Overview
O-Nitrotoluene is also known as 2-nitrotoluene, 1-methyl-2-nitrobenzene, o-methylnitrobenzene, methyl-o-nitrobenzene, o-nitrotoluene, o-nitrobenzene, O-nitrotoluene. Slightly soluble in water (0.061 at 30°C), soluble in benzene, chloroform and petroleum ether, miscible with ethanol and ether. Evaporates with water vapor.
Due to the strong electron-withdrawing property of the nitro group, the methyl group is easily oxidized. Depending on the oxidation conditions, o-nitrobenzaldehyde or o-nitrobenzoic acid can be generated; when reduced under the action of a catalyst, o-toluidine can be generated, continue Nitrification can produce 2,4 or 2,6 dinitrotoluene; it can also be chlorinated to produce nitrobenzyl chloride; it can also produce azo compounds. Rat oral LD50 801mg/kg. O-Nitrotoluene is mainly used as dye raw material to prepare dyes such as 4-chloro-2-nitrotoluene, 6-chloro-2-nitrotoluene, o-toluidine, di-o-toluidine and 2,6-dichlorobenzaldehyde. Intermediates; 4-chloro-2-nitrotoluene is also a pharmaceutical raw material; o-toluidine is also a raw material for pesticides and fungicides and a raw material for spices; preparation of 2,2′-dinitrobenzyl, o-nitrobenzyl bromide and hexyl bromide alkane and other medical raw materials; prepare indole as a raw material for amino acids and plant growth regulators; prepare dinitrotoluene as a raw material for gunpowder; o-toluidine can also be used as a vulcanization accelerator; and prepare o-nitrobenzoic acid as a pharmaceutical raw material.
Production use
O-nitrotoluene can be used as an intermediate for dyes and pesticides, and is also used in the production of coatings, plastics and medicines. It is mainly used in the production of o-toluidine and benzidine, and is also used in dyes, coatings, plastics and medicines. important raw materials. In the pharmaceutical industry, it can be used to produce nifedipine, Tongjingning, imipramine hydrochloride, bromexamine hydrochloride, diclofenac penicillin sodium, etc.
Synthetic route
Synthetic route one[1]:

Synthetic route two[2]:

