature is slowly heated to about 160 degrees through the interlayer heating of the dissolving tank and maintained for 30-60 minutes until all the raw materials are dissolved and the solution is clear.
In the second step of preparation, add 100 kilograms of prepared food-grade emulsifier to the above solution and keep stirring for 10-20 minutes to disperse the emulsifier evenly.
In the third step of preparation, start the 2000L mixer and add 500 kg of silica. In the mixed state, slowly add the solution prepared in the second step to the mixer through pump pressure, so that the addition is completed in 10-15 minutes. And after completion, keep the mixing state for 10-15 minutes to obtain 10% fenbendazole solid pharmaceutical preparation.
Main reference materials
[1] Yan Jiaqing. Improvement of the synthesis process of fenbendazole [J]. Zhejiang Chemical Industry, 2016, 47(01):8-11.
[2] CN201510339859.X Preparation method of fenbendazole microcrystals
[3] CN201410812790.3 Preparation method of high-dissolution fenbendazole pharmaceutical preparation

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

