(1) Polymer chelating agent whose coordinating atom is oxygen
There are many such chelating agents, the simplest and most easily available is polyvinyl alcohol (PVA ). It is obtained by hydrolyzing polyacetate B and is a polymer chelating agent with hydroxyl coordination groups. Its chemical reaction formula is as follows:
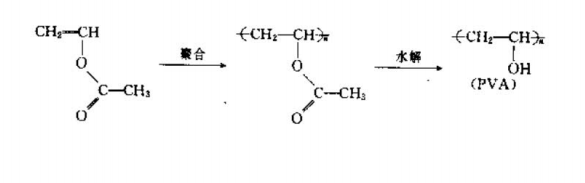
The generated PVA can chelate with a variety of metal ions, such as Cu2, Ni2+, CO2, Fe2+, Mn2-, Ti3+, Zn2+, etc., to form polymer complexes , among which the chelates with tung, iron, and titanium are particularly stable. The stability of the complex between PVA and divalent transition metal ions increases in the order of Co2+<Ni2+<Zn2+<Cu2+.
Although PVA chelates very strongly with Cu2+, it does not chelate with Cu+. Put the water-insoluble PVA film with heavy objects hanging on it into the aqueous solution of Cu3(PO4)2. Since Cu2+ is chelated with one OH on the film, the polymer shrinks and the sagging heavy objects are lifted up. When Cu2+ is reduced to monovalent Cu+, because PVA cannot cooperate with Cu+, copper ions are released from the complex. And make the PVA film stretch. This phenomenon provides a useful revelation for the conversion of chemical energy into mechanical energy.
(2) Polymer chelating agents whose coordinating atoms are nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, etc.
This type of polymerchelateThere are also many types of chelating agents, such as chelating agents containing thiourea, sulfite, phosphoric acid, arsenic acid and other coordinating groups. They have different chelating abilities for different metals, as shown in the following reactions:
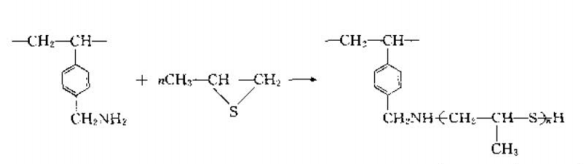
This product is a new functional resin containing a thioether structure. It can selectively adsorb gold in the concentration range of 0.1~2mol/I and hydrochloric acid. The adsorption capacity is 239. 5mgAu (I)/g.
In addition to the above-mentioned polymer chelating agents, there are also those with crown ether structures Macromolecule coordination resins and many varieties of natural polymer chelating agents are not introduced here. In short, there are many types of polymer chelating agents with different properties. Factors such as the type, combination, and structure of functional groups all affect the performance of the resin. On the other hand, the generated chelates containing metal ions often have many properties, such as catalysis, photosensitivity, conductivity, deoxidation, oxygen absorption, magnetism, energy conversion, etc., and are being widely studied and applied.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

