Background and Overview
Phenylmagnesium bromide is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H5BrMg.
Preparation[1]
Synthesis of phenylmagnesium bromide Grignard reagent:
In a 500mL round-bottomed flask equipped with mechanical stirring, reflux condenser, dropping funnel, and thermometer, add 9.95g (0.41mol) magnesium chips and 1.47g (0.008mol) 1,2-dibromoethane. 65mL of anhydrous 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, purge with nitrogen, seal the device, raise the temperature to initiate the reaction, slowly add bromobenzene’s 2-methyltetrahydrofuran solution (containing 61.23g of bromobenzene, 60mL of anhydrous 2-methyltetrahydrofuran) dropwise, and complete the dripping Raise the temperature to 60°C and react for 4 hours. Take 1 mL of the reaction solution and dilute it with 3 mL of methanol to make a sample. After GC detection: bromobenzene 0.9%, benzene 98.7%, and biphenyl 0.2%. GC detection conditions: gas phase column: SE-54 (50m), sample input temperature: 280°C, detector temperature: 280°C, carrier gas N2 flow rate 2mL/min, column oven program temperature rise: 100 Keep at ℃ for 3 minutes, then increase to 260°C at 20℃/min, and keep for 6 minutes.
Apply [1-3]
1. Preparation of 1,1-diphenylethylene
1,1-Diphenylethylene is a very useful pesticide and pharmaceutical intermediate. The development of a synthetic method for 1,1-diphenylethylene has good commercial and market prospects.
1) Xavier Creary (J.Org.Chem., Vol.52, No.22, 1987) reported that at -78°C, a phenylmagnesium bromide solution was slowly dropped into ethyl acetate, and then 0 1,1-diphenyl ethanol is obtained by mechanical stirring at ~25°C; EP1167372A1 uses toluene as the solvent, and 1,1-diphenyl ethanol is refluxed and dehydrated under the catalysis of p-toluenesulfonic acid for two hours to obtain 1,1-diphenylethylene. . The reaction process route is as follows:
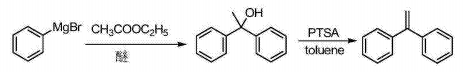
2) CN1651371A reports the synthesis of phenylmagnesium bromide Grignard reagent using bromobenzene as the starting material, iodine as the initiator, and diethyl ether as the solvent at 30 to 35°C, and then dripping the diethyl ether of acetophenone The solution is hydrolyzed by sulfuric acid, recrystallized from ethyl acetate to obtain 1,1-diphenylethanol, and then refluxed and dehydrated in glacial acetic acid to obtain 1,1-diphenylethylene. The reaction process route is as follows:
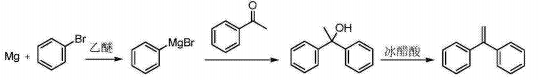
3) CN201310738734.5 provides a 1,1-diphenylethylene preparation method with short reaction steps, mild conditions, simple operation, high product yield, low production cost, environmental friendliness, and suitable for industrial production. The present invention The technical route is as follows:
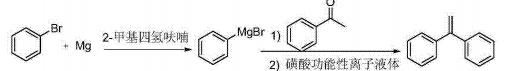
The technical solution adopted in this invention includes the following steps:
(A) Add magnesium chips into the reaction vessel, use anhydrous 2-methyltetrahydrofuran as the solvent, submerge the magnesium chips, and under the protection of N2, add the initiator, heat to initiate the reaction, and drop Add the 2-methyltetrahydrofuran solution of bromobenzene, and after the dripping is completed, heat it up to 60-80°C and react for 2-4 hours to prepare the phenylmagnesium bromide Grignard reagent; the feed materials of the bromobenzene, magnesium chips, and initiator are The amount ratio is 1.0:1.0~1.3:0.01~0.06; the initiator is 1,2-dibromoethane or bromobenzene;
(B) Drop acetophenone into the phenylmagnesium bromide Grignard reagent prepared in step (A). After the dripping is completed, raise the temperature to 40~80°C and react for 3~8 hours. After the reaction is completed, cool to 5 ~15°C, add hydrochloric acid aqueous solution dropwise until the reaction solution pH=6~7, continue the reaction at room temperature for 0.5~1h, add the sulfonic acid functional ionic liquid catalyst, raise the temperature to the reflux temperature for dehydration reaction for 0.5~2h, the reaction is completed, the reaction solution is After treatment, 1,1-diphenylethylene is obtained; the acetophenone and the feed material of bromobenzene, the raw material for preparing phenylmagnesium bromide Grignard reagent, and the sulfonic acid functional ionic liquid catalyst described in step (A) The quantity ratio is 1:1.0~1.3:0.002~0.05.
