Background and overview[1][2]
The selenium reagent is abbreviated as DAB, and its scientific name is 3,3′-diaminobenzidine. It reacts with Se (W) in an acidic medium to form a yellow stem. DAB is an alkali that darkens quickly in the air. Its hydrochloric acid Salt is a white needle-shaped substance, soluble in water, and its aqueous hydrochloride solution can be used as a color developer. 3,3′-Diaminobenzidine (DAB) has a wide range of uses and is widely used in chemistry, biochemistry, materials and other research fields. At present, in countries with developed aerospace and military industries, DAB has begun to be focused on research and used as a monomer to prepare high-end polymer materials. It is mainly used to synthesize heat-resistant polymer resins and synthetic fibers. However, it is used as a color developer in analysis Applications in the field of chemistry are found only in the photometric determination of selenium.
Structure
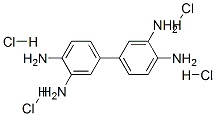
Apply[1][3][4][5]
3,3′-Diaminobenzidine (DAB) has a wide range of uses and is widely used in chemistry, biochemistry, materials and other research fields. Examples of its application are as follows:
1. Used to detect diacetyl content in food.
Use 3,3′-diaminobenzidine as a pre-column derivatization reagent for the accurate detection of diacetyl content in samples, and provide an HPLC method for determining the diacetyl content in food (especially alcohol samples) . The detection principle is as follows:
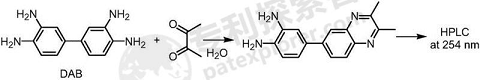
The specific implementation steps are as follows:
(1) Add 0.2-1.0mL of 1-5mM 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) aqueous solution to 1.8-6.0mL of the sample to be tested, mix and react at 25-50℃ for 15-30min;
(2) The reaction-completed sample is filtered with a 0.22μm filter membrane, and the filtrate is detected by HPLC. 3,3′-diaminobenzidine is used as a derivatization reagent to detect diacetyl. The reaction can be completed in 5-10 minutes at room temperature and is less dependent on pH value. Compared with previously reported derivatization reagents, it has The advantages of easy and fast operation.
2. Direct determination of selenium in antimony products using selenium reagent photometry.
Using the principle that selenium quantitatively sublimates and is captured by sodium carbonate-magnesium oxide during roasting at 750~800°C to directly eliminate matrix interference such as antimony. After using hydrochloric acid to convert Se (Ⅵ) into Se (Ⅳ), it can be directly Color development assay. The method is simple to operate and has less environmental pollution. After sample verification, the measurement results are satisfactory. This method is suitable for the determination of selenium mass fraction in antimony products between 0. 001% and 0. 1%.
3. Synthesis of poly-2,2’-5,5’-benzimidazole and poly-2,5-benzimidazole.
The method includes the following steps:
(1) Use polyphosphoric acid (PPA) (chemically pure, content: P2O5 ≥ 80.0wt%) as the solvent to perform a polycondensation reaction, add a certain amount of the above-mentioned PPA to a round-bottomed flask of a certain volume, and under nitrogen protection (flow rate: 40-50mL/min), heat and stir to raise the temperature to 140°C, slowly add a certain amount of 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB·4HCl·2H2O, 97wt% ), dissolve 3,3′-diaminobenzidine in PPA and the HCl gas contained therein is completely volatilized, and slowly add the same amount of isophthalic acid (chemically pure, ≥99wt%);
(2) After stirring and mixing is complete, transfer the mixed liquid to the microwave oven. First, program the temperature to 170°C for 0 to 60 minutes, then program the temperature to 200°C for 40 to 160 minutes. The microwave power is 300 to 500W;
p>
(3) Pour the reaction product into deionized water while it is hot, let it stand for 10 to 15 hours, wash it with water until it is close to neutral, and add saturated sodium bicarbonate solution to neutralize it;
(4) Filtration under reduced pressure, washed with water multiple times (n≥3), absolute ethanol (analytically pure, content: CH3CH2OH≥99.7 wt%) washed multiple times (n≥3);
(5) Dry at 100~140℃ for 24~36h;
(6) Grind into powder and set aside.
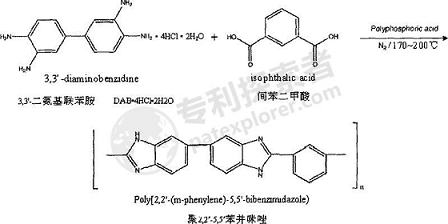
4. Prepare a slow-release flue gas denitrification agent.
Using 3,3′-diaminobenzidine, 3,4-diaminobenzoic acid and isophthalic acid as precursors, polyphosphoric acid as the solvent, and catalytically synthesizing polybenzoic acid at low temperature under ultraviolet light irradiation imidazole copolymer, and then coating urea, including the following steps:
1) Dissolve 3,3′-diaminobenzidine, 3,4-diaminobenzoic acid, and isophthalic acid in the polyphosphoric acid solvent under nitrogen protection, slowly heat to 120°C, and keep temperature for 24 h, then cooled to room temperature;
2) Dissolve urea and sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate in water, then add the solution in 1) drop by drop with a syringe while stirring with nitrogen bubbling;
3) Filter the particles obtained in 2) and dry them at low temperature to obtain a slow-release flue gas denitrification agent.
Main reference materials
[1] Wang Xueying, Bo Fengying. Determination of trace selenium in steel and selenium-added iodized salt using selenium reagent photometry [J]. Chemical Analysis and Metrology, 2001, 10(1): 18-20.
[2] Guo Hancheng, Zhong Meifang. Direct determination of selenium in antimony products using selenium reagent photometry [J]. Physical and Chemical Testing: Chemistry Volume, 2000, 36(12): 566-566.
[3] Gao Wenyun; Wang Jiyu; Li Heng; Huixian; Gan Quan. Use of 3,3`-diaminobenzidine and its quinoxaline analogues in diacetyl detection and detection methods CN201610497512.2, application date 20160629
[4] He Ronghuan; Sun Baoying; Zhao Hanmei; Che Quantong; Yang Jingshuai. Method for microwave synthesis of poly-2,2”-5,5”-benzimidazole and poly-2,5-benzimidazole. CN200710010916.5, application date 20070410
[5] A method for preparing a sustained-release flue gas denitrification agent. CN201610968647.2, application date 20161106

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

