Background and overview[1][2]
Meta-dichlorobenzene is an important organic chemical raw material and is widely used in the organic synthesis industry, such as the synthesis of 2,4-dichloroaniline, 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene and broad-spectrum antifungal drugs. Conazole. With the increasing development of the pharmaceutical industry and the introduction of new drugs, high-content m-dichlorobenzene is used as an intermediate for a variety of drugs, and the demand has greatly increased. Especially in recent years, the demand for high-content m-dichlorobenzene in the international market has developed rapidly, and the total annual domestic production was only about 1,000 tons, which was far from meeting the market demand. Therefore, this product has broad prospects.
Meta-dichlorobenzene is also known as 1,3-dichlorobenzene. Colorless liquid. Molecular weight 147.00. Melting point -24.7℃. Boiling point 173℃. Relative density 1.2884 (20/4℃). Refractive index 1.5459. Flash point 63℃. Soluble in ethanol, ether, benzene, insoluble in water. Meta-dichlorobenzene is used in organic synthesis.
Meta-dichlorobenzene can be used as an intermediate for the broad-spectrum antifungal drug miconazole. Its traditional synthesis method is: 1) Diazotization reaction between m-phenylenediamine, sulfuric acid and sodium nitrite to produce diazo salt, and then chlorinated; 2) m-chloroaniline is diazotized and chlorinated. The diazotization method of m-chloroaniline has a low synthesis rate and low productivity; 3) m-dinitrobenzene directly catalyzes chlorine Chemical method; 4) Benzene chlorination method. The process control conditions of the benzene chlorination method are difficult and the separation efficiency is not high. Among them, the synthesis process of diazotization of m-phenylenediamine is complicated and has been eliminated.
The explosive meta-dinitrobenzene exists in the chlorination method of m-dinitrobenzene, and the synthesis process poses great safety risks. In addition, the synthesis methods of m-dichlorobenzene include: chlorobenzene by-product recovery method. The production process for preparing resorcinol in the chemical industry is relatively complex, and the purity of the production is relatively low, making it difficult to meet the needs of human production and life.
Apply[3]{4}}
Meta-dichlorobenzene can be used as an intermediate in the synthesis of pesticides, medicines, dyes and pigments. In terms of pesticides, m-dichlorobenzene is mainly used in the synthesis of fungicides such as propiconazole, difenoconazole, imazalil, hexaconazole, furconazole, pentoconazole and amidazole, and herbicides such as triacetazole. , diflufenac, oxazolefen, thiazolimines, triazolinone compounds and other new herbicides.
In medicine, m-dichlorobenzene is used to synthesize highly efficient, safe and broad-spectrum antifungal drugs such as econazole, myconazole and ketoconazole, and the anti-inflammatory and analgesic drug diclofenac sodium (trade name: Voltaren ), new non-steroidal antibiotic antipyretic and analgesic drugs flufenac, etc. In the dyeing and pigment industry, dichlorobenzene is used to synthesize ASITR, naphthol AS-LG and pigment solid magenta FB, etc. Its development prospects are very broad. Examples of its application are as follows:
1. Synthesis of resorcinol.
Resorcinol is an important fine organic chemical raw material, widely used in agriculture, dyes, coatings, medicine, plastics, rubber, electronic chemicals and other fields. Using m-dichlorobenzene as raw material and lanthanum oxide as catalyst, it is hydrolyzed in KOH aqueous solution to generate resorcinol. Experimental results show that the suitable process conditions for the hydrolysis of m-dichlorobenzene are: reaction temperature 260°C, reaction system pH 13.4, V (water): V (m-dichlorobenzene): 15:1, and stirring rate 400 r /min. Under the above process conditions, the conversion rate of m-dichlorobenzene is >70%, and the yield of resorcinol is >20%.
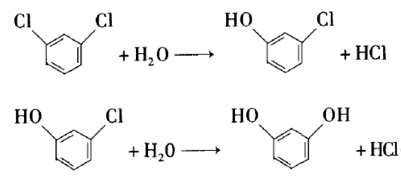
2. Preparation of m-chloroanisole.
Meta-chloroanisole is an important pharmaceutical and chemical intermediate, widely used in medicine and organic synthesis. The main use in medicine is to replace m-bromoanisole in the production of tramadol hydrochloride, and it is also a raw material for the synthesis of 3-methoxythiophenol. Meta-chloroanisole is favored by many users because of its high quality and low price.
