Background and overview[1]
Modafinil is a new type of central nervous system stimulant drug. Compared with traditional central nervous system stimulant drugs such as caffeine, amphetamine, and methylphenidate, modafinil has the advantages of fast onset, low side effects, and no dependence. , is expected to replace methylphenidate as the drug of choice for the treatment of narcolepsy. In addition, it is also widely used as an anti-fatigue drug and sleep regulator, and has good application prospects. Diphenylmethylthioacetamide, as an important intermediate in the synthesis of modafinil, also has broad market prospects.
According to current literature reports, the preparation methods of diphenylmethylthioacetamide mainly include the following three routes: The first route: using diphenylcarbinol as the starting material, first reacting with thiourea to prepare diphenylmethylsulfide Alcohol, then react with chloroacetic acid to produce benzylthioacetic acid, then react with sulfoxide chloride to produce benzylthioacetyl chloride, and finally react with ammonia to produce benzylthioacetamide. The disadvantages of this route are that the reaction route is long, the process is complex, the yield is low, and the corrosive agent thionyl chloride is used, which causes great pollution to the environment. The second route: using benzyl alcohol as the starting material, first react with thioglycolic acid to obtain benzylthioacetic acid, then react with thionyl chloride to obtain benzylthioacetyl chloride, and finally react with ammonia water The reaction produces benzylthioacetamide. Compared with the first route, this route reduces the reaction steps and simplifies the process, but still requires the use of the corrosive agent thionyl chloride, which causes greater pollution to the environment. The third route: using benzyl alcohol as the starting material, first react with thiourea to prepare benzyl mercaptan, then react with methyl chloroacetate to prepare methyl benzyl thioacetate, and finally react with ammonia water Preparation of benzylthioacetamide. Compared with the first two routes, this route reduces the reaction steps, simplifies the process, does not use the corrosive agent thionyl chloride, and has little environmental pollution. However, it still has the following shortcomings: the intermediate product diphenylmethylmercaptan has a foul odor. The intermediate product methyl diphenylthioacetate needs to be separated and purified before undergoing an aminolysis reaction. The operation is complicated and the yield is low.
Preparation[1]
Diphenylmethylthioacetamide is prepared as follows:
a. Preparation of diphenylmethylthioacetic acid
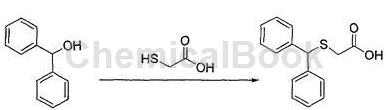
Calculate the amount of raw materials based on the theoretical production amount of benzylthioacetic acid of 56g; in a 500mL three-neck round-bottom flask, add 40g of benzyl alcohol and 32g of glacial acetic acid, and raise the temperature to 40°C under stirring conditions to complete Dissolve, slowly add 48g of hydrobromic acid dropwise, after the addition is completed, raise the temperature to 60°C, add 16g of thioglycolic acid, continue to raise the temperature to 80°C, stir and react for 2.5 hours, use thin layer chromatography (TLC) to monitor the reaction progress, wait until the reaction After completion, cool the reaction solution to a temperature of 20°C, filter, wash the filter cake with water, and dry it under vacuum at a temperature of 55°C to obtain 51.8g of benzylthioacetic acid, with a purity of 99.0% and a yield of 92.5%;
b. Preparation of methyl diphenylthioacetate
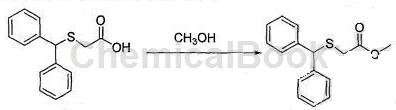
Calculate the amount of raw materials based on the theoretical production amount of diphenylmethylthioacetamide: 39.85g; in a 500mL three-neck round-bottom flask, add 40g of diphenylmethylthioacetic acid and 80mL of methanol obtained in step a, and stir until complete Dissolve, slowly add 10 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid dropwise, and after completion of the dropwise addition, raise the temperature to 65°C and reflux for 3 hours, and use TLC to monitor the reaction progress until the reaction is complete;
c. Preparation of diphenylmethylthioacetamide
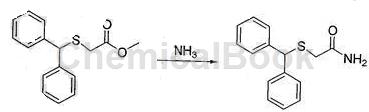
Cool the reaction solution obtained in step b in an ice-water bath to a temperature of 25°C, add ammonia gas, and stir tightly at room temperature for 24 hours. Use TLC to monitor the reaction progress. After the reaction is complete, cool to a temperature of 20°C, filter, and filter. The cake was washed with water at a temperature of 10°C and vacuum dried at a temperature of 55°C to obtain 30g of the product diphenylmethylthioacetamide, with a purity of 99.3% and a yield of 75.3%. There are 3 steps of reaction from starting raw materials to final product, and the total yield is 69.7%.
Main reference materials
[1] Preparation method of CN200810237161.7 diphenylmethylthioacetamide

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