Synthetic route three[3]:
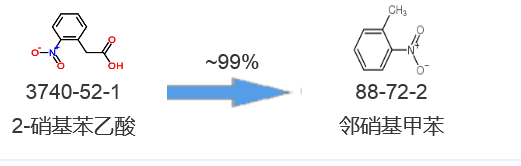
Synthetic route four[4]:
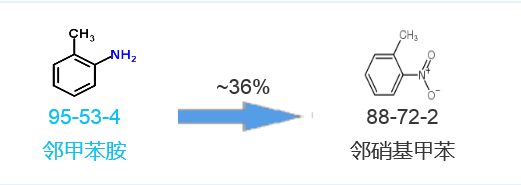
Synthetic route five[5]:
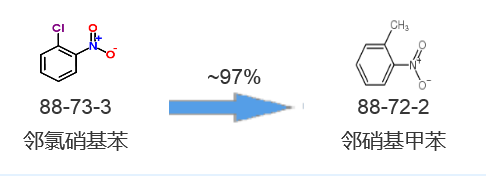
Upstream and downstream product information
Downstream products include: o-methylaniline–>4-nitrotoluene–>indole–>2,6-dichlorotoluene–>2,4-dichlorotoluene–>3-nitrotoluene Toluene–>2-cyanomethylbenzenesulfonamide–>o-nitrobenzaldehyde–>3-chloro-2-methylaniline–>quinclorac–>2,4-dinitro Toluene–>4-Chloro-2-nitrotoluene–>2-chloro-6-nitrotoluene–>Nifedipine–>Chromogen Brilliant Red B–>Iminostilbeneformyl chloride– >5-Methyl phenazine sulfate–>5-chloro-o-toluidine–>Dicloxacillin sodium–>O-nitrobenzoic acid–>2-nitrobenzyl bromide–>2,6- Dinitrotoluene–>O-nitrobenzyl alcohol–>Carbamazepine–>Iminodibenzyl
Upstream raw materials include: sodium hydroxide–>sulfuric acid–>toluene–>nitric acid–>4-nitrotoluene
Production methods
Toluene is first nitrated with mixed acid to generate mixed nitrotoluene, which is mainly o-nitrotoluene (accounting for about two-thirds) and p-nitrotoluene (accounting for about one-third). After separation, pure Taste. Then add toluene into the reactor, cool it to below 25°C, add the prepared mixed acid (i.e. nitric acid 25-30%, sulfuric acid 55-58% and water 20-21%), and adjust the temperature so that the temperature does not exceed 50°C. Stir continuously for 1-2 hours, then let it stand for 6 hours, then separate the generated nitrotoluene, wash with water and alkali to remove unreacted toluene and aliphatic compounds. The composition of the crude nitrotoluene product is o-nitrotoluene 55- 60%, interposition 2-5%, counterposition 35-40%. The yield is 90-95%. The isomers can be separated by crude distillation and crystallization using the difference between boiling point and melting point. That is, the crude nitrotoluene is first subjected to vacuum distillation to separate most of the o-nitrotoluene, and the remaining fraction containing more p-nitrotoluene is separated by vacuum distillation, cooled, crystallized, and separated to obtain Finished product. High-boiling tar-like substances remain in the still. Meta-nitrotoluene is contained in the mother liquor after separation of the para-mer, and is obtained by distillation after repeated accumulation. The purity of ortho- and para-nitrotoluene can reach 98% and 99% respectively. The domestic process involves two pots connected in series, with the reaction temperature of the main pot being 40-45°C and the secondary pot being 50-55°C. The preparation of mixed acid is roughly similar, 26-28% nitric acid, 56-57% sulfuric acid, and 16-18% water. Raw material consumption quota: toluene (98%) 800kg/t, nitric acid (98%) 470kg/t, sulfuric acid (92.5%) 450kg/t, caustic soda (42%) 100kg/t.
Emergency treatment methods:
1. Emergency response to leakage includes: rapid evacuation of personnel in the leaked contaminated area to a safe area, isolation, and strict restriction of access. Cut off the fire source. It is recommended that emergency responders wear self-contained positive pressure respirators and protective clothing. Do not come into direct contact with spilled material. Cut off the source of the leak as much as possible. Prevent entry into restricted spaces such as sewers and flood ditches. Small leakage: Use sand or other non-combustible materials to absorb or absorb. Large leakage: Construct a dike or dig a pit to contain the leakage; use a pump to transfer the leakage to a tanker or special collector, and recycle or transport it to a waste treatment site for disposal. Waste disposal method: Controlled incineration is recommended. Ensure complete combustion. When large amounts of material are incinerated, nitrogen oxides emitted from the incinerator are removed through scrubbers.
��. Protective measures include:
Respiratory system protection: When the concentration in the air exceeds the standard, it is recommended to wear a self-priming filter gas mask (half mask).
Eye protection: Wear safety glasses.
Body protection: Wear breathable protective clothing.
Hand protection: Wear benzene- and oil-resistant gloves.
Others: Smoking, eating and drinking are prohibited at the work site. Change and wash work clothes promptly. Do not drink alcohol before and after work, and bathe with warm water. Conduct pre-employment and regular physical examinations.
3. First aid measures include:
Skin contact: Take off contaminated clothing immediately, wash skin thoroughly with soap and water before seeking medical advice.
Eye contact: Lift your eyelids and rinse with running water or saline before seeking medical advice.
Inhalation: Leave the scene quickly to fresh air. Keep your airway open. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. If breathing stops, perform artificial respiration immediately and then seek medical attention.
Ingestion: Drink plenty of warm water, induce vomiting, and seek medical attention.
Fire-fighting methods: Firefighters must wear gas masks and full-body firefighting suits. Fire extinguishing media: foam, dry powder, carbon dioxide.
References
[1] Yadav R R, Vishwakarma R A, Bharate S B. ChemInform Abstract: Catalyst-Free ipso-Nitration of Aryl Boronic Acids Using Bismuth Nitrate[J]. Cheminform, 2013, 44(4):no-no.
[2] Wu Y, Guan M, Hai L, et al. Design, Synthesis and Anticancer Activity Evaluation of Diazepinomicin Derivatives[J]. Letters in Drug Design & Discovery, 2013, 10(4):-.
[3] Toussaint, Olivier; Capdevielle, Patrice; Maumy, Michel Tetrahedron, 1984, vol. 40, # 17 p. 3229 – 3234
[4] Kumar, Dharmendra Asian Journal of Chemistry, 2010, vol. 22, # 7 p. 5555 – 5560
[5] Shenglof, Margarita; Molander, Gary A.; Blum, Jochanan Synthesis, 2006, # 1 art. no. Z12205SS, p. 111 – 114

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