The synthesis method is to mix m-dichlorobenzene, sodium methoxide and the first organic solvent, and add copper salt as a catalyst. The molar ratio of m-dichlorobenzene: sodium methoxide: copper salt is 1:0.5~8:0.005~ 0.1, add 1.5 to 3.5 ml of the first organic solvent to each gram of m-dichlorobenzene, stir and react at a reflux temperature of 75 to 150°C for 3 to 24 hours. After the reaction is completed, the organic solvent is evaporated, water is added to the residual liquid, and the first organic solvent is added. Two organic solvents are extracted, and the organic liquid is distilled or rectified to obtain the compound m-chloroanisole.
The present invention has high quality, low price, and has great market advantages; the present invention uses m-dichlorobenzene as raw material, reacts with sodium methoxide solution under a homemade copper salt catalyst, and obtains m-chloroanisole conveniently and economically ; The present invention is a one-step synthesis method with simple process, convenient operation, short production cycle, little environmental pollution, high product yield, and good development prospects.

Preparation[5][6]
Method 1: Benzene-nitrification-high temperature chlorination process. After benzene undergoes mononitration and dinitration, a mixed dinitrobenzene containing m-dinitrobenzene with a mass fraction of 88% is obtained. After adding sodium (hydrogen) sulfite aqueous solution, p-nitrobenzene sulfonic acid is generated that is soluble in water. After being separated by sodium, a high content of meta-dinitrobenzene is obtained. After chlorination and denitrification, dichlorobenzene is obtained. This reaction is a free radical substitution reaction, generally carried out under the action of a free radical initiator (such as azobisisobutyronitrile, benzoyl peroxide, etc.) or under ultraviolet light irradiation.
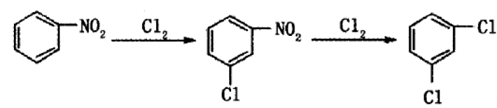
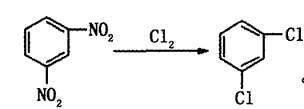
Method 2: One-step chlorination of m-dinitrobenzenebe made of.
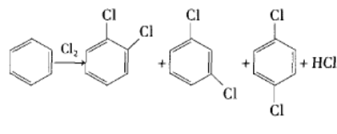
Method 3: Isomerization of p-/o-dichlorobenzene. In the process of preparing dichlorobenzene by chlorination from benzene or chlorobenzene as raw material, the obtained o-dichlorobenzene and p-dichlorobenzene account for a larger proportion, and m-dichlorobenzene only accounts for 2% to 3%. The mixed dichlorobenzene Dichlorobenzene is obtained by catalytic isomerization of chlorobenzene and then separation.
Many catalytic isomerization preparation methods have been reported in the literature. The early catalysts used were mainly strongly acidic aluminum trichloride, HF-BF, etc. This type of Lewis acid easily absorbs water and releases hydrogen chloride and hydrogen fluoride when it encounters water, which is highly corrosive; Lewis acid hydrate is difficult to dry, and it is difficult to regenerate this type of catalyst (for example, heating aluminum trichloride hydrate will release hydrogen chloride without obtaining Pure anhydrous aluminum trichloride) and was therefore eliminated. After the 1970s, research on this type of catalyst focused on zeolites, and many reactions used zeolites instead of liquid acids as catalysts. O-/p-dichlorobenzene is catalytically translocated under the action of acidic zeolite catalyst to produce m-dichlorobenzene with high yield.
Main reference materials
[1] Ming Dynasty Fine Chemical Dictionary
[2] Jiang Fangfang; Wang Jingzhu. A preparation method of m-dichlorobenzene. CN201710200205.8, application date 20170330
[3] Yang Huihui, Zhang Yue, Yan Shenghu, et al. Preparation of resorcinol from hydrolysis of m-dichlorobenzene[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 29(2): 30- 33.
[4] Wang Delin; Huang Xumin; Wang Peikun; Shao Qianfei. A synthesis method of m-chloroanisole. CN201410035767.8, application date 20140124
[5] She Weimin, Xu Xiaoliang, Wu Chunjiang, et al. Production process of m-dichlorobenzene through isomerization of o-dichlorobenzene[J]. Chlor-Alkali Industry, 2017, 53(7): 24-25.
[6] Tang Qin, Ding Kehong. Comparison of two kinds of m-dichlorobenzene production processes[J]. Chlor-Alkali Industry, 2011, 47(3): 24-29.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

