Background and overview[1][2]
Photoinitiator refers to a substance in a photopolymerization imaging system that is directly sensitive to light and promotes the polymerization of monomers into polymer compounds. It can improve the sensitivity of photopolymerizing materials, expand the color range, and play a spectral sensitization role. Commonly used compounds include the following: carbonyl compounds (benzophenone, polynuclear quinone), with a color sensitive range of 360 to 420 nanometers; azo compounds (azobisisobutyronitrile, diazonium salts), with a color sensitive range of 340 nm ~400 nanometers; organic sulfur compounds (thiols) have a color sensitivity range of 280 to 400 nanometers; halides have a color sensitivity range of 300 to 400 nanometers; sensitizing dyes have a color sensitivity range of 400 to 700 nanometers; zinc oxide has a color sensitivity range Wavelength 300~380 nanometers.
In light-initiated curing or polymerization systems, such as UV-curing inks, varnishes, adhesives, and silicones, this chemical can break certain chemical bonds when exposed to light. Reactive groups are formed, which then initiate polymerization or cross-linking reactions. Generally called a catalyst. Some UV-curable silicone systems are catalyzed with photosensitive chelates. UV radiation breaks the chelates, causing them to initiate a curing reaction.
Photoinitiator MBF, also known as methyl benzoylformate. Methyl benzoylformate is a colorless or light yellow liquid, soluble in organic solvents such as alcohol, ether, benzene and toluene, but difficult to dissolve in water. Methyl benzoylformate is a new type of photoinitiator developed in recent years. It has the advantages of high initiating efficiency, good thermal stability, low yellowing, and low odor. It plays a particularly prominent role in light-cured transparent products. .
Structure
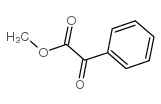
Apply[3[4]
Methyl benzoylformate is a new type of photoinitiator developed in recent years. It has the advantages of high initiating efficiency, good thermal stability, low yellowing, and low odor. It is widely used in light-cured transparent products. The status is particularly prominent. Examples of its application are as follows:
1. Used to prepare a photoinitiator composition that can be used in UV-LED light sources,
Thioxanthone photoinitiator: methyl benzoylformate: acylphosphine oxide photoinitiator is (1~2): (1~2): (2~4) photocurable composition. This composition has very high photoinitiation efficiency under UV-LED light source, which greatly improves the current common problem of poor surface drying. The second is to provide a photo-curing composition with excellent performance: epoxy acrylate 20-40%; acrylic resin containing tertiary amine structure 5-20%; reactive diluent 20-60%; photoinitiator composition 1-5 %; additives -0.1~5%; pigments 0~30%.
The photoinitiator composition has the characteristics of long light absorption wavelength, low odor, high initiating activity, and small dosage. It can meet the UV requirements for deep curing, high activity, good surface dryness, and low yellowing. -The use of LED light source curing, especially suitable for thin film coatings.
2. Prepare a one-component low-VOC UV-curable water-based ink composition,
The ink composition includes: photoinitiator, co-initiator, polymerized monomer, water-based polyester resin/water-based polyester acrylate, water-based polyurethane resin/water-based polyurethane acrylate, silicone surface additives, color Slurry, water-based wetting and dispersing agents, water-based defoaming agents, inorganic additives, phosphorylated acrylates, phosphate ester surfactants and solvents.
The ink composition contains: 3-10 parts of photoinitiator, 0-5 parts of co-initiator, 10-30 parts of polymerized monomer, 10-30 parts of water-based polyester resin/water-based polyester acrylate , 10-40 parts of water-based polyurethane resin/water-based polyurethane acrylate, 0.1-3 parts of silicone surface additives, 0.1-3 parts of color paste, 0-6 parts of water-based wetting and dispersing agent, 0.1-1 part of water-based defoaming agent , 5-40 parts of inorganic additives, 0.5-3 parts of phosphorylated acrylate, 0.5-3 parts of phosphate surfactant and 0-10 parts of solvent.
The photoinitiator is selected from 1-hydroxycyclohexyl phenyl ketone, 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propanone, 2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl -Diphenylphosphine oxide, photoinitiator MBF, photoinitiator BP, photoinitiator TPO-L, photoinitiator 819, photoinitiator 819W, photoinitiator 2959, photoinitiator 907, photoinitiator 369, light One or more of initiator BDK and photoinitiator 754.
Preparation[5]
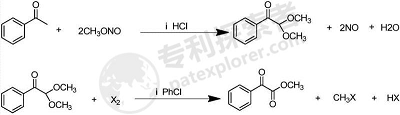
A new process for the production of photoinitiator and the intermediate methyl benzoylformate, which uses acetophenone as the starting material and reacts with methyl nitrite under the action of hydrogen chloride to obtain intermediate 2. 2-Dimethoxyacetophenone; 2,2-dimethoxyacetophenone is chlorinated with chlorine (or brominated with bromine) under the action of the catalyst 4-methyl-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol. Finally, a portion of the alkyl halide is removed to obtain methyl benzoylformate. The catalyst used in the production of 2,2-dimethoxyacetophenone is hydrogen chloride gas, and the catalyst used in the production of methyl benzoylformate is 4-methyl-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol.
The solvents used in the production process of 2,2-dimethoxyacetophenone are methanol, toluene and cyclohexane, etc. The solvents used in the production process of methyl benzoylformate are chlorobenzene, 1, 2-Dichloroethane and cyclohexane, etc. Preferably, the raw material for the halogenation elimination reaction of 2,2-dimethoxyacetophenone is chlorine or bromine. The material ratio in the production of 2,2-dimethoxyacetophenone is (weight ratio): acetophenone: hydrogen chloride: methyl nitrite = 1:0.3:1.1.
Materials in the production process of methyl benzoylformate�� is (weight ratio): 2,2-dimethoxyacetophenone: 4-methyl-2,6-di-tert-butylphenol: halogen=1:0.1:1. 2,2-dimethoxy The reaction temperature for the production of acetophenone is 35-40°C. The reaction temperature during the production of methyl benzoylformate is 110-120°C. Using acetophenone as the starting material and hydrogen chloride gas as the catalyst, it reacts with methyl nitrite to obtain 2,2-dimethoxyacetophenone, and further halogenation elimination reaction obtains methyl benzoylformate. Compared with the traditional process, the reaction route of the synthesized methyl benzoylformate has the advantages of low price and no environmental pollution, providing a more economical and environmentally friendly process for the industrial production of methyl benzoylformate.
Main reference materials
[1] Concise Photography Dictionary
[2] Illustrated Encyclopedia of Labeling Technology
[3] Dong Yueguo; Yao Na; Zhang Yan; Zhang Wenjing; Wang Xiaomeng; Zhao Guohui; Zhang Qi. A photoinitiator composition that can be used for UV-LED light sources. CN201711020814.1, application date 20171027
[4] Xu Tengfei; Lin Songxiang; Ming Yaoqiang; He Run. A one-component low VOC UV-curable water-based ink composition. CN201810651694.3, application 20180622
[5] Wang Youming. New synthesis process of methyl benzoylformate. CN201610548031.X, application 20160712

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

