overview[1]
2-oxo-4-phenylbutyric acid can be used as a pharmaceutical synthesis intermediate, such as the preparation of 2-oxo-4-phenylbutyl ethyl ester (eopb), 2-oxo-4-phenyl butyl ethyl ester is an important intermediate for the synthesis of the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (acei) series of drugs such as lisinopril and benazepril. acei has significant effects on hypertension and congestive heart failure. the therapeutic effect has attracted many pharmaceutical and chemical scientists to study its synthesis.
preparation[1-2]
2-oxo-4-phenylbutyric acid is prepared as follows:
method 1: add 1.5g of hydantoin 4 to a three-neck flask equipped with a reflux condenser and a separator, and place it under an argon atmosphere. after adding naoh (20%, 32 ml), flush the equipment again with argon. the mixture was heated to reflux for 3 hours, then cooled to 0°c and adjusted to ph 7 by slowly adding hclconc. after adding 650 mg nahco3, the mixture was extracted with diethyl ether in a liquid-liquid extraction device for 3 hours. then 9 ml hcl was added and further extraction was performed to extract the product into the organic phase. the solvent was removed in vacuo to give a yellow oil, which was taken up in 70 ml h2o and readjusted to ph 7 by adding 1m naoh. freeze with liquid nitrogen and lyophilize to obtain white crystals of 2-oxo-4-phenylbutyric acid (864 mg, 4 mmol, 61%).
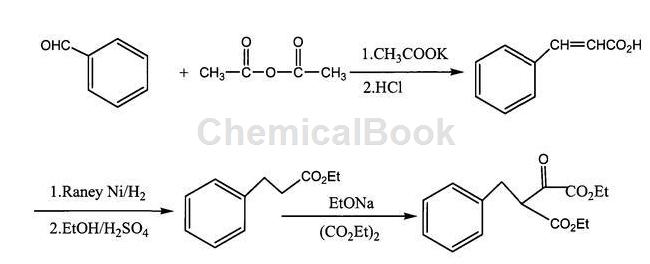
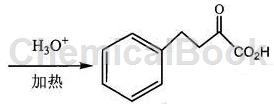
method 2: using benzaldehyde as the starting material, condensation with acetic anhydride, hydrogenation and esterification of cinnamic acid to obtain ethyl phenylpropionate, and condensation of ethyl phenylpropionate and diethyl oxalate to obtain 3-benzyl-2 – diethyl oxosuccinate, and finally 3-benzyl-2-oxosuccinate diethyl is hydrolyzed and esterified to produce 2-oxo-4-phenylbutyric acid.
main reference materials
[1] ep 2574667
[2] cn200810025051.4 preparation method of 2-oxo-4-phenylbutyric acid ethyl ester preparation method of ester

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