2. Used to prepare (S)-(-)-1,1,2-triphenyl-1,2-ethylene glycol
(S)-(-)-1,1,2-triphenyl-1,2-ethylene glycol is an important intermediate for the preparation of optically active medicines, pesticides and functional materials. CN201810211017.X provides a method for preparing (S)-(-)-1,1,2-triphenyl-1,2-ethylene glycol with high yield and fast reaction. It is characterized in that methyl mandelate and phenyl magnesium bromide are respectively dissolved in a solvent to prepare a methyl mandelate solution and a phenyl magnesium bromide solution. The molar concentration of the methyl mandelate solution is 0.1 to 3 mol/L. 0.1~2 mol/L of methyl mandelate solution, the solvent is ether, tetrahydrofuran or 2-methyltetrahydrofuran; the prepared methyl mandelate solution and phenyl magnesium bromide solution are respectively input into the first microchannel through a metering pump The reactor performs the main reaction, and the reaction solution obtained after the reaction flows directly into the second microchannel reactor. While the reaction solution flows into the second microchannel reactor, the acidic aqueous solution is input into the second microchannel reactor through a metering pump for quenching. Reaction, quenching the reaction, the reaction solution is obtained, the reaction solution is separated into layers to take the organic phase, the organic phase is dried and concentrated under reduced pressure, and then recrystallized with toluene to obtain the finished product (S)-(-)-1,1,2 – Triphenyl-1,2-ethylene glycol; the main reaction residence time in the first microchannel reactor is 0.5min~5min, the reaction temperature is 10~50℃, methyl mandelate solution and phenyl bromide The molar ratio of magnesium solution input is 1:1~1:3; the quenching reaction residence time in the second microchannel reactor is 0.5min~1.5min, the quenching reaction temperature is -10~30℃, and the acidic aqueous solution The molar concentration is 0.05mol/L~4mol/L, and the molar input amount of acid in the acidic aqueous solution is 1~2 times that of phenylmagnesium bromide.
3. Used to prepare 9,9’-spirobifluorene derivatives
Fluorene organophosphine derivatives are a class of luminescent materials with broad application prospects. In order to improve the comprehensive luminescent properties of fluorene materials, introducing large groups or side chains with steric hindrance effects at the 2 or 7 position of fluorene has proven to be an effective way to reduce inter-chain interactions and prevent the formation of complexes. Methods to improve the thermal stability and spectral stability of polyfluorene. 9,9’-Spirobifluorene diphenylphosphine derivative is one of the representatives. CN201310291849.4 provides a simple and low-cost method for synthesizing 9,9’-spirobifluorene derivatives to meet the needs of industrial production.
In order to achieve the purpose of the present invention, the present invention uses low-price o-bromohalobenzene as raw material to synthesize bromo-9,9’-spirobifluorene, and then reacts with lithium diphenylphosphine to obtain the target compound. The specific method is as follows: under the protection of inert gas, o-bromohalobenzene reacts with phenylmagnesium bromide in methyltetrahydrofuran solvent. After the reaction is completed, the above reaction liquid is dropped into the diethyl ether solution of bromofluorenone, and the reaction is refluxed. Hydrolyze and filter to obtain a solid. The solid is reacted in mixed acid to obtain a crude solid after filtration. Bromo-9,9′-spirobifluorene is obtained through column separation. Then bromo-9,9′-spirobifluorene reacts with lithium diphenylphosphine in a tetrahydrofuran solvent, and is filtered to obtain a crude solid, which is separated by column layers to obtain the target product. The synthesis process is simple to operate, the raw materials are easily available, and the cost is low. Compared with the synthesis method that directly uses 2-bromobiphenyl as the raw material, the cost is reduced by more than 60%, meeting the needs of industrial production.
Main reference materials
[1] CN201310738734.5 A preparation method of 1,1-diphenylethylene
[2] Preparation method of CN201810211017.X (S)-(-)-1,1,2-triphenyl-1,2-ethylene glycol
[3] CN201310291849.4 Synthesis method of a type of 9,9’-spirobifluorene derivatives

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

